* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3:Tectonic Processes
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
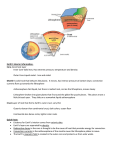
November 14, 2011 I will return your exams tomorrow. (Grades Look Good) Pick up a textbook from the library We will start Unit 3 today( Tectonic Processes) This unit has a lot of vocabulary words. Please download the vocabulary pdf from my website. Let's look at Tectonic Processes. These are the forces that are trying to build the earth. Physical evidence of this happening includes volcanoes, earthquakes, folds, and faults. Knowledge has come from studying seismic waves which are generated by earthquakes and are registered on seismographs 1) Body Waves: travel through the interior of the earth a) primary (P) or compression waves: travel fastest through any material b) secondary (S) or shearing-deformation waves: travel only through solid materials Surface Waves: travel only through the crust (i.e. L or long waves) Crust or Lithosphere 5 to 64 km thick brittle shell of solid rock that cracks, warps, and bends thinnest on the ocean floors Sial (i.e. light granitic rock): major component of the continents Sima (i.e. dense basaltic rock): major component of the ocean basins approx. 2900 km thick upper part is known as the asthenosphere very hot, approx. 1650 deg. C in upper part driving force for volcanoes, mountain building, and continental drift approx. 2900 km thick Outer core: likely made of liquid iron Inner core: believed to be solid iron, 4000 to 6000 deg. C, inner heat believed to be caused by the decay of radioactive rock located in the upper mantle - partially molten (i.e. approx. 10%) - lithosphere "floats" on top of the asthenosphere - zones that have become molten, or partially molten, can develop convection currents - convection currents in the asthenosphere are responsible for plate movement Convection currents in the outer core are partially responsible for the earth's magnetic field but do not drive the tectonic plates convection: transmission of heat within a liquid or gas by movement of heated particles. molten: liquefied by heat