* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
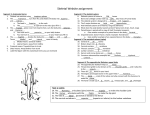
Name: _____________________ Homeform: _______ The Skeletal System When investigating the musculoskeletal system, it is important to understand the anatomical position. The anatomical position is with the body erect, with the arms at the sides and the palms forward. The anatomical position is of importance in anatomy because it is the position of reference. It is also important to understand how to refer to part of the body using specific terminology. Functions: The adult human skeletal system consists of 206 bones, as well as a network of tendons, ligaments and cartilage that connects them. The skeletal system performs many vital functions: 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 3. ________________________ 4. ________________________ 5. ________________________ 6. Types of Bones: There are 4 main types of bones in the body. Give examples of where these bones can be found: Long:_________________________ Short: ________________________ Irregular: _____________________ Flat: __________________________ Define the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ The Human Skeleton Vertebrae: The human vertebral column is the vertebral column (backbone or spine) of the human skeleton, consisting of articulating vertebrae and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. The vertebrae in the column are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. It houses and protects the spinal cord in its spinal canal. Vertebrae Region Cervical No. of Vertebrae Abbreviation 12 L Joints: A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the location at which bones connect. They are constructed to allow movement (except for skull, sacral, sternal, and pelvic bones) and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally. There are 3 different types of joints. 1. Immoveable or fibrous joint – where two bones are joined by connective tissue, there is no joint cavity (space between the bones filled with synovial fluid), and there is little or no movement. For example the bones of the pelvic girdle. 2. Slightly moveable or cartilaginous joint – the bones are connected by a ligament and cartilage, there is no joint cavity, and there is only limited movement. For example bones of the vertebrae. 3. Freely moveable or synovial joints – there is a gap between the joints (joint cavity) containing synovial fluid. There is far greater movement between bones connected by synovial joints. The extent of the movement varies due to the shape of the bones, and the ligaments and tendons that surround the joint. An example is the knee joint. Synovial Joints: ***Draw a line to match the type of joint to the correct definition. Then draw a line linking the definition to the correct example. Type of Joint Ball & Socket Pivot Hinge Saddle Gliding Condlyoid Definition Example Allows movement in one direction only Movement is biaxial because the movement is restricted to two axis with rotation restricted Movement is restricted to rotation around a single axis Two flat surfaces in which some movement, including slight rotation, is possible These are biaxial joints. One bone surface is concave the other convex Where one bone has a ball end, which fits into a socket of adjacent bone. Allows a wide amount of movement in almost every direction Elbow Hip Base of Thumb Wrist Vertebrae Radius & Ulna Define the following connective tissues: Tendon: ___________________________________________________________________ Ligament: __________________________________________________________________ Cartilage: ___________________________________________________________________ Fascia: _____________________________________________________________________ The Muscular System The Muscular System is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person’s body weight. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves. The 3 Types of Muscle Type of Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Appearance Voluntary or Involuntary Function Skeletal Muscle Fibres: Type 1 (Slow Twitch): __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Type 2 (Fast Twitch): __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________