Visit the National Academies Press online, the authoritative source
... the link between diet, health, and chronic disease, and the emergence of advanced technologies that could measure small changes in individual adaptations to various nutrient intakes. Additionally, the use of fortified or enriched foods and the increased consumption of nutrients in pure form, either ...
... the link between diet, health, and chronic disease, and the emergence of advanced technologies that could measure small changes in individual adaptations to various nutrient intakes. Additionally, the use of fortified or enriched foods and the increased consumption of nutrients in pure form, either ...
- The Center for Best Practices
... the link between diet, health, and chronic disease, and the emergence of advanced technologies that could measure small changes in individual adaptations to various nutrient intakes. Additionally, the use of fortified or enriched foods and the increased consumption of nutrients in pure form, either ...
... the link between diet, health, and chronic disease, and the emergence of advanced technologies that could measure small changes in individual adaptations to various nutrient intakes. Additionally, the use of fortified or enriched foods and the increased consumption of nutrients in pure form, either ...
SCIENTIFIC OPINION Benfotiamine, thiamine
... females is 1.2 and 0.9 mg/day, respectively. In most other countries recommended intake is between 1.0 and 1.4 mg/day for adult males and 0.8 and 1.1 mg/day for adult females. Estimates based on food intake indicate that reported mean intake of vitamin B1 in some European countries varied from 1.10 ...
... females is 1.2 and 0.9 mg/day, respectively. In most other countries recommended intake is between 1.0 and 1.4 mg/day for adult males and 0.8 and 1.1 mg/day for adult females. Estimates based on food intake indicate that reported mean intake of vitamin B1 in some European countries varied from 1.10 ...
Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012
... individuals with diseases and for other groups with special needs or diets, dietary composition might have to be adjusted accordingly. After a thorough revision in which experts have reviewed a vast amount of scientific publications, most of the recommendations from the 4th edition (2004) remain unc ...
... individuals with diseases and for other groups with special needs or diets, dietary composition might have to be adjusted accordingly. After a thorough revision in which experts have reviewed a vast amount of scientific publications, most of the recommendations from the 4th edition (2004) remain unc ...
Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012
... individuals with diseases and for other groups with special needs or diets, dietary composition might have to be adjusted accordingly. After a thorough revision in which experts have reviewed a vast amount of scientific publications, most of the recommendations from the 4th edition (2004) remain unc ...
... individuals with diseases and for other groups with special needs or diets, dietary composition might have to be adjusted accordingly. After a thorough revision in which experts have reviewed a vast amount of scientific publications, most of the recommendations from the 4th edition (2004) remain unc ...
Guidelines on food fortification with micronutrients
... All rights reserved. Publications of the World Health Organization can be obtained from WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland (tel: +41 22 791 3264; fax: +41 22 791 4857; email: [email protected]). Requests for permission to reproduce or translate WHO pu ...
... All rights reserved. Publications of the World Health Organization can be obtained from WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland (tel: +41 22 791 3264; fax: +41 22 791 4857; email: [email protected]). Requests for permission to reproduce or translate WHO pu ...
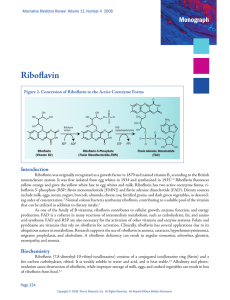
Figure 1. Conversion of Riboflavin to the Active
... Riboflavin was originally recognized as a growth factor in 1879 and named vitamin B2 according to the British nomenclature system. It was first isolated from egg whites in 1934 and synthesized in 1935.1,2 Riboflavin fluoresces yellow-orange and gives the yellow-white hue to egg whites and milk. Ribo ...
... Riboflavin was originally recognized as a growth factor in 1879 and named vitamin B2 according to the British nomenclature system. It was first isolated from egg whites in 1934 and synthesized in 1935.1,2 Riboflavin fluoresces yellow-orange and gives the yellow-white hue to egg whites and milk. Ribo ...
2011-2012 Product Catalog Leaders in Innovation and Purity
... The following is a list of inactive ingredients used in some of our products. These are fillers and excipients as defined by the Food Chemical Codex, nutrient compounds utilized for their physical properties to aid in the supplement production process. Derived from edible sources, they are generally ...
... The following is a list of inactive ingredients used in some of our products. These are fillers and excipients as defined by the Food Chemical Codex, nutrient compounds utilized for their physical properties to aid in the supplement production process. Derived from edible sources, they are generally ...
National Academy Press.
... prepared a draft of this edition that, after an outside review overseen by the Report Review Committee of the National Research Council (NRC), was postponed for further consideration (Press, 1985). The second panel, a subcommittee of the Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) itself, was appointed in 1987 t ...
... prepared a draft of this edition that, after an outside review overseen by the Report Review Committee of the National Research Council (NRC), was postponed for further consideration (Press, 1985). The second panel, a subcommittee of the Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) itself, was appointed in 1987 t ...
Full-Text PDF
... and nuts) is 220 g/day and the mean fruit intake is 166 g/day, with >50% of the countries of the World Health Organisation European Region consuming lower than 400 g/day of fruit and vegetables [104]. Nationwide, it is evident that consumption of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables is poor and fu ...
