* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzyme Mechanisms: Serine Proteases Questions
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteases in angiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
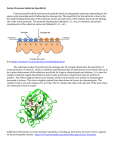
1/30/2013 Enzyme Mechanisms: Serine Proteases C483 Spring 2013 Questions 1. The substrate specificity of serine proteases is primarily due to A) a specificity pocket in the protein. B) the positions of specific side chains of serine, histidine, and aspartate. C) distinct backbone conformations of the individual proteins. D) A and B. E) A, B and C. 2. The role of serine at the active site of serine proteases is to act as a(n) ________ catalyst, while the histidine residue serves as a(n) ________ catalyst. A) strong; weak B) weak; strong C) acid‐base; covalent D) covalent; acid‐base E) anionic; ionic 3. Experiments on the bacterial serine protease subtilisin show that even when all three residues of the catalytic triad are mutated, the catalytic rate of the enzyme is still 3000 times the uncatalyzed reaction rate. Which mode of catalysis is likely responsible for this remaining catalytic activity? A) Acid‐base catalysis. B) Covalent catalysis. C) Induced fit. D) Hydrophobic effects. E) Transition‐state stabilization. 1 1/30/2013 Proteases • Role in Digestion • Zymogens • Serine Proteases – Chymotrypsin – Trypsin – Elastase • Homology Selectivity of Serine Proteases 2 1/30/2013 Mechanism of Serine Proteases: Catalytic Triad Chemical Mechanism • Substrate binding affects Histidine base strength • Covalent catalysis • Oxyanion hole • Covalent intermediate 3 1/30/2013 Chemical Mechanism • Read from bottom! • General acid‐base catalysis • Oxyanion hole • Return to initial state • Compare/contrast to Main Protease Answers 1. A 2. D 3. E 4