* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pancreatic Hormones Introduction
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
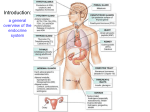
Pancreatic Hormones 11 • Introduction to the pancreas, its cell types, its hormones, its functional organization, its venous output to liver and its regulation • Overview of intermediary metabolism and enzyme sites of major actions of insulin and glucagon • Pancreatic hormones, insulin, glucagon, SS and PPY. Their structure, synthesis, related peptides, secretion, regulation, receptors and effects. Effect of exercise on insulin and on its counter-regulatory hormones • Regulation of pancreatic hormones, Diabetes Mellitus, hypoglycemia, fasting, NIDDM Introduction Pancreas and “story lines” Page 1 Glucose metabolism Introduction • Endocrine pancreas glycemia • Intermediary metabolism insulinemia • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus S Plasma levels of glucose and insulin in relation to meal intake E Introduction • Endocrine pancreas Source of glucose used in fasting conditions glucose • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones glycogen gluconeogenesis • Diabetes mellitus S Time course of the origin of glucose under fasting conditions E Page 2 Introduction • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus S Quantitative turnover of substrates in the basal state after fasting for 24 hours E Introduction • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism FUEL METABOLISM IN ANABOLIC AND CATABOLIC PHASES State Hormones anabolism insulin Fuel Source diet glycogen synth. triglycerid synth. protein synth. storage depots glycogenolysis lipolysis proteolysis ketogenesis glucagon • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus S catabolism insulin glucagon Process The opposite direction of plasma insulin and glucagon define the metabolic state E Page 3 Introduction • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus S • • • • • • • • pancreas, main regulator of sugar metabolism sugars from food digestion and from glycogen endocrine (islets) & exocrine pancreas (acinar) the islets of Langerhans (triads: , ß, , cells) hormones: insulin, glucagon, SS, PPY pancreatic endocrine secretion to portal vein blood glucose decreased by insulin, SS, IGFs blood glucose increased by glucagon, CAs, glucocorticoids, GI hormones, GH, CRH, ACTH, T3 / T4, Ang II, food (arginine). The opposite direction of plasma insulin and glucagon define the metabolic state E Metabolic pathways • Endocrine pancreas glycogen glycogen phosphorilase glycogen synthetase G-1-P G-6-Pase • Intermediary metabolism glucose hexokinase F-6-P PFK F-1,6-diPase • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus S glucose G-6-P F - 1,6 -diP transaminases insulin glucagon epinephrine glucocorticoids triose amino acids pyruvate proteins Krebs cycle acetyl CoA fats JP’s colorful version indicating the main action site of various metabolic hormones E Page 4 Metabolic pathways • Endocrine pancreas Glucose Glycogen Glycogenesis • Intermediary metabolism Glycolytic pathway Glucokinase • Pancreatic hormones Glycogen synthetase Glycogen phosphorilase • Diabetes mellitus Glycogenolysis S Hadley’s textbook version of the intermediary metabolic pathway E Metabolic pathways • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus some associations to remember for an endocrine regulatory viewpoint S E Page 5 Metabolic pathways • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus some associations to remember for an endocrine regulatory viewpoint S E Metabolic pathways • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus some associations to remember for an endocrine regulatory viewpoint S E Page 6 Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it S E Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones • Endocrine pancreas insulin infusion Epi • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones cortisol + glucagon + epinephrine Nepi Glucagon glucagon + epinephrine Cortisol epinephrine • Diabetes mellitus GH glucagon control Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it S E Page 7 Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones hormone effects on metabolism in adipocytes • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Insulin Epi + Nepi GH Cortisol T3 hormone effects of glucose metabolism in muscle Insulin Epi + Nepi GH Cortisol T3 Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it S E Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones hormonal regulation of metabolism in liver • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism Insulin glucagon Epi + Nepi GH Cortisol T3 hormonal effects on insulin secretion and sensitivity of target cells to insulin • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Insulin glucagon Epi + Nepi GH Cortisol T3 Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it S E Page 8 Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones control • Endocrine pancreas fasting plasma glucose GH-deficient treated with GH • Intermediary metabolism normal • Pancreatic hormones GH-deficient • Diabetes mellitus days Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it S E Insulin and its counterregulatory hormones control • Endocrine pancreas fasting plasma glucose GH-deficient treated with GH • Intermediary metabolism normal • Pancreatic hormones glucose • Diabetes mellitus glycogen GH-deficient gluconeogenesis days Insulin decreases blood glucose while all counter-regulatory hormones increases it Page 9 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Insulin secreted from