... and nuts) is 220 g/day and the mean fruit intake is 166 g/day, with >50% of the countries of the World Health Organisation European Region consuming lower than 400 g/day of fruit and vegetables [104]. Nationwide, it is evident that consumption of antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables is poor and fu ...
about CALCIUM VITAMIN D - Live Healthy Iowa Kids
... Calcium is most commonly associated with bone health; however, emerging evidence suggests that calcium also may influence other aspects of health. Cancer—Studies examining calcium and cancer are strongest relative to the risk and incidence of colorectal cancer. Adequate, not excessive, calcium intak ...
... Calcium is most commonly associated with bone health; however, emerging evidence suggests that calcium also may influence other aspects of health. Cancer—Studies examining calcium and cancer are strongest relative to the risk and incidence of colorectal cancer. Adequate, not excessive, calcium intak ...
Klaire Catalog
... Probiotics are beneficial living microorganisms that support healthy gastrointestinal and immune systems. Hundreds of diverse microbial species, some essential for health, others pathogenic, inhabit or pass through the gastrointestinal tract. In a healthy digestive system, these microorganisms coexi ...
... Probiotics are beneficial living microorganisms that support healthy gastrointestinal and immune systems. Hundreds of diverse microbial species, some essential for health, others pathogenic, inhabit or pass through the gastrointestinal tract. In a healthy digestive system, these microorganisms coexi ...
Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New
... consistent with good health. In children and pregnant and lactating women, the EER is taken to include the needs associated with the deposition of tissues or the secretion of milk at rates consistent with good health. ...
... consistent with good health. In children and pregnant and lactating women, the EER is taken to include the needs associated with the deposition of tissues or the secretion of milk at rates consistent with good health. ...
Kirkman catalogue
... used in popsicles (vitamins are especially good to add to popsicles; try Super Nu-Thera® powder and liquids); ...
... used in popsicles (vitamins are especially good to add to popsicles; try Super Nu-Thera® powder and liquids); ...
2008 The Nutritional Wellbeing of the British Population
... This analysis of British dietary surveys indicates that there have been positive changes in the diet of the British adult population over the last fifteen years. For example the evidence shows a fall in the intake of fat and saturated fat, a decrease in the consumption of red meat, processed meat an ...
... This analysis of British dietary surveys indicates that there have been positive changes in the diet of the British adult population over the last fifteen years. For example the evidence shows a fall in the intake of fat and saturated fat, a decrease in the consumption of red meat, processed meat an ...
22 Years and Counting
... guarantee nearly perfect conditions for these plants to thrive. The dark purple berries of the Acai plant (Euterpe Oleracea) contain up to 33 times the antioxidant content as red wine grapes. These amazing berries have traditionally been used to increase energy, stamina, vitality, and to promote ove ...
... guarantee nearly perfect conditions for these plants to thrive. The dark purple berries of the Acai plant (Euterpe Oleracea) contain up to 33 times the antioxidant content as red wine grapes. These amazing berries have traditionally been used to increase energy, stamina, vitality, and to promote ove ...
Vitamin K
Vitamin K refers to a group of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamins the human body needs for complete synthesis of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation, and also certain proteins that the body uses to control binding of calcium in bone and other tissues. The vitamin K-related modification of the proteins allows them to bind calcium ions, which they cannot do otherwise. Without vitamin K, blood coagulation is seriously impaired, and uncontrolled bleeding occurs. Low levels of vitamin K also weaken bones and promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.Chemically, the vitamin K family comprises 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (3-) derivatives. Vitamin K includes two natural vitamers: vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Vitamin K2, in turn, consists of a number of related chemical subtypes, with differing lengths of carbon side chains made of isoprenoid groups of atoms.Vitamin K1, also known as phylloquinone, phytomenadione, or phytonadione, is synthesized by plants, and is found in highest amounts in green leafy vegetables because it is directly involved in photosynthesis. It may be thought of as the ""plant"" form of vitamin K. It is active as a vitamin in animals and performs the classic functions of vitamin K, including its activity in the production of blood-clotting proteins. Animals may also convert it to vitamin K2.Vitamin K2, the main storage form in animals, has several subtypes, which differ in isoprenoid chain length. These vitamin K2 homologues are called menaquinones, and are characterized by the number of isoprenoid residues in their side chains. Menaquinones are abbreviated MK-n, where M stands for menaquinone, the K stands for vitamin K, and the n represents the number of isoprenoid side chain residues. For example, menaquinone-4 (abbreviated MK-4) has four isoprene residues in its side chain. Menaquinone-4 (also known as menatetrenone from its four isoprene residues) is the most common type of vitamin K2 in animal products since MK-4 is normally synthesized from vitamin K1 in certain animal tissues (arterial walls, pancreas, and testes) by replacement of the phytyl tail with an unsaturated geranylgeranyl tail containing four isoprene units, thus yielding menaquinone-4. This homolog of vitamin K2 may have enzyme functions distinct from those of vitamin K1.Bacteria in the colon (large intestine) can also convert K1 into vitamin K2. In addition, bacteria typically lengthen the isoprenoid side chain of vitamin K2 to produce a range of vitamin K2 forms, most notably the MK-7 to MK-11 homologues of vitamin K2. All forms of K2 other than MK-4 can only be produced by bacteria, which use these forms in anaerobic respiration. The MK-7 and other bacterially derived forms of vitamin K2 exhibit vitamin K activity in animals, but MK-7's extra utility over MK-4, if any, is unclear and is a matter of investigation.Three synthetic types of vitamin K are known: vitamins K3, K4, and K5. Although the natural K1 and all K2 homologues and synthetic K4 and K5 have proven nontoxic, the synthetic form K3 (menadione) has shown toxicity.