* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts and Functions of a Flower PPT
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
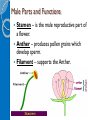
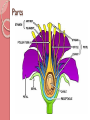
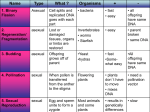
Parts and Functions of a Flower Male Parts and Functions Stamen – is the male reproductive part of a flower. Anther – produces pollen grains which develop sperm. Filament – supports the Anther. Female Parts and Functions Pistil – is the female reproductive part of a flower. Stigma – sticky pollen-receptive part of the pistil. Style – the stalk of the pistil down which the pollen tube grows. Ovary – contains the ovules and becomes the fruit. Ovule – becomes the seeds when sperm cells fertilize the egg cells. Other Parts and functions Petal – colorful part of a flower used to attract insects and birds. Sepal – protects the bud of a young flower. Receptacle – reproductive parts of a plant are attached here. Roots – provides the stems and leaves with water and dissolved minerals from soil. Roots Parts Pollination Pollination is the process in which pollen is transferred in the reproduction of plants. Cross-pollination Is when pollen is delivered to a flower from a different plant. Self-pollination Is when pollen from one flower pollinates the same flower of the same plant. Some methods of pollination ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Animals (birds, reptiles, mammals) Insects (bees and butterflies mostly) Wind WATER Steps to Flower/Plant Reproduction ***Reproduction of a plant takes place in the flower*** Pollination 1. The Anther produces pollen 2. That pollen is transferred to the stigma of itself or another flower through pollination. Fertilization 3. Pollen travels down the style to the ovary to fertilize the eggs. The eggs grow into a seed or seeds and can now reproduce. What controls flowering????? The length of Night! 1. During the day plants taken in light, water and nutrients needed to go through photosynthesis. 2. Then at night it uses the glucose (food) to grow and reproduce…FLOWER. Video View Brain Pop on Pollination!!!!!!!!!!!!