the pancreatic ß cells decreases blood glucose levels S E Insulin physiological • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones diseaserelated genetic • Diabetes mellitus S environmental E Overview of factors affecting insulin signaling Page 10 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus • it has 51 aa, 2 chains, 3 S-S bonds, C-peptide • stimulates anabolism and favors energy storage • increases glycogen storage and inhibits both glycogen breakdown and gluconeogenesis • increases fatty acid synthesis and decreases lipolysis and ketogenesis • stimulates transport of glucose and of some amino acids into striated muscle and adipose tissue • increases protein synthesis in liver, muscle, adipose • Like growth factors it has a growth promoting effect An overview of the main effects of pancreatic insulin S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas insulin • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus glucose An overview of blood glucose stimulation of insulin secretion and effect S E Page 11 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus An overview of blood glucose stimulation of insulin secretion and effect S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus An overview of blood glucose stimulation of insulin secretion and effect S E Page 12 Insulin CNS • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones adipose gut glucose muscle liver • Diabetes mellitus An overview of blood glucose stimulation of insulin secretion and effect S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas Cys residues kinase NH2 hydrophobic aa Cys rich • Intermediary metabolism • ECF membrane • Pancreatic hormones ICF EGF • Diabetes mellitus JAK2 insulin PDGF COOH • GH Prl cytokines ANP The insulin receptor contains an intrinsic protein kinase that specifically catalyzes the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues on proteins Cystein and its thiol (SH) group linking the aa to another Cystein aa may form part of a binding cleft for ligands The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Page 13 Insulin Binding of insulin and its receptor in the extracellular domain causes phosphorylation of the intracellular domain of the receptor. This elicits a conformational change in the tyrosine kinase portion of the receptor, thus activating its enzyme activity • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Insulin Binding of insulin and its receptor in the extracellular domain causes phosphorylation of the intracellular domain of the receptor. This elicits a conformational change in the tyrosine kinase portion of the receptor, thus activating its enzyme activity • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Page 14 Insulin Binding of insulin and its receptor in the extracellular domain causes phosphorylation of the intracellular domain of the receptor. This elicits a conformational change in the tyrosine kinase portion of the receptor, thus activating its enzyme activity • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Page 15 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism Cys rich hydrophobic aminoacids kinase insulin NH2 • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus ECF Tyr-P of docking protein IRS - 1 SH2SOS domain phosphatidyl mediated ras inositol -3 -P complex formation raf Ser - Thr kinase cascade memb ICF COOH DNA synthesis and gene transcription MEKK stimulation of glucose p90rsk transport MAPK PP1G glycogen synthase The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The insulin receptor is a one transmembrane domain tyrosine kinase receptor S E Page 16 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The effect of insulin on the Glut - 4 transporter S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The effect of insulin on the Glut - 4 transporter S E Page 17 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The effect of insulin on the enzyme 6 phosphofructokinase S E Insulin • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The effect of insulin on the enzyme glycogen synthetase S E Page 18 Insulin • Endocrine pancreas Insulin suppress glucose production by inhibiting the flux of gluconeogenic precursors (alanine, pyruvate, lactate, glycerol), energy substrates (free fatty acids) and glucagon secretion. All these suppress glucose release by the liver. • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus The effect of insulin on the enzyme glycogen synthetase S E Insulin Organ • Endocrine pancreas liver Net effect glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis ketogenesis glycogen synthesis fatty acid synthesis • Intermediary metabolism Chief mechanism phosphorylase (glucose-dependent de-P) PEPCK (transcriptional regulation) FDPase-2 (enzyme dephosphorylation) substrate (alanine) delivery from muscle substrate (FFA) delivery from fat glycogen synthase (enzyme de-P) acetyl CoA carboxylase (transcription) fatty acid synthase • Pancreatic hormones muscle proteolysis protein synthesis glucose uptake glycogen synthesis multiple mechanisms activity at multiple steps recruit glucose transporter to cell surface glucose uptake glycogen synthase (enzyme de-P) • Diabetes mellitus fat hormone sensitive lipase (enzyme de-P) delivery of tryglyceride from liver lipoprotein lipase lipolysis triglyceride synthesis Main actions of insulin on metabolic pathways S E Page 19 Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Glucagon secreted by the pancreatic alphacells increase blood glucose levels S E Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus • main counterregulator to insulin together with catecholamines (Epi) & cortisol • 29 aa, member of a related family peptides that includes VIP, GIP, and secretin • determines glycemia in postabsorptive state by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis • glucose, insulin and SS inhibit its release • aa, exercise and CAs stimulate its release • gene expression is restricted to cells in islet and is negatively regulated by insulin • glycentin, GI specific proteolytic processing Glucagon is the main counter-regulatory hormone to insulin S E Page 20 Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones R cell membrane Gs AC phosphodiesterase ATP ----------> cAMP -----------> 5’AMP inactive PKA ----------> active PKA inactive PKb <----------> active PKb glycogen phosphorilase b <-----> glycogen phosphorilase b glycogen + Pi --> glucose - 1 - P • Diabetes mellitus cell membrane T blood glucose Glucagon is the main counter-regulatory hormone to insulin S E Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Glucagon is the main counter-regulatory hormone to insulin S E Page 21 Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Glucagon’s main mechanism of action is through cAMP S E Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Amplification, an important event in the mechanism of action of glucagon S E Page 22 Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism Organ liver Net effect glycogenolysis glycogen phosphorylase (cAMP-dep- P) glycogenesis glycogen synthase (phosphorylation) F - 1,6 - diPase (phosphorylation) pyruvate kinase (phosphorylation) substrate delivery, r eleasing inhibition of carnitine palmytoil transferase, allowing mitochondrial transfe r and FA oxidation gluconeogenesis • Pancreatic hormones Chief mechanism glycolysis ketogenesis • Diabetes mellitus Main actions of glucagon on metabolic pathways S E Insulin and Glucagon • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Effect of large carbohydrate meal (left) and of arginine infusion (right). S E Page 23 SS and PPY • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • SS has 14 aa and 1 disulfide bond. It was discovered and named for its GH inhibiting activity. SS inhibits a wide variety of endocrine and exocrine secretory activities in the pituitary and in the GI tract. In the pancreas, SS inhibits insulin, glucagon, PPY and exocrine secretion • PPY release is largely neurally mediated. Sensing of food in the CNS causes its vagal-mediated secretion. Food in proximal GI tract also stimulates its release. PPY affects GI motility, secretory activity of stomach, intestine and pancreas • Diabetes mellitus Somatostatin & Pancreatic Polypeptide Y are two of the many GI peptides S E Effect of exercise glucose • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism glycogen • Diabetes mellitus working muscle Epi Nepi nonglycogen working glucose muscle lactate fuels consumed by leg muscles of man during mild prolonged exercise (O2 uptake) lactate glucagon • Pancreatic hormones glucose insulin cortisol GH min Plasma glucose Plasma FFA Muscle glycogen 40 27 37 36 90 41 37 22 180 36 50 14 240 30 62 8 Somatostatin & Pancreatic Polypeptide Y are two of the many GI peptides S E Page 24 Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas • • • • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • • • Diabetes mellitus • hallmark of insulin hyposecretion and insulin resistance is hyperglycemia in the fasting state hyperglycemia, polyuria (diabetes = siphon), urine sweetens (mellitus = honey), polydipsia precise mechanism for the deleterious effect of high glucose is not known. Whether from non-enzymatic glycation of proteins or from regulatory effects of excess glucose, blood vessels are damaged, resulting in turn in damage to the retina and kidney, and circulation compromise to the heart, brain and extremities. Main morbidity causes are blindness, renal failure, heart attack, stroke, amputations glucose tolerance test, diabetes mellitus, insulin deficit / resistance insulin resistance: prereceptor resistance (autoantibodies, mutant insulin), receptor resitance (decreased number and affinity, point mutation, impaired kinase expression), & post-receptor resistance (down regulation of Glut4 or autoantibodies of Glut2 transporters, mutation of glucokinase gene, ßcell exhaustion as in GH abuse) diabetic ketoacidosis, dehydration due to hyperglycemic diuresis, negative nitrogen balance, tissue wasting, poor resistance to infections, metabolic acidosis, fruity smell of ketosis in breath, cardiovascular involvement, hyperglycemic vs hypoglycemic coma Diabetes mellitus has been linked to every step in the mechanism of action of insulin S E Page 25 Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas Type 1 diabetes – regulation of glucose homeostasis • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus A good example of “pushing the regulatory feedback envelop” in endocrinology S E Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Diabetes mellitus has been linked to every step in the mechanism of action of insulin S E Page 26 Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism normal normal • Pancreatic hormones diabetic • Diabetes mellitus 100g glucose 100g glucose Diabetes mellitus has been linked to every step in the mechanism of action of insulin S E 100 g glucose Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Diabetes mellitus has been linked to every step in the mechanism of action of insulin S E Page 27 Diabetes • Endocrine pancreas • Intermediary metabolism • Pancreatic hormones • Diabetes mellitus Diabetes mellitus has been linked to every step in the mechanism of action of insulin S E Page 28