* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Side effects
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Lithium (medication) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
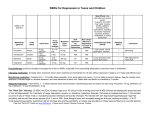
Medical University of Sofia, Faculty of Medicine Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology •Antidepressants •Mood stabilizers •Psychostimulants •Nootropic drugs •CNS stimulants (Abstract) Assoc. Prof. Ivan Lambev (e-mail: [email protected]) Depression is a heterogeneous disorder. A simplified classification based on presumed origin is as follows: (1) brief reactive or secondary depression (most common), occurring in response to real stimuli such as grief, illness, etc; (2) major depression (melancholic and recurrent depression) a genetically determined biochemical disorder manifested by an inability to experience ordinary pleasure or to cope with ordinary life events; (3) manic-depressive depression (depression associated with bipolar affective disorder) Pharmacologic treatment of depressions is very important, although a continuing role for electroconvulsive therapy for severe forms of life-threatening depression is also noted. Depression is one of the most common psychiatric disorders. At any given moment, about 3–5% of the population is depressed, and an estimated 10% of people may become depressed during their lives. The symptoms of depression are often subtle and unrecognized both by patients and by physicians. Patients with vague complaints that resist explanation as manifestations of somatic disorders and those who might be simplistically described as "neurotic" should be suspected of being depressed. Soon after the introduction of reserpine in the early 1950s, it became apparent that the drug could induce depression by inhibiting the neuronal storage of amine neurotransmitters such as 5-HT and NE. Reserpine induced depression and depleted stores of amine neurotransmitters. It was reasoned, depression must be associated with decreased functional amine-dependent synaptic transmission. NA (noradrenaline) = NE (norepinephrine Rauwolfia serpentina Benth. (a small indian shrub) •Reserpine •Ajmaline Pathogenesis of depression. Mechanism of action of antidepressants The idea that depression must be associated with decreased functional amine-dependent synaptic transmission provided the basis for what became known as the amine hypothesis of depression. By extension, drugs that increased amine function in appropriate synaptic areas would relieve depression. The amine hypothesis has provided the major experimental models for the discovery of new antidepressants. All currently available antidepressants, except bupropion, are classified as having their primary actions on the metabolism, reuptake, or selective receptor antagonism of 5-HT, NE, or both. (5-HT) (NE) (DA) The effects of DA, 5-HT and NE on the brain functions Raised neurotransmitter concentrations produce immediate alterations in postsynaptic receptor activation, leading to changes in second messenger (intracellular) systems and to gradual modifications in cellular protein expression. Antidepressants increase a cyclic AMP response-element binding (CREB) protein which in turn is involved in regulating the transcription of genes that influence survival of other proteins including brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) which exerts effects on neuronal growth. The role of BDNF in depression is supported by the observation that stress both reduces its expression and impairs neurogenesis. The monoamine hypothesis of depression is an oversimplification of a complicated picture. Other systems that are implicated in the etiology of depression (and which provide potential targets for drug therapy) include the hypothalamopituitarythyroid axis and the hypothalamopituitary-adrenal axis (HPA). The finding that 50% of depressed patients have elevated plasma cortisol concentrations constitutes evidence that depression may be associated with increased HPA drive. Sites of action of antidepressants NE – norepinephrine NERIs – norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors 5-HT – serotonin SSRIs – selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors TCAs – tricyclic antideperssant MAO – monoaminooxidase The evolution of antidepressants and classification by mechanism of action Structural relationships between various tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). Their structures are similar to phenothiazines. