* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Essential Nutrients
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Overeaters Anonymous wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Vitamin D deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
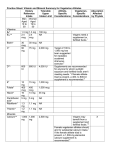
Essential Nutrients Six Essential Nutrients 1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Fats 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Fiber 7. Water Carbohydrates • What are they? – The basic building block of every carbohydrate is a sugar molecule, made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – 4 calories per gram Function: source of energy 2 Types of Carbohydrates Simple Carbohydrates – Simple carbohydrates are made up of one or two sugar molecules linked together – 4 calories per gram – Examples: glucose, fructose, and natural fruit sugar What does 200 calories look like? AVOCADO 125 grams= 4 ounces CELERY 1425 grams= 50 ounces or 3 POUNDS DORITOS 41 grams= 2 ounces SNICKERS 41 grams= 2 ounces CARROTS 570 grams= 20 ounces 1.5 POUNDS 2 Types of Carbohydrates • Complex Carbohydrates – are chains of three or more single sugar molecules – Takes a longer time for your body to break them down – Stay full longer – Includes fiber – Examples • Whole grain products, vegetables Protein • What is it? – Chains of amino acids • Functions: builds and repairs bones, muscles, cartilage, skin, and blood • 4 calories per gram • Example: meat Fat • What is it? – Chain of fatty acids • Function – source of energy, help maintain body temperature, and protect body tissues and organs 9 Calories per gram Healthy Fat Monounsaturated • • Monounsaturated fat tends to lower LDL cholesterol (the "bad" cholesterol). found in both plant and animal products, such as olive oil, canola oil, peanut oil, and in some plant foods such as avocado. Polyunsaturated • • Polyunsaturated Fat tends to lower blood cholesterol levels. found mostly in plant sources. (safflower, sunflower, soybean, corn, cottonseed). Unhealthy Fats Saturated • • • • increase blood cholesterol levels solid at room temperature found mostly in meat and dairy products, as well as some vegetable oils, such as coconut and palm oils Butter is high in saturated fat, while margarine tends to have more unsaturated fat. Trans • • raise your bad (LDL) cholesterol levels and lower your good (HDL) cholesterol levels. Eating trans fats increases your risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and developing type 2 diabetes. Cholesterol – a fatlike substance in the liver of all animals and therefore found only in foods of animal origin. • Bad-LDL –Good-HDL • It can elevate blood cholesterol levels which can be a major risk factor for heart and circulatory diseases. – It helps in the production of sex hormones and vitamin D (in the presence of sunlight) and of the protective shield around nerve fibers. Vitamins They are compounds that help regulate many vital body processes. (such as: digestion, absorption, and metabolism of other nutrients.) Vitamins Vitamins Amount of Intake for Women Amount of Intake for Men Types of Food that contain it Vitamin A 700 mcg-3000mcg 900 mcg-3000mcg Yellow, orange , and dark green vegetables, eggs, fish Vitamin B1 Thiamin 1.1 mg 1.2 mg Vitamin B2 Riboflavin 1.1 mg 1.3 mg Wild rice, pasta, whole grains Vitamin B3 Niacin 14 mg- 35mg 16 mg- 35 mg Bread, yeast, nuts seeds, dried fruit Vitamin B6 1.3 mg- 100 mg 1.3 mg- 100 mg Cereals, brown rice, brown bread Vitamin B12 2.4 mcg 2.4 mcg Meat, poultry, fish ,eggs Folate 400 mcg-1000mcg 400 mcg-1000mcg Brussel sprouts, broccoli, yeast, fruit juices, oranges Vitamins Vitamins Amount of Intake for Women Amount of Intake for Men Types of Food that contain it Biotin 30 mcg 30 mcg Whole grain products, egg yolks, bran cereals Vitamin C 75 mg- 2000mg 90 mg- 2000 mg Fruits, vegetables Kiwi, Brussel sprouts Vitamin D 5 mcg- 50 mcg 5 mcg- 50 mcg Dairy products, fish, egg yolks Vitamin E 15 mg- 1000 mg 15 mg- 1000 mg Nuts, seeds, avocado, egg yolk , whole grains Vitamin K 90 mcg 120 mcg Broccoli, green leafy vegetables Minerals Minerals Daily Intake Amount for Women Daily Intake Amount for Men Boron 20 mg 20 mg Calcium 1000-2500 mg 1000-2500mg Chromium 25 mcg 35 mcg Copper 900 mcg- 10,000 mcg 900 mcg- 10,000 mcg Fluoride 3 mg- 10 mg 4 mg- 10 mg Iodine 150 mcg- 1000 mcg 150 mcg – 1000 mcg Iron 18 mg- 45 mg 8 mg -45 mg Calcium---30 years old • Calcium - Gives structure to your bones and helps develop and maintain bone strength. (If you don’t get enough calcium during your teen years your bones will lack density and in later life you may suffer from osteoporosis.) Iron Iron - During the teen growing years iron is important to help the hemoglobin in your blood (hemoglobin carries oxygen throughout the body.) Without iron you would feel fatigue and have little endurance. Minerals cont. Minerals Daily Intake Amount for Women Daily Intake Amount for Men Magnesium 310 mg- 350 mg 350 mg- 400 mg Phosphorus 700 mg- 4000 mg 700 mg- 4000mg Selenium 55 mcg- 400 mcg 55 mcg- 400 mcg Zinc 8 mg- 40 mg 11 mg- 40 mg Water Recommended Daily Intake –60 percent of your body weight in ounces –Examples • 120lbs – 120 x .6 = 72 ounces WHY DO WE NEED ALL OUR ESSENTIAL NUTRITENTS? If we don’t……. • Weak immune system • increased susceptibility to disease • impaired physical and mental development • reduced productivity Unit 2 Vocabulary SEDENTARY- involving little physical activity. APPETITE- the psychological desire for food.. EATING DISORDERS- extreme, harmful eating behaviors that can cause serious illness or even death. BODY IMAGE- the way you see your body NUTRIENTS- substances in food that your body needs to grow, to repair itself, and to supply you with energy. CALORIES- a unit of heat used to measure the energy your body uses and the energy it receives from food. MY PLATE- icon chosen as an easy way to remind people to be mindful of what they put on their plate. METABOLISM- the process by which the body breaks down substances and gets energy from food. NUTRITION- the process by which your body takes in and uses food. VEGETARIAN- a person who eats mostly plant-based foods. Vocabulary unit 2 • VEGAN- a person who eats only plant-based foods. • NUTRIENT DENSE- foods that have a high ratio of nutrients to calories. • OBESE- having an excess of body fat. • FAD DIETS- weight loss plans that tend to be popular for only a short time. • OSTEOPOROSIS- a condition in which the bones become fragile and break easily.