* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Republic established (Oligarchy)
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
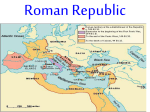
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Rome
1000 Years
only 200 years of peace – Pax Romana
Megalopolis
VALUES:
International Culture
Practical
Rational
Hard Working
Group Oriented
Thrift, Honesty, Loyalty
Self-deprecating
Art’s main function – Entertainment, not Enlightenment
2 Major Periods: Republic & Empire
2 Foundation Myths
•Republican – Romulus & Remus
•Hard Work
•Roman success more important than
family ties
•Imperial – Aeneas
1)Long-suffering
2)Total dedication to destiny
Roman Cultural Timeline
Early Influences:
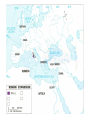
800 – 308 BC – North/Central Italy controlled by the Etruscans
Southern Italy controlled by Greeks
Beginnings:
509 BC - Roman Republic established (Oligarchy)
Patricians – wealthy landowners (10% of population)
Plebeians – landless masses (90% of population)
Government:
Two Consuls (Patricians) – executive heads
300 member Senate (Patricians)
Dictator (Patrician) – military leader in time of war
Tribunes (Patricians) – protectors of the Plebeians’ interests
Law:
Twelve Tables – (Greek based, but on Draco, not Solon)
Land Ownership:
Large estates controlled by Patricians
As time goes on, Plebeians forced into virtual slavery
Welfare system created out of necessity
Military:
Most organized in ancient world
Based on the Legions
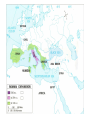
Punic Wars (264-146 BC) vs. Carthage begins move towards empire
Most of Mediterranean / Northwestern Europe conquered
Citizenship offered to conquered peoples
Cosmopolitan culture develops
End of Republic:
Period of Civil War follows (130-45 BC)
Gaius Julius Caesar becomes Dictator in 45 BC but is assassinated
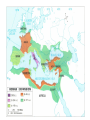
Empire:
Caesar’s nephew, Octavian maneuvers to become virtual Emperor by 27 BC
Bureaucracy established – so efficient that it can withstand bad rulers
Pax Romana (27-180 BC) – no major wars, stability throughout the Mediterranean
180 BC – death of Marcus Aurelius, last truly great Emperor
180-476 BC – Decline and collapse of the Empire
Growth of Christianity
Constantinople established – foundation of Byzantine culture
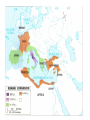
Etruscan Culture and Art {Etruria}
Origins in Lydia/Asia Minor?
Control N.Italy for 400 yrs.
Undeciphered unique language
Pursuit of the good life
Confederations of city-states ruled
by warrior aristocrats
rule Rome for 100 yrs. until driven
out in 3rd Century BC
Most of what we know is from their
tombs
Accused of hedonism by the
Romans
Greek influences
Borrow nothing from the Romans,
but huge influence on Rome
Religion –
Asian origins
Divination
Gods similar in function to Greco-Roman
Human Sacrifice – origins of gladiatorial combat
Art is distinctive – earthy, vigorous, sometimes
homespun
Unique elements but also Hellenic & Hellenistic
influences
Sculpture – Terra-cotta is their favorite medium,
but also use of bronze
Painting – Murals
Strong, black-outlined figures with
bright colors
Religious, Leisure, & Greek-based
subjects
Jewelry – highly skilled goldsmiths
Architecture Cities - Rectangular, planned,
fortified on hilltops
Greek elements in buildings –
colonnades
used Atriums, Aqueducts, Bridges,
Sewers BEFORE Romans