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Pharmacokinetics The antidepressants are generally well absorbed after oral administration. Steady-state plasma concentrations of TCAs show great individual variation but correlate with therapeutic effect. Antidepressants in general are inactivated principally by metabolism by hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP 2D6 and CYP 3A4 etc.). Other P450 enzymes are CYP 1A2 inhibited by the SSRI fluvoxamine, and induced by cigarette smoking, substrates include caffeine and the atypical psychotics (clozapine and olanzapine). Several of these drugs produce active metabolites which prolong their action (e.g. fluoxetine is metabolized to norfluoxetine, t1/2 200 h). The metabolic products of certain TCAs are antidepressants in their own right, e.g. nortriptyline (from amitriptyline), desipramine (from imipramine). Half-lives of TCAs and SSRIs are long (> 15 h). Around 7% of the Caucasian population have very limited CYP 2D6 enzyme activity. Such “poor metabolizers” may find standard doses of tricyclic antidepressants intolerable and it is often worth starting at a very low dose. Clinical indications for antidepressants The major indication is to treat depression, but a number of other uses have been established by clinical experience. Antidepressants may benefit most forms of anxiety disorder (panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress, obsessive-compulsive disorder and social phobia), migraine. SSRIs are effective in milder cases of the eating disorder bulimia nervosa, particularly fluoxetine (in higher doses than are required for depression). This effect is independent of that on depression (which may co-exist) and may therefore involve action on transmitter systems other than those involved in modulating depression. Antidepressants appear to be ineffective in anorexia nervosa. SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are used in: •chronic anxiety •depression •bulimia neurosa (fluoxetine – in higher doses) Schematic representation of the time course of panic treatments Adapted from Bennett and Brown (2003) Mode of use The action of TCAs in ameliorating mood is usually absent in the first 2 weeks of therapy and at least 4 weeks must elapse to constitute an adequate trial. Where a minimal response is noted in this period, it is reasonable to extend the trial to 6 weeks to see if further benefit is achieved. Dose titration is often necessary. By contrast, patients may experience unwanted drug effects immediately on starting treatment (and they should be warned), but such symptoms often diminish with time. TCAs are given either in divided doses or, for the more sedative compounds, as a single evening dose. SSRIs have advantages over tricyclics in simplicity of introduction and use. Dose titration is often unnecessary since the minimum therapeutic dose can usually be tolerated as a starting dose. Divided doses are not required and administration is by a single morning or evening dose. Evidence suggests that patients commencing treatment on SSRIs are more likely to reach an effective dose than those starting on TCAs. Venlafaxine is licensed for treatment-resistant depression by gradual titration from 75 to 375 mg/day. There is some need for dose titration when using MAOIs although recommended starting doses may be effective. When changing between SSRIs and/or TCAs, doses should be reduced progressively over 2–4 weeks. Where a new drug is to be introduced its dose should be gradually increased as that of the substituted drug is reduced. Changes to or from MAOIs must be handled with great caution due to the dangers of unwanted interactions between antidepressants: MAOIs cannot safely be introduced within 2 weeks of stopping paroxetine, sertraline or TCAs (3 weeks). When a patient achieves remission, the antidepressant should be continued for at least 9 months at the dose which returned mood to normal. When ceasing use of an antidepressant, the dose should be reduced over at least 6 weeks to avoid a discontinuation syndrome. Side effects of TCAs Anticholinergic (atropine-like): dry mouth, blurred vision, accommodation disturbances, increased ocular pressure, constipation, urinary retention, sweating, adynamic ileus (very rare). CNS: dizziness, tiredness, confusion, tremor, insomnia, seizures, sudden falls, exacerbation of psychotic symptoms. CVS: hypotension, sinus tachycardia, arrhythmia, impaired AV conduction. Blood: leucopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia. Other