* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download baclofen
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Ciprofloxacin wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
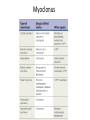
Treatment of Hyperkinetic Movement Disorders: Part II Tim McDowell Stiff-Person Syndrome • Combo therapy of benzodiazepines and baclofen in high dosage. • These drugs may decrease the superimposed severe spasms, but are not entirely effective in controlling the background sustained continuous muscle hyperactivity • Sodium valproate and tizanidine have also been reported to be beneficial • Intrathecal baclofen has been used • Patients have been reported to respond to steroid therapy, intravenous human immunoglobulin (IVIg) infusions and plasmapheresis, but others have gained no benefit from plasmapheresis. • A double-blind, placebo-controlled study documented the value of IVIg • Another study has shown improvement in quality of life with IVIg • Rituximab has been reported to be useful in a few patients Baclofen • precise mechanism of action of baclofen is not fully known. • Can inhibit monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes at the spinal level, ? actions at supraspinal sites • baclofen is an analog of the putative inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (not proven that this is its mechanism of action) • Has CNS depressant properties • Rapidly and extensively absorbed and eliminated. Can be reduced with increasing doses. • Kidney excretion, large intersubject variation in absorption and/or elimination. Baclofen • Oral: 5 mg 3 times/day, may increase 5 mg/dose every 3 days to a maximum of 80 mg/day • Intrathecal: • Test dose: 50-100 mcg, doses >50 mcg should be given in 25 mcg increments, separated by 24 hours. A screening dose of 25 mcg may be considered in very small patients. Patients not responding to screening dose of 100 mcg should not be considered for chronic infusion/implanted pump. • Maintenance: After positive response to test dose, a maintenance intrathecal infusion can be administered via an implanted intrathecal pump. Initial dose via pump: Infusion at a 24-hourly rate dosed at twice the test dose. Avoid abrupt discontinuation. Tizanidine • Tizanidine hydrochloride – alpha-2-adrenergic agent • short-acting drug for the management of spasticity. • should be reserved for those daily activities and times when relief of spasticity is most important • common adverse events make it prudent to begin treatment with single oral doses of 4 mg. Increase the dose gradually (2 mg to 4 mg steps) to optimum effect • The dose can be repeated at 6 to 8 hour intervals, as needed, to a maximum of three doses in 24 hours. The total daily dose should not exceed 36 mg. Tizanidine • Side effects: dizziness, somnolence, weakness, • Strong interaction with ciprofloxacin, do not use together – Ciprofloxacin decreases the metabolism of tizanidine significantly • Caution with elderly (anticholinergic properties) • Monitor LFTS at baseline, 1,3,6 months, BP and renal function • Pregnancy risk C Myoclonus Myoclonus • The drugs used to treat myoclonus generally possess anticonvulsant properties), usually by enhancing gamma-aminobutyric (GABA) inhibitory activity. • Electrophysiologic evidence suggests that antimyoclonic drugs may exert different actions on the sequence of events responsible for myoclonus, at least for those concerned with cortical myoclonus. Some drugs which decrease cortical myoclonus increase the size of the giant sensory evoked potential, while others have the opposite effect. Myoclonus thus often responds best to a combination of drugs Myoclonus Cont’d Clonazepam (Rivotril) • Start at 1.5mg daily, in three doses, go up to 15mg. Taper off • Side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, behavioral • Watch for delirium in elderly • Can increase phenytoin levels • Carbamazepine can increase metabolism • Pregnancy Risk D, not recommended for breastfeeding • Monitor CBC, LFTs Painful Legs-Moving-Toes • Very difficult to treat; some success has been claimed with the following: – Nerve blocks, guanethidine infusions, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation – Anticonvulsants, antidepressants, adenosine • It is the pain that causes the major disability, and unfortunately, this is very difficult to treat. A few patients have responded to sympathetic blockade, but in the majority, this is ineffective. A course of guanethidine blocks into the affected limb is worth trying. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimu-lation applied to the leg or foot might help the pain. Carbamazepine, diphenylhydantoin, amitriptyline, and pheno-thiazines occasionally help. There is one report of adenosine being useful. One patient responded to gabapentin 600 mg three times per day. Epidural block may be helpful, as may epidural spinal cord stimulation. Wilson’s Disease Paroxysmal Dyskinesias • Paroxysmal Kinesogenic: – anticonvulsants • Paroxysmal Nonkinesogenic: – Clonazepam, other benzos, acetazolamide, antimuscarinics • Paroxysmal Exertional: acetazolamide,antimuscarinics, benzodiazepines Episodic Ataxia • Acetazolamide should be tried • Most effective in EA2 (?50-75%, no RCTs), also EA3, EA5, and EA6 • Can also try anticonvulsants for EA1 Acetazolamide • • • • Aka Diamox Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Dosing 250-1000mg/day, twice daily dosing Side Effects: Dizziness, anorexia, metallic taste in mouth, numbness and tingling in hands, feet and mouth, kidney stones • Careful for sulfa allergies • Monitor electrolytes • Pregnancy Category C RLS Augmentation: Onset of symptoms earlier or extension to arms/trunk. Difficult to treat, see ‘Refractroy RLS‘above Suggested Reference