* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
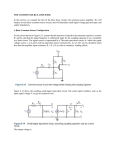
UNIVERSITY OF TEHRAN Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Electronic Circuits lab I Experiment 6 BJT Signal Amplifiers II Common Collector and Common Base Stage 1. Objectives In this experiment, you will test some general characteristics of the common base amplifier, including low input resistance, high voltage gain and acceptable performance at high frequencies. Common collector amplifier, as a general buffer stage with high input, low output resistance and unity gain is also tested. The frequency response for both amplifiers is also included. 2. Necessary Equipments You will need two NPN BJT (2N3904), two 100F capacitors and 100, 1k, 56k, 10k resistors. Other necessary equipments include two DC power supplies, an oscilloscope, a function generator, a breadboard, an ohmmeter and enough wires. 3. Pre-lab A) 3.1 The small signal model for a common base amplifier is shown below. Find appropriate expression for input /output resistances and (VO/VS) voltage gain. r v Vo gm v Rc RS Vs RE B) Using the expression you derived, calculate the said parameters for the circuit below. (Output resistance of the current source is very high.) Prior to that calculate Ra so that the circuit will have a DC bias current of 6mA. (=100) C) Find the maximum possible output voltage swing for this circuit. (Hint: find maximum and minimum values for VO and compare it to DC bias voltage for VO. Remember to take Q2’s saturation into account, as the current source must not be saturated. D) What are the capacitors in the circuit for? E) Explain how the gain factor will change if each of R1 and R2 are changed respectively. 3.2 A) The figure below shows the AC small signal model for a common collector circuit. Find appropriate expression for output / input resistances as well as gain factor. RS Vs r v gm v Rc Vo RE B) Using the expression you just derived calculate the said parameters for the circuit below. Prior to that find Ra so that the circuit will be biased for: ICQ = 6mA (=80) C) Find the maximum swing for VO and the thresholds at which the output peaks are flattened or distorted. Determine V1 and V2 values when distortion occurs. Vo(ac) V1 t V2 D) Do R1 and R2 have any effect on the input resistance? If any explain it. E) How does the load resistance RL affect the gain factor? F) How does RL affect the distortion thresholds? (Hint: discard the current source and consider the AC load line.) 4. Procedure 4.1 Common Base Amplifier 4.1.1 Construct Circuit 1. (Similar to previous experiment find Ra so that the circuit is biased at 6mA.) Circuit 1 4.1.2 Exert a sinusoid input voltage. (10kHz frequency and 1V peak-to-peak are recommended.) 4.1.3 Measure the gain of the amplifiers for small signals. (VZ / VS, VZ / VE) Now increase the input voltage. Pay attention to the distortion in the output signal. Write the values of input and output voltages when the peaks of the output signal are distorted. (Hint: you may decrease R1 to gain larger input.) 4.1.4 Measure the input resistance seen from emitter. 4.1.5 Measure the base-emitter AC voltage when the output signal is going to be distorted. 4.1.6 Measure the frequency response of this circuit similar to the previous one and calculate fL. fIN VO AV 20 50 100 500 1k 5k 10k 50k 100k Table 1 4.2 Common Collector Amplifier with Larger Load Circuit 2 4.2.1 Construct Circuit 2. 4.2.2 Apply sinusoid input voltage. (10kHz frequency and 1V peak-to-peak are recommended.) 4.2.3 Measure the gain of the amplifier for small signals. (VY / VS, VY / VX) Now increase the input voltage. Note the distortion in the output signal. Write the values of input and output voltages when the output peaks are distorted. Explain why distortion happens. 4.2.4 Measure the input resistance seen from the point X. 4.2.5 Measure the output resistance when: I. X is input II. S is input 4.3 Common Collector Amplifier with Small Load 4.3.1 Substitute 1kload resistance with a 56 resistance and measure the gain factor as well as input and output resistances. 4.3.2 Compare these two experiments (especially regarding the output signal distortion) and explain the effect of the load resistance. 4.4 Comparison According to your observations compare these three amplifiers in the following aspects: 1. Voltage gain 2. Input resistance 3. Output resistance 4. Frequency response What are the applications of these three amplifiers? You may use PSPICE for frequency response analysis.