* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
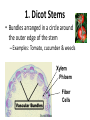
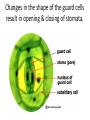
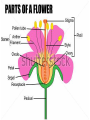
Plants Zebra Book Page 608 • Copy the Plant Kingdom phylogenetic tree in your notes • Fill out the Nonvascular vs. Vascular Plant chart using pages 610-621 *(Alligator book pgs. 617-622) Plant Structure & Function Don’t make it more complicated than it is! Stems • 2 Functions – Support the leaves (hold them up to the light) – Transport water & food within the plant via its vascular system Vascular System • Xylem – Plant tissue that transports water & dissolved minerals from the roots up toward the leaves • Phloem – Plant tissue that transports glucose from the leaves down the plant Xylem & Phloem are arranged in vascular bundles 3 Types of Stems 1. Dicot Stems • Bundles arranged in a circle around the outer edge of the stem – Examples: Tomato, cucumber & weeds Phloem Fiber Cells 2. Monocot Stems • Randomly arranged bundles of vascular tissue • Examples: – Grasses, corn, lilies 3. Woody Stems • Have a thin layer called cambium (also called the growing layer) between the xylem & phloem – New cambium grows 1x per year, thus giving us tree rings! • Bark = outer portion of stem – Inner portion of bark contains phloem • If you peel the bark, you could kill the tree Roots • Functions: – Absorb water and dissolved minerals – Anchor the plant to the soil Structure of Roots • Primary root – First root to grow out of a seed • Taproot – If the primary root grows down into the soil and remains the largest root, we call it the taproot • Ex. Carrots, beets, turnips & sweet potatoes are taproots that store food • Fibrous root – If the primary root develops into many small roots near the surface of the soil, we call it a fibrous root • Ex. Many monocots such as grasses & orchids * Note - Root hairs increase absorptive surface area Leaves • Function #1: – Photosynthesis (plants make sugar for food) & Respiration • Function #2: – Transpiration (gas exchange in leaves that occurs through the stomata) Changes in the shape of the guard cells result in opening & closing of stomata. Stomata Lab Procedure: 1. Paint a thick patch (at least one square centimeter) of clear nail polish on the underside of the leaf surface being studied. 2. Allow the nail polish to dry completely. 3. Tape a piece of clear tape to the dried nail polish patch. 4. Gently peel the nail polish patch from the leaf by pulling on a corner of the tape and "peeling" the polish off the leaf. This is the leaf impression you will examine. 5. Tape your peeled impression to a microscope slide. Things to Consider: 1. Under scanning and low power, the slide will look like smeared nail polish! 2. Under medium power, you should be able to see the stomata! Article: 32,000 Year Old Plant Brought Back to Life – Oldest Yet! National Geographic News February 21, 2012 As a group, answer the following questions: 1. How do scientists know how old the seeds are? 2. How were scientists able to germinate 32,000 year old seeds? 3. What is permafrost? Why could it be important to understanding the past? 4. How could this discovery be important to us in the future? Plant Reproduction Angiosperms Flower – Primary unit of angiosperm reproduction 5 Parts of a flower (refer to handout) • • • • Receptacle Sepals Petals Stamen – Anther & filament • Pistil – Stigma, Style & Ovary Pollination • The transfer of pollen from the anther to a stigma of a flower of the same species by wind or animal • 2 Types – Cross Pollination – transfer of pollen from 1 plant to another of the same species – Self-pollination – transfer of pollen from one flower to another on the same plant Fertilization • Union of gametes (pollen & ovule) • Steps: 1. Pollen grain lands on stigma 2. A pollen tube grows from the stigma down the style and into the ovary 3. The sperm then travels down the tube into the ovary where it fuses with the ovule 4. The zygote (baby plant) begins to develop & will eventually form a seed (the ovary will develop into the fruit)