* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IHD - Heart Line
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
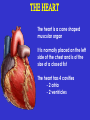
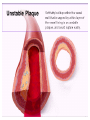
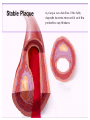
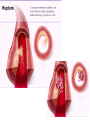
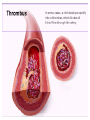
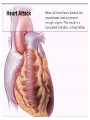
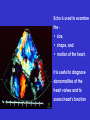
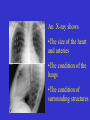
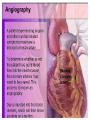
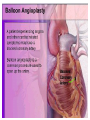
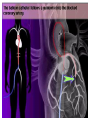
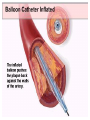
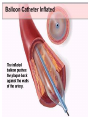
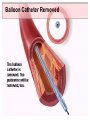
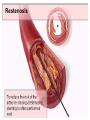
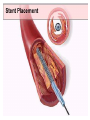
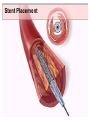
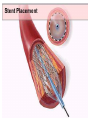
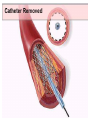
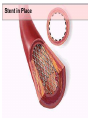
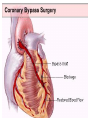
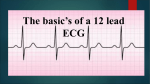
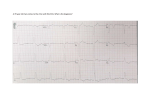
SWEET HEART THE HEART The heart is a cone shaped muscular organ It is normally placed on the left side of the chest and is of the size of a closed fist The heart has 4 cavities - 2 atria - 2 ventricles HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? ‘Pacemaker of the heart’ (shown as 1 in the picture) Weak electrical activity starts from the Pacemaker Electrical activity travels along a certain path (shown in red) This stimulates all the parts of the heart, thereby causing the entire heart to contract and relax alternatively Contraction is called as ‘Systole’. Blood is pumped out of the heart in this phase. SYSTOLE Relaxation is called as ‘Diastole’. Blood is collected in the heart in this phase. DIASTOLE HDL LD L Normal blood vessel Deposition of ‘bad cholesterol’ Increased deposition of ‘bad cholesterol’ This is known as atherosclerosis WARNING SYMPTOMS... •Difficulty in breathing •Chest Pain •Blue Discoloration •Black out •Swelling of the body, especially of the feet •Awareness of heart beats •Cough •Coughing out blood •Fatigue (Dysnpnoea) (Angina) (Cyanosis) (Syncope) (Edema) (Palpitation) (Hemoptysis) HOW TO KNOW OF HEART DISEASE? •BP measurement •Blood cholesterol measurements •Blood sugar measurements •E C G •Echocardiogram / Doppler •T M T / Stress Test •X-ray •Angiography E C G (ELECTROCARDIOGRAM) An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of the heart's electrical activity as a graph or series of wave lines on a moving strip of paper. This gives the doctor important information about the heart. POSITION OF ECG LEADS 6 or 12 E C G leads are placed on the chest to obtain the ECG AN E C G LOOKS LIKE THIS... HOLTER MONITORING A Holter monitor is a portable ECG that monitors the electrical activity of a freely moving patient’s heart for one to five days, 24 hours around the clock ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY An Echocardiogram uses sound waves to image the heart Echo is used to examine the - • size, • shape, and • motion of the heart, It is useful to diagnose abnormalities of the heart valves and to assess heart’s function TMT (TREAD MILL TEST / STRESS TEST) An ECG performed while the patient exercises in a controlled manner on a treadmill or stationary bicycle at varied speeds and elevations. This test helps detect heart irregularities, disease and damage. The outcome of T M T is similar to the E C G SCAN Depending on the precision required the following scans can be performed • X Ray Least Precise • CT Scan • MRI Scan • Spect Thallium Scan Most Precise All of these are painless procedures wherein X rays are taken An X-ray shows •The size of the heart and arteries •The condition of the lungs •The condition of surrounding structures “Early in life people give up their health to gain wealth…. ….In later life, people give up their wealth to regain some of their health.” - KEN BLANCHART & MARJORIE