* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Lies Beyond
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Planetary nebula wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
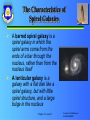
What Lies Beyond Warm Up Questions CPS Questions (1-2) Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Lesson Overview Other Galaxies and Their Classifications Five Types of Space Objects The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Big Bang Theory Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Quick Write What other example can you give, either in history or from your own life, of an important discovery made on the search for something else? (Note to teacher: Use “Pick a Student” button in CPS) Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Other Galaxies and Their Classifications Edwin Hubble divided galaxies into three major groups Spiral Elliptical Irregular Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of California Institute of Technology The Characteristics of Spiral Galaxies A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy in which the spiral arms come from the ends of a bar through the nucleus, rather than from the nucleus itself A lenticular galaxy is a galaxy with a flat disk like a spiral galaxy, but with little spiral structure, and a large bulge in the nucleus Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of Todd Baronson NOAO/AURA/NSF The Characteristics of Elliptical Galaxies An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy with a smooth spheroidal shape Science classifies elliptical galaxies according to how they appear from Earth, from round to very elongated Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of NOAO/AURA/NSF The Characteristics of Irregular Galaxies An irregular galaxy is a galaxy of irregular shape that cannot be classified as spiral or elliptical The Magellanic Clouds are usually classified as irregular galaxies Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of NOAO/AURA/NSF The Brightness, Luminosity, and Motions of the Stars Apparent magnitude is a measure of the amount of light received from a celestial object This measure contrasts with luminosity – the rate at which electromagnetic energy is emitted from a celestial object Proper motion is the term for the angular velocity of a star as measured from the Sun Proper motion is opposed to observed motion that is due to Earth’s movement Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Optical Doubles and Binary Star Systems Optical double is two stars that, from Earth, appear to be very close but are not actually gravitationally bound Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Interstellar Clouds and Nebulae Fluorescence is the process of absorbing radiation of one frequency and re-emitting it at a lower frequency An emission nebula is a cloud of interstellar gas receiving ultraviolet radiation and fluorescing Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Interstellar Clouds and Nebulae, cont. A reflection nebula is a cloud of interstellar dust that becomes visible because it refracts and reflects light from a nearby star A dark nebula is an interstellar molecular cloud whose dust blocks light from stars on the other side of it Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of Hubble Heritage Team (STScl)/NASA The Discovery of Pulsars Jocelyn Bell stumbled upon pulsars in 1967 while searching for quasars A pulsar is a pulsating radio source with a regular period, between a millisecond and a few seconds, believed to be associated with a rapidly rotating neutron star Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of NASA Theories About Dark Matter in Space Missing mass is the difference between the mass of clusters of galaxies as calculated from Keplerian motions and the amount of visible mass Dark matter — matter that can be detected only by its gravitational interactions Dark energy — an exotic form of energy whose negative pressure speeds up the expansion of the universe Chapter 4, Lesson 2 The Types of Electromagnetic Waves The Electromagnetic spectrum is the entire array of electromagnetic waves Celestial objects emit waves up and down the spectrum Scientists learn a great deal from the invisible radiation emitted by celestial objects Chapter 4, Lesson 2 The Types of Electromagnetic Waves, cont. Chapter 4, Lesson 2 The Atmospheric Absorption of Wavelengths Visible light and part of the radio spectrum can cut through the atmosphere The atmosphere blocks most of the electromagnetic spectrum Chapter 4, Lesson 2 The Big Bang Theory The big bang is the theoretical initial explosion that began the expansion of the universe In 1948 scientists theorized that cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB) would be striking the Earth from all directions but that it should be very faint Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Other Evidence for the Big Bang Theory The sky is dark at night because the universe is finite A finite universe doesn’t have enough stars to light up all of space The observed proportions of light chemicals are consistent with a process of nuclear fusion in the first few minutes of a hot young universe Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Learning Check CPS Questions (3-4) Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Activity 1: What Lies Beyond Puzzle Use your textbook to complete the crossword puzzle. Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Activity 2: Space Objects Review information about your assigned space object in the textbook (pages 166172) and other materials, if available As a group prepare a five-minute presentation about your topic Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Activity 3: Vocabulary Academic Challenge “Family Feud” style activity Name the correct vocabulary word Each correct answer is worth 100 points Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Technology Enrichment: Final Shuttle Mission to Hubble Using the website provided, work in small groups to learn more about the final shuttle mission to repair the Hubble Telescope Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Review Edwin Hubble divided galaxies into three major groups: spiral, elliptical, and irregular There are five types of space objects – stars, binary star systems, clouds and nebulae, pulsars, and dark matter The electromagnetic spectrum is the entire array of electromagnetic waves The big bang is the theoretical initial explosion that began the expansion of the universe Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Review Questions CPS Questions (5-6) Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Summary Other Galaxies and Their Classifications Five Types of Space Objects The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Big Bang Theory Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Next… Done – What Lies Beyond Next – Why Explore Space? Chapter 4, Lesson 2 Courtesy of NASA/JPL