* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter_03 - Welcome to people.pharmacy.purdue.edu!
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
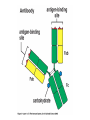
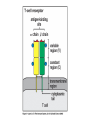
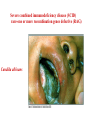
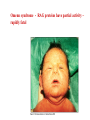
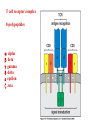
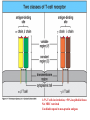
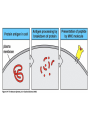
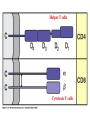
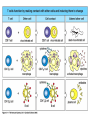
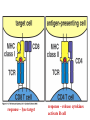
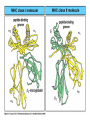
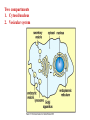
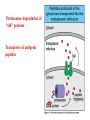
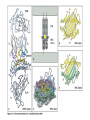
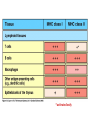
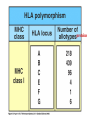
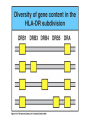
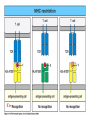
Peter Parham The Immune System Second Edition Chapter 3 Antigen Recognition by T Lymphocytes Copyright © 2005 by Garland Science Publishing Figure 3-1 part 1 of 2 Figure 3-1 part 2 of 2 Figure 3-2 Figure 3-3 Severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) rare-one or more recombination genes defective (RAG) Figure 3-4 Candida albicans Omenn syndrome - RAG proteins have partial activity – rapidly fatal Figure 3-5 T cell receptor complex 8-polypeptides a alpha b beta g gamma d delta e epsilon z zeta Figure 3-6 Figure 3-7 1-5% T cells in circulation, >50% in epithelial tissue Not MHC restricted Can bind/respond to non-protein antigens Figure 3-8 Figure 3-9 Helper T cells Figure 3-10 Cytotoxic T cells Figure 3-11 Figure 3-12 response – lyse target response – release cytokines activate B cell Figure 3-13 part 1 of 2 Figure 3-13 part 2 of 2 Figure 3-14 Figure 3-15 Two compartments 1. Cytosol/nucleus 2. Vesicular system Figure 3-16 Proteasome- degradation of “old” proteins Figure 3-17 Transporter of antigenic peptides Figure 3-18 Figure 3-19 Figure 3-20 Figure 3-21 Figure 3-22 part 1 of 2 *activated only Figure 3-22 part 2 of 2 microglia cells are + Human MHC – Human leukocyte antigen complex HLA-A,B,C -present peptide Abs used to ID MHC molecules react with leukocytes not RBCs antigens to CD8 Tcells and interact with NK-cells Figure 3-23 HLA-E,G -interact with NK-cells HLA-F -? HLA-DP,DQ,DR - present peptide antigens to CD4 Tcells HLA-DM,DO -regulate peptide loading of DP,DQ,DR Figure 3-24 part 1 of 2 proteins Figure 3-24 part 2 of 2 Figure 3-25 Figure 3-26 Figure 3-27 Figure 3-28 part 1 of 2 Figure 3-28 part 2 of 2 Figure 3-29 L-lysine Y-tyrosine V- valine R-arginine W-tryptophane Figure 3-30 Co- Figure 3-31 Large circles- total # antigenic peptides that can be presented via MHCI & MHCII small circles- total # antigenic peptides that can be presented via an individual MHCI & MHCII haplotype Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Aug 23 Introduction Aug 25 Chapter 1 Aug 30 Chapter 1 Sept 1 Chapter 2 Sept 6 Labor Day Sept 8 Chapter 2 Sept 13 Chapter 3 Sept 15 Chapter 3 Sept 20 Chapter 4 Sept 22 Review Sept 27 Exam 1 Sept 29 Chapter 4 Advantages for heterozygous for the MHC Figure 3-32 part 1 of 2 Figure 3-32 part 2 of 2 Recombination between alleles of the same gene Figure 3-33 part 1 of 2 Generation of new MHC alleles DP,DQ,DR HLA B*5301Found in African populations and associated with resistance to severe malaria Figure 3-33 part 2 of 2 Recombination between alleles of the different gene Generation of new MHC alleles HLA B*4601- Found in southeast Asian populations and associated with susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Figure 3-34 Red – heterozygous for all the highly polymorphic HLA I and II Yellow - Homozygous for one locus Blue - Homozygous for two or three loci