side-effects: hypo- or hyperthermia, impaired respiration, libido changes, exanthema, tinnitus, GI complaints, liver function disturbances, increased body weight, neurological symptoms. TCAs – Interactions Potential results MAOIs hyperthermia, palpitations, excitation Adrenomimetics hypertension, hyperthermia, tachycardia Alcohol effect of alcohol may be increased Clonidine, Methyldopa decreased hypotensive effects T3, T4 enhanced potential for CV toxicity Physostigmine antagonism Anticholinergics additional anticholinergic activity Neuroleptics inhibition of metabolism of antidepressants Levodopa overreaction of levodopa Lithium the therapeutic response is increased in some cases and suppressed in others Precautions: close supervision, especially in early phase of treatment (suicide risk of TCAs). The possibility of unmasking a latent psychosis should be considered. A switch into a manic or hypomanic condition may occur (“switch process”). Caution in CVD, history of urinary retention, narrow-angle glaucoma and in thyroid disease. Side-effects of SSRIs (mainly during the 1st and 2nd weeks of treatment): CNS: headache, restleness; CVS: bradycaria; GIT: nausea, diarrhoea The serotonin syndrome is a rare but dangerous complication and features restlessness, tremor, convulsions, coma and death. Risk is increased by co-administration with MAOIs, the antimigraine drug sumatriptan and St. John's Wort. Side-effects of SNERIs (Reboxetine) Dermatological: skin reactions CVS: hypertension (at high doses). Side-effects of MAOIs General: headache, perspiration, anorexia, hypotension, neuritis. CNS: insomnia, agitation, restlessness, confusion, dizziness. CVS: arrhythmia, tachycardia, palpitations. Other effects: leucopenia, agranulocytosis, icterus (small risk). Following foods and beverages should be avoided: Tyramine containing nutrition: maturated cheese (“cheese syndrome”), broad beans, smoked or pickled fish, meat extracts containing brewer's yeast, fermented sausages (e.g. salami); red wine, sherry, beer and excessive amounts of alcohol. Side-effects of 5-HT & NERIs Venlafaxine produces some unwanted effects that resemble those of SSRIs with a higher incidence of nausea. Sustained hypertension (due to blockade of noradrenaline reuptake) is a problem in a small percentage of patients at high dose and blood pressure should be monitored when > 200 mg/day is taken. Side-effects of presynaptic alpha-2-blockers Mirtazapine also has benefits in rarely being associated with sexual dysfunction and in improving sleep independent of mood but like TCAs it may cause unwanted sedation and weight gain. Trazodone has structural similarities with TCAs but probably acts by antagonism of central presynaptic alpha-2-adrenoceptors. It is an option for depressed patients where heavy sedation is required. Trazodone also has the advantages of lacking antimuscarinic effects and being relatively safe in overdose. Males should be warned of the possibility of priapism (painful penile erections), attributable to the drug's blockade of periferal apha-1-adrenoceptors. Mianserin has the advantages of lacking antimuscarinic effects too, but this antidepressant rarely used due to associations with aplastic anaemia. St John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) St John's Wort Many patients with mild to moderate depression are aware of the benefits of the herbal remedy St. John's Wort. The active ingredients in the hypericum extract have yet to be identified and their mode of action is unclear, although it has been postulated that several of the known mechanisms of existing antidepressants are incorporated (inhibition of monoamine reuptake and the monoamine oxidase enzyme, as well as a stimulation of GABA receptors). A large multicentre trial found only limited evidence of benefit for St. John's Wort over placebo in significant major depression. Use of St. John's Wort is complicated by the lack of standardization of the ingredients. Those who wish to take St. John's Wort should be made aware that it may cause dry mouth, dizziness, sedation, GI disturbance and confusion. Importantly also, it induces hepatic P450 enzymes (CYP 1A2 and CYP 3A4) with the result that the plasma concentration and therapeutic efficacy of warfarin, oral contraceptives, some anticonvulsants, antipsychotics and HIV protease/reverse transcriptase inhibitors are reduced. Concomitant use of tryptophan and St John's Wort may cause serotoninergic effects including nausea and agitation. