* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White Blood Cell Abnormalities
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
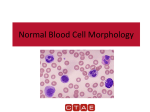
White Blood Cell Abnormalities Laboratory Procedures Let us recall what looks Normal. Some terminology for morphology • -penia: decreased number of cells in the blood (Neutropenia, lymphopenia). • -philia or –cytosis: increased number of cells in the blood (neutrophilia, lymphocytosis). • Macrocytosis: larger than normal cells • Microcytosis: smaller than normal cells • Anisocytosis: cells that are unequal in size • Left shift: presence of immature neutrophils in blood. Nuclear Hyposegmentation • Can be found in cells that contain lobulated or segmented nuclei. • Which cells would this be? • What could this indicate? Pelger-Huet Anomaly • Hyposegemented neutrophils that function normally. • Hereditary disorder; failure of the nucleus in mature cells to undergo segmentation. Nuclear Hypersegmentation • Recall what can cause this. Toxic Neutrophils • Characterized by ctyoplasm basophilia, Dohle bodies, toxic granulation, and/or foamy cytoplasm. • Cells have decreased functional abilities. • Animal with toxic, degenerative shift may be compromised by lack of adequate cell number and decrease ability of cells to function. Dohle Bodies • Blue cytoplasmic inclusions. • Low numbers may be found in healthy cats. • Indicates toxicity in other species. Normal vs. Toxic Neutrophils Intracytoplasmic Neutrophil Inclusions • Found in neutrophils of animals with certain infectious diseases. • Ehrlichia species. Atypical or Reactive Lymphocytes • Contain azurophilic granules. • Generally associated with disease such as ehrlichiosis • May have cleaved nuclei • May have increased cytoplasm • May have increased basophilia in cytoplasm • Changes caused by antigenic stimulation secondary to vaccination or infection. Lysosomal Storage Disorders • Rare • Inherited disease where substance is abnormally is stored within the cells due to enzyme deficiency. • Can cause skeletal or neurologic disorders • May contain vacuoles or certain granules. Birman Cat Neutrophil Granulation Anomaly • Contain fine eosinophilic to magenta granules. • Inherited autosomal-recessive trait • Neutrophil function is normal and cats are healthy. Chediak-Higashi Syndrome • Neutrophils in cats have large fused lysosomes within the cytoplasm. • Stain pink or eosinophilic. • May have tendency to bleed because platelet function is abnormal. • Generally are healthy cats. Smudge Cells • May be called basket cells • Degenerative leukocytes that have ruptured. • Small numbers are not considered significant. • May be artifact when blood is held too long. • May be associated with leukemia.