* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coronary Artery Bypass
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
By: Brittney Mathis RN, BSN
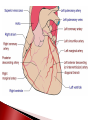
Saphenous
Circumflex
vein -> Right Coronary Artery and
Internal
Mammary Artery-> Left Anterior
Descending Coronary Artery
Patency over 90% after 10 years
If
more are needed, upper extremity veins can
be used but patency is less than 40% after 5
years
Explain the lines that will be in place after
surgery-ET tube, ART, Cortis, chest tubes, Foley
Explain use of IS following surgery and its
importance. Go ahead and practice
Educate on proper body mechanics and sternal
precautions that will be used for 6-8 weeks. Go
ahead and practice.
Chest and both legs are to be shaved completely
The night before and morning of surgery,
patient is to take a chlorohexadine bath and
swish/swallow
Intraoperative Care
Video of Bypass
Connect patient to proper monitors
STAT CBC, PT, PTT, BMP, MG, ABG, and glucose
STAT EKG, CXR
Connect chest tubes to suction and MONITOR
CHEST TUBES: q15mins for 1 hour and then
hourly. Call physician if output >150 mL first
hour or >100 mL/hr thereafter
◦ If it is greater, draw STAT PT/PTT, CBC, and
Fibrinogen and call surgeon
Vitals signs every 15 minutes, including CVP,
PA, CO/CI, and SVO2. Record an SVR every 4
hours or so, you may need to look up how to
calculate it.
See Handout
Patient CVP needs to 7-12 mm Hg for hearts.
CI >2.2
If these are low=patient needs volume
This allows a proper amount of volume to
keep the new grafts open and patent
Standing orders for volume: 1Liter NS, 1 Liter
Albumin (start with this), and sometimes 1
Liter of Hesban (don’t give if actively
bleeding)
Can give one unit of PRBC if Hgb<8
MAP is usually to be kept between 65-75
A MAP greater than 75 puts the patient at risk
for rupturing a bypass suture and increases
bleeding (chest tube output) from the suture
line.
There will always be either Cardene,
Nitroglycerin gtt, or sometimes Nipride
ordered
If the patient systolic blood pressure is less
than 90 and not responding to volume, call
physician.
Potassium is to be kept >4.0 mmol/L
Magnesium is to be kept >1.8
Calcium is to be kept >8.5
If at any time a CV surgeon rounds and these
are not correctly, I can guarantee him to get
angry.
Tamponade is the filling of the pericardium
with fluid, pus, or blood.
This can happen if bypass was not stitched
well and the chest tubes cannot drain fast
enough or the chest tubes are not
patent
Signs: increased CVP above PA
pressures, decreased BP, increased
HR, muffled heart sounds, pulsus
paradoxus, and decreased CO/CI
There is a Cardiac Weaning Protocol for Fast
track.
Best Practice: extubated in 6 hrs, OOB in 2 hours
Criteria-no acute ischemia, hemodynamically
stable, absence of new arrhythmia, blood loss
<2 mL/kg.hr, awakening from anesthesia
(following commands and lifting head off pillow),
core temp >97.0 F
1. Pt placed on CPAP
2. ABG in 30 mins
3. NIF and VC
4. Call anesthesiologist for orders
These are to be followed for 6-8 weeks to allow
proper healing of the sternum.
Do not lift more than 5-8 pounds. (Roughly a half
gallon of milk)
No pushing or pulling with your arms.
Do not reach behind your back or reach both arms
out to the side.
Do not reach both arms overhead.
Brace sternum with pillow while getting up, sitting
down, coughing, and sneezing.
Failure to follow these directions can result in sternal
wires breaking and a surgical procedure to fix them
will be needed.
Incentive Spirometer is to be done a
minimum of 10 times every hour
Coughing and deep breathing (use sternal
precautions)
Proper analgesics (promote deep breathing)
Early ambulation
All of these decrease the risk for postoperative
pulmonary complications that include:
pneumonia and atelectasis.
Antifibrinolytic Agent-minimizes bleeding
and decrease need for transfusion
Dose:
Monitor: incision sites for bleeding and chest
tubes for clots
Mechanism of Action: calcium channel blocker than
inhibits calcium ions from entering cardiac and
vascular smooth muscle cells. causes arteries to
dilate and blood pressure to decrease
Use: decrease BP, Increase CO, decrease SVR
Dosage: premixed bag of 40 mg in 200 mL.
recommended starting dose at 5 mg/hr for max
dose of 15mg/hr
Can be mixed in pharmacy for higher concentration
on CRRT patients
(Cardene I.V., 2013)
Dosage: 5 - 200 mcg/min
Must be mixed in glass bottle & administered
is special tubing
Mechanism of Action: Relaxes vascular smooth
muscle to reduce afterload & preload
Use: decrease blood pressure
Dosage: 0.5 - 8 mcg/kg/min
Precautions: Protect from light and monitor
serum Thiocyanate levels. Nipride metabolizes to
cyanide. Cyanide toxicity can develop within 1 hr
with infusions >10 mcg/kg/min
Phosphodiesterase inhibitor; positive inotrope
with little chronotropic effect; direct
vasodilator (decreases both preload &
afterload) activity
Uses: heart failure
Dosage: Load: 50 mcg/kg IVP over 10 minutes.
Then 0.375-0.75 mcg/kg/min IV infusion
("Medscape Reference," 2013)
Mechanism of Action: Strong alpha effects resulting
in increased peripheral vascular resistance and blood
pressure; decreases cardiac output and renal
perfusion
Use: Severe hypotension or shock
Dosage:20mg/250ml D5W at 100-180 mcg
increments IV bolus, THEN 40-60 mcg/min
continuous IV infusion
Side effects: pulmonary edema, V-tach, metabolic
acidosis
Mechanism of Action: inotropic agent whose primary
activity results from stimulation of the b-receptors of
the heart
Use: Increase contractility and CO in heart failure
Dosage:2.5 -10 mcg/kg/min
Warnings: may precipitate or exacerbate ventricular
ectopic activity
Weaning: 1mL/hr, weaning too quickly can cause
arrhythmias
Milrinone. (2013). Retrieved June 11, 2013,
from
http://reference.medscape.com/drug/milrinon
e-342433#0
Cardene I.V. (2013).
http://www.cardeneiv.com/c1_cardeneiv_ov.sh
tml