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) involves the passage of a small electric charge across the brain by electrodes applied to the frontotemporal aspects of the scalp with the aim of inducing a tonic-clonic seizure. ECT requires the patient to be receiving a general anaesthetic, carrying the small risks equivalent to those associated with general anaesthesia in minor surgical operations. It may cause memory deficits although this is generally transient. ECT is usually reserved for psychiatric illness where pharmacotherapy have been unsuccessful for instance the severely depressed patient who has stopped eating or drinking. Modern-day ECT is a safe and effective alternative to pharmacotherapy and remains a first-line option in clinical circumstances where rapid, response is desired, when it can be life-saving. Mood stabilizers In bipolar affective disorder patients suffer episodes of mania, hypomania and depression, classically with periods of normal mood in between. Manic episodes involve greatly elevated mood, often interspersed with periods of irritability or undue excitement, accompanied by biological symptoms (increased energy, restlessness, decreased need for sleep, increased sex drive), loss of social inhibitions, irresponsible behaviour and grandiosity. Psychotic features may be present, particularly disordered thinking manifested by grandiose delusions and “flight of ideas” with rapid speech. Hypomania is a less dramatic and dangerous presentation but retains the features of elation or irritability and the biological symptoms, abnormalities in speech and in social conduct to overfamiliarity and mild recklessness. Depressive episodes include depressive symptoms described before and may include psychotic features. Lithium salts are ineffective for prophylaxis of bipolar affective disorder in around 35% of patients and cause several unwanted effects. The search for alternatives has produced drugs that are more familiar as anticonvulsants, notably carbamazepine and sodium valproate, and possibly lamotrigine. The mode of action is not fully understood. The main effect of lithium is probably to inhibit hydrolysis of inositol phosphate, so reducing the recycling of free inositol for synthesis of phosphatidylinositides. These intracellular molecules are part of the transmembrane signaling system that is important in regulating intracellullar calcium ion concentration, which subsequently affects neurotransmitter release. Other putative mechanisms involve the cyclic AMP “second messenger” system and monoaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmitters. Effect of lithium on the IP3 and DAG second-messenger system. The schematic diagram shows the synaptic membrane of a neuron. (PIP2, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate; PLC, phospholipase-C; G, coupling protein; EFFECTS, activation of protein kinase C, mobilization of intracellular Ca2+, etc.) Lithium, by inhibiting the recycling of inositol substrates, may cause depletion of the second-messenger source PIP2 and therefore reduce the release of IP3 and DAG. Knowledge of pharmacokinetics of lithium is important for successful use since the therapeutic plasma concentration is close to the toxic concentration (low therapeutic index). Lithium is a small ion that, given orally, is rapidly absorbed throughout the gut. High peak plasma concentrations are avoided by using sustained-release formulations which deliver the peak plasma lithium concentrations in about 5 h. With chronic use the plasma t1/2 of lithium is 15–30 h. Lithium is usually given 12-hourly to avoid unnecessary fluctuation (peak and trough concentrations) and maintain a plasma concentration just below the toxic level. A steady-state plasma concentration will be attained after about 5–6 days (i.e. 5 x t1/2). Lithium carbonate is effective treatment in > 75% of episodes of acute mania or hypomania. Because its therapeutic action takes 2–3 weeks to develop, lithium is generally used in combination with lorazepam or diazepam (or with a neuroleptics where there are also psychotic features). For prophylaxis, lithium is indicated when there have been two episodes of mood disturbance in two years, although in some cases it is advisable to continue with prophylactic use after one severe episode. When an adequate dose of lithium is taken consistently, around 65% of patients achieve improved control of their illness. Lithium is also used to augment the action of antidepressants in treatment-resistant depression. Monitoring. The difference between