* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
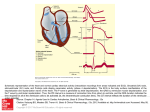
SIGNAL AVERAGED ECG INTRODUCTION Signal-averaged electrocardiography (SAECG) is a special electrocardiographic technique, in which multiple electric signals from the heart are averaged to remove interference and reveal small variations in the QRS complex, usually the so-called "late potentials". These may represent a predisposition towards potentially dangerous ventricular tachyarrhythmias INTRODUCTION A signal-averaged electrocardiogram is a more detailed type of ECG. During this procedure, multiple ECG tracings are obtained over a period of approximately 20 minutes in order to capture abnormal heartbeats which may occur only intermittently. A computer captures all the electrical signals from the heart and averages them to provide the physician more detail regarding how the heart’s electrical conduction system is working. Signal-averaged ECG is one of several procedures used to assess the potential for dysrhythmias/arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms) in certain medical situations. INTRODUCTION Other related procedures that may be used to assess the heart include resting electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, exercise electrocardiogram (ECG), cardiac catheterization, chest x-ray, computed tomography (CT scan) of the chest, echocardiography, electrophysiological studies, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart, myocardial perfusion scans, radionuclide angiography, and ultrafast CT scan. Procedure A resting electrocardiogram (ECG) is recorded in the supine position using an ECG machine equipped with SAECG software; this can be done by a physician, nurse, or medical technician. Unlike standard basal ECG recording, which requires only a few seconds, SAECG recording requires a few minutes (usually about 7-10 minutes), as the machine must record multiple subsequent QRS potentials to remove interference due to skeletal muscle and to obtain a statistically significant average trace. For this reason, it is important for the patient to lie as still as possible during the recording. Significance Late potentials are taken to represent delayed and fragmented depolarisation of the ventricular myocardium, which may be the substrate for a micro-re-entry mechanism, implying a higher risk of potentially dangerous ventricular tachyarrhythmia. This has been used for the risk stratification of sudden cardiac death in people who have had a myocardial infarction, as well as in people with known coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathies, or unexplained syncope. Still, the real predictive value of these findings is questioned. Late potentials may be found in 0-10% of normal volunteers. When used as a prognostic factor for the development of ventricular tachycardia, they have a sensitivity of 72% and a specificity of 75%, yielding a positive predictive value of 20% and a negative predictive value of 20%. ADVANTAGE OF SAECG Filtered ECG that is able to detect low amplitude potentials filtered out of standard ECGs. Myocardial scar (infarction, ARVD) creates zones of slow conduction that appear as low amplitude late potentials on SAECG. Areas of slow conduction are necessary components for reentry. Late potentials from within scar sometimes are not detected in SAECG – Bundle branch block delays depolarization ipsilateral to the site of block. The delayed conduction may conceal late potentials on SAECG. – The base of the left ventricle is the last area to depolarize when bundle branch block is not present. Inferior scar is easier to detect on SAECG than anterior scar because the inferior scar boarder zone is activated later than the anterior wall. Therefore, the late potentials are not concealed by depolarization in other areas of the ventricle. Criteria for abnormal SAECG Root mean squared voltage of the terminal 40 msecs is less than 20 microvolts. This shows low voltage potentials late in ventricular depolarization and reflect depolarization in slowly conducting scar boarder zones Total QRS duration greater than 114 msec Duration of the low amplitude signal that is less than 40 microvolts is greater than 38 msec