* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 14* Magnetic Induction
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
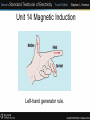
Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Objectives: • Discuss magnetic induction. • List factors that determine the amount and polarity of an induced voltage. • Discuss Lenz’s law. • Review the formula for R-L time constants. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Current flowing out Current flowing in Current flowing through a conductor produces a magnetic field around the conductor. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction A voltage is induced when a conductor cuts magnetic lines of flux. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Reversing the direction of movement reverses the polarity of the voltage. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Reversing the polarity of the magnetic field reverses the polarity of the voltage. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Left-hand generator rule. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Voltage is induced by a moving magnetic field. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction A single-loop generator. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Increasing the number of turns increases the induced voltage. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Lenz’s Law An induced voltage or current opposes the motion that causes it. Please note: Inductors always oppose a change of current! Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Inductance is determined by the physical construction of the coil. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction R-L Time Constants T=L/R T = time in seconds L = inductance in henrys R = resistance in ohms This formula describes the time necessary for current in an inductor to reach its full Ohm’s law value. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Review: 1. When current flows, a magnetic field is created around the conductor. 2. When a conductor is cut by a magnetic field, a voltage is induced in the conductor. 3. The polarity of the induced voltage is determined by the polarity of the magnetic field. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Review: 4. Three factors that determine the amount of induced voltage are: a. the number of turns of wire. b. the strength of the magnetic field. c. the speed of the magnetic flux cutting action. Unit 14 Magnetic Induction Review: 5. Induced voltage is always opposite in polarity to the applied voltage. 6. Inductors oppose a change of current. 7. Inductance is measured in units called henrys (H). 8. Iron core inductors are wound on cores of magnetic material.