therapeutic and toxic doses is narrow and therapy must be guided by monitoring of the plasma concentration once a steady state is reached. Increments are made at weekly intervals until the concentration lies within the required range of 0.4–1 mmol/L (maintenance at the lower level is preferred for elderly patients). The plasma concentration should be checked every three months. Thyroid function and renal function (plasma creatinine and electrolytes) should be measured before initiation and every 3 months during therapy. Side-effects of Lithium General reactions: in case of overdose: nausea, thirst. CNS: ataxia, dysarthia, choreotetoid disturbances, extrapyrimidal symptoms, confusion, tremor, epileptic seizures, spasms, stupor, sedation, lethargy. CVS: arrhythmia, hypertension, circulatory collaps. Other effects: weight increase, muscular hypotonia, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, rash, acneiform eruptions, incontinence, dehydration, dry mouth, polyuria, albuminurea, glycosuria, myxoedema, fatigue, leucocytosis, hyperthyroidism. The manic phase in bipolar affective disorder often requires treatment with neuroleptics (chlorpromazine, haloperidol), though lithium or valproic acid supplemented with high-potency benzodiazepines (eg, lorazepam or clonazepam) may suffice in milder cases. Recent controlled trials support the efficacy of monotherapy with atypical antipsychotics in the acute phase (up to 4 weeks) of mania, and olanzapine has been approved for this indication. Psychostimulants Psychostimulants have predominant cortical action. Their psychic effects are more important then those on medullary vital centres. (1) Methylxanthines Three methylxanthines are pharmacologically important: caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. All of them occur naturally in certain plants. Only caffeine is used as a CNS stimulants. It is widely consumed in the form of beverages, including as infusions or decoctions, derived from these plants. Methylxanthines (purine alkaloids) Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine Coffea arabica (seeds) In an average cup of coffee: Caffeine 75 mg Theobroma Cola acuminata cacao (cocoa) (Guru nuts) In an average In 200 ml bottle cup of cocoa: of cola drink: Caffeine 4 mg Caffeine 30 mg Theobromine 200 mg Thea sinensis (leaves) In an average cup of tea: Caffeine 50 mg Theophylline 1 mg Actions of methylxanthines They block adenosine-1-receptors. Adenosine acts as a local mediators in CNS, CVS and other organs. Adenosine contracts bronchial muscles, dilates cerebral blood vessels, depressed cardiac pacemaker and inhibits gastric secretions. Methylxanthines inhibite phosphodiestarease which degrades intracelullarly cAMP. Theophylline-containing preparations enhance cAMP accumulation. It results in bronchodilation, vasodilation and cardiac stimulation. Caffeine and theophylline are CNS stimulants, primarily affect the higher centres. Caffeine (150 to 250 mg) produces a sense of wellbeing, alertness, beats boredom, allays fatigue; thinking becomes clear, improves performance and increases motor activity. As a CNS stimulant caffeine is more active than theophylline. In higher doses caffeine causes nervousness, restlesness, panic, insomnia and excitement. Still higher doses produces tremor, arrhythmia, delirium and convulsions. Methylxanthines, especially caffeine, also stimulate medullary vagal, respiratory and vasomotor centres (analeptic effect). Vomiting in high doses is due to both to gastric irritation and stimulation of chemoreceptor trigger zone. Methylxanthines directly stimulates the heart and increase force of myocardial contraction. They tend to increase heart rate by direct action, but also decrease it by vagal stimulation. Net effect is variable. Tachycardia is more common with theophylline, but caffeine generally decreases heart rate. Cardiac output is increased. This action is more marked in CHF patients. At high doses cardiac arrhythmias may produced. Methylxanthines, specially theophylline, dilate systemic blood vessels, including coronaries. However, cranial vessels are constricted by caffeine: this is one of the bases of its use in migraine. Effect of blood pressure is variable and unpredictable. Usually a rise in systolic and fall in diastolic BP is observed. Antiasthmatic (bronchodilatation) effect of theophylline is more potent then those of caffeine. Slow but sustained dose related bronchodilatation is produced and vital capacity is increased. Caffeine > 300 mg/d: 5–6 