* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Muscle Cells and Tissue
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
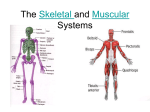
Muscle Cells and Tissue Time for a Movie Discovery Channel Pushing the Limits: Muscle Fibers 10:39: Describe skeletal muscle fibers (muscle cells). 11:21 How many skeletal muscle fibers do we normally use at any one time? 12:19 What body structure is needed to trigger our skeletal muscle fibers? 13:15 When is the only time we can trigger all of our skeletal muscle fibers at once? 13:40 What is the cost of using all of our skeletal muscles at once? Learning Target: Compare skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells and tissue. Involuntary Voluntary Involuntary Learning Target: Compare skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells and tissue. Striated Striated Non-striated Learning Target: Compare skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells and tissue. Branched Not branched Tapered Learning Target: Compare skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle cells and tissue. Single nucleus Multinucleated Single nucleus True or False Smooth muscle is found primarily in the musculature of the extremities. Baloney Smooth muscle is found lining organs and it is the type of muscle making up the iris of the eye. True or False 2. The two muscle cells that contract without conscious thought are cardiac and smooth. Truth True or False 3. Skeletal muscle cells have many nuclei. Truth Long skeletal muscle cells can have 1000 nuclei. True or False 4. Without skeletal muscle tissue you would not have any facial expression. Truth Skeletal muscles attach to facial bones such as the zygomatic bone. True or False 5. The only type of muscle cell lacking striations is smooth. That’s right- It’s smooooth. What type of cells are these? What type of cells are these? What type of cells are these? Tissues associated with the muscular system Skeletal muscle tissue Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Smooth muscle tissue Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Cardiac muscle tissue Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Dense Regular Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Dense Irregular Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Nervous Tissue Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart Tissues associated with the muscular system Blood Supplies nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissue and carries away waste products Covers and holds muscles in place (fascia) Aids in skeletal movement and facial expression Forms tendons Transmits impulses and messages to muscles Contracts hollow internal organs Allows for rhythmic contraction of the heart