* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Mrs. Malm`s 5th Grade
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
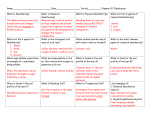
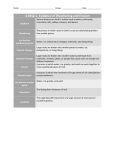
Name: __________________________ Science Test Date: _________________ Earth Science Test Review Anticipated test dates: Wales- 1/14, Malm 1/15 Check the box if you know it I. Rocks o Igneous – formed when melted rock cools o Sedimentary – formed when small bits of rocks and minerals are deposited on the bottom of the ocean and undergo tremendous pressure over a long time o Metamorphic – formed when rocks undergo both pressure and heat II. Minerals o A mineral is an inorganic, naturally occurring, chemical substance with a definite crystal structure. o Quartz and diamond are two minerals. o Minerals can be identified by checking their (1) color, (2) luster, (3) density, (4) streak, and (5) hardness. III. Soil o Soil is formed by a mixture of organic and inorganic materials, air and water o Inorganic materials for soil come from weathered rocks and minerals. o Organic materials for soil come from dead, decomposing plants and animals, microbes, and small organisms such as worms, all of these things provide nutrients to help plants grow. o Soil is fertile when it has a good balance of the four ingredients o Properties of soil include: color, texture (size of particles), the ability to retain water, and the ability to support plant growth IV. Weathering o Weathering is the breaking down of rocks and minerals into smaller pieces. o Weathering agents, such as liquid water, wind, plants’ roots, and ice all work to slowly break rocks down. V. Erosion o Erosion is the movement of weathered rocks and minerals to a new location. o Erosion can be caused by wind, running water, ice, humans, or gravity. o Erosion can occur slowly, as when a rock is moved by a glacier, or quickly, as when it is moved by a landslide. VI. Water Cycle o Evaporation – when liquid water gets enough heat energy to become water vapor o Condensation – when water vapor begins to cool and form clouds, fog, or dew o Precipitation – when condensed water falls from the sky as rain (liquid water), snow (frozen crystals), sleet (a mix of rain and ice), or hail (balls of ice) o Infiltration – when precipitation hits the earth and seeps into the soil and goes underground o Run-off – when precipitation hits the earth and stays on the surface, running into larger bodies of water o Water evaporates (or boils) at 100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit o Water freezes/melts at 0 degrees Celsius or 32 degrees Fahrenheit o Water can be a liquid, solid, or gas VII. Weather o Weaterh is particular to a specific time and place. o Components of weather: (1) temperature (2) precipitation (3) wind speed, (4) wind direction, and (5) humidity (or moisture in the air) VIII. Climate o Climate is the average weather conditions in a place or region and is determined over a long period of time IX. Astronomy Review–Yes! Just because you’ve already been tested on it doesn’t mean you should forget it! o Identify the 8 moon phases o Know the 8 planets and their order from the sun o Understand rotation and how it causes night and day o Understand revolution and how one revolution equals a year o Explain why we have seasons TEST FORMAT -Draw, label the 5 stages of the water cycle. -Label a rock cycle diagram -Multiple choice (MCAS style questions) -Matching definitions -Fill in the blank -Short Answer -Open response