coffee cups daily (–) ATP AC cAMP 3’, 5’-AMP Hypercholesterolemia (+) Lipolysis PD (+) Cholesterol synthesis Methylxanthines are mild diuretics. They act by inhibiting tubular reabsorption of Na+ and water. Theophylline and theobromine are more potent diuretics than caffeine. At high dose caffeine enhances contractile power of skeletal muscle: it increases release of Ca2+ from sarcoplasmatic reticulum by direct action. In addition, caffeine facilitates neuromuscular transmission by increasing ACh release. Its central action relives fatigue and increases muscular work. Methylxanthines enhance secretion of acid and pepsin in stomach, even on parenteral application. They are gastric irritants – theophylline more than caffeine. Caffeine is an alkaloid with pKb 0.8. It is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. It is < 50% bound to plasma proteins. Its t1/2 is 4 h. Caffeine is nearly completely metabolized in liver by demethylation and oxidation, and excreted in urine. Caffeine is to be avoided in peptic ulcer patients. It is not contraindicated in gout because it is not converted in the body to uric acid. Moderate coffee drinking does not contribute to development of hypertension. Uses of caffeine • In analgesic drug combinations: caffeine benefits headache probably by allaying fatigue and boredom. • Migraine attacks: in combination with ergotamine. • To counteract hypnotic overdose, but its value is doubtful, better not use. Amphetamines Amphetamines are central adrenomimetics. Compared to amphetamine, higher central and peripheral activity ratio is exhibited by dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine. Amphetamine are indirect sympathomimetic and they stimulate mental than motor activity. Convulsive doses are much higher. Abuse potential of amphetamine is very high. Methylphenidate is chemical and pharmacological similar to amphetamine. Both act by releasing NE and DA in the brain. Both produce increase in mental activity at doses which have little action on other central and peripheral functions. Methylphenidate is considered superior to amphetamine for treatment of hyperkinetic children (attention deficit disorder) because it causes less tachycardia and growth retardation. Behaviour and learning ability are improved in 75% of cases. Methylphenenidate can also used for concentration and attention defect in adults, and for narcolepsy. It is well absorbed orally, metabolized and excreted in urine. It plasma t1/2 is 4 h. Side effects of methylphenidate are anorrhexia, insomnia, abdominal discomphort and bowel upset. Cocaine is an alkaloid from leaves of Erythroxylon coca, a south American plants. The native of Peru and Bolivia habitually chew the these leaves. Cocaine use sometimes in ocular anesthesia as eyes drops. It should be never be injected because can causes tissue necrosis. After system absorption cocaine produces prominent CNS stimulation with marked effect on mood and behaviour. It induces a sense of wellbeing, delays fatigue and increases power of endurance. In susceptible individuals it produces strong psychological, but not physical dependence. Cocaine is unique among drugs of abuse, because it is not produce tolerance on reputed use. It also stimulate vagal, vasomotor, vomiting and thermoregulatory centres. In periphery it blocks reuptake of NA and adrenaline and acts indirectly as a sympathomimetic. Nootropic drugs (cognition enhancers) Piracetam is a cyclic GABA derivative without GABA like activity. Piracetam selective improves efficiency of higher encephalic integrative activity by: • Enhancement of learning and memory • Facilitation of interhemisphere information transfer • Increased tonic cortical control of subcortical areas • Improves ATP/ADP ratio in encephalon • Stimulate synaptic transmission etc. The indications of piracetam are: • Senile dementia of Alzheimer type, multi infarct dementia etc. • Mental retardation and learning problems in children • Cerebrovascular accident: to hasten recovery • To reduce impairment of consciousness following brain trauma or brain surgery, memory impairment after electroconvulsive therapy, and central vertigo. The validity of evidence for drug induced cognition enhancement has not been established. Side effects include: gastric discomfort, excitement, insomnia, dizziness, skin rash. Pramiracetam has the similar properties and indications. CNS Stimulants – classification 1. Psychostimulants • Caffeine, Amphetamines, Cocaine etc. 2. Analeptics (Respiratory stimulants) • Doