* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weathering and Erosion Study Guide
River bank failure wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
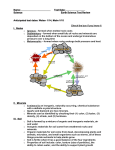
Weathering and Erosion Study Guide Vocabulary Mechanical Weathering Chemical Weathering No-till farming Erosion Leaching Soil Soil profile Ice Wedging Humus Terracing Contour Farming Oxidation ____________________ When chemical reactions dissolve or alter the minerals in rocks or change them into different minerals ____________________ When rocks are broken apart by physical processes ____________________ Process in which surface materials are worn away and transported from one place to another by agents such as gravity and water ____________________ Occurs when some materials are exposed to oxygen and water. ____________________ The removal of minerals that have been dissolved in water. ____________________ a mixture of weathered rock, decayed organic matter, mineral fragments, water, and air. ____________________ Method for reducing soil erosion; plant stalks are left in the field after harvesting and the next year’s crop is planted within the stalks without plowing ____________________ Occurs in temperate and cold climates where water enters cracks in rocks and freezes. ____________________ All of the horizons of soil ____________________ Decayed organic matter that turns into a dark-colored material ____________________ Planting along the natural contours of the land to reduce soil erosion. ____________________ Method in which steep-sided, level topped areas are built onto the sides of steep hills and mountains so that crops can be grown. Write a P (physical change) or C (chemical change) next to each characteristic. Change in Color ________ Change in odor ________ Change in energy ________ Change in state ________ Change in shape ________ Ability to dissolve ________ Write a M (mechanical weathering) or a C (chemical weathering) next to each example. Plant Roots ________ Living Organisms ________ Abrasion ________ Water ________ Oxygen ________ Animal Actions ________ Acid Rain________ Freezing and thawing ________ Release of Pressure ________ Carbon Dioxide ________ Fill in the Blank The layer of soil that contains the most humus as well as smaller rock and mineral particles than the other horizons is the __________ horizon. The organic material in humus includes ___________________________________. What is the main difference between mechanical and chemical weathering? (thinkchemical composition) ___________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ In order for oxidation to occur ___________, ______________, and ______________ need to be present. Litter is found in which horizon _____________. What is the piling of sediment in a new area? ____________________. Write A (A-horizon), B (B-horizon), or C (C-horizon) next to each picture and statement about soil horizons. Contains course sediments and parent material of soil __________ Contains leached material from other layers ___________ Dark, fertile coil containing humus ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ Write W (weathering), E (erosion), D (deposition) next to each example Flood water pounding against a canyon wall and wearing it down ___________ Rain washing away soil from a hillside ___________ Layers of sediment forming at the bottom of the ocean ___________ A mudslide flowing down a steep hill ___________ Caves being formed by acid rain dissolving underground limestone ___________ Waves dropping sane on the beach ___________ Name the five factors that affect soil erosion. 1. _______________________ 4. _______________________ 2. _______________________ 5. _______________________ 3. _______________________ Explain the difference between soil in a desert and soil in a tropical rain forest (think about the pores of the soil). _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Evaluate why soil erosion is a serious problem for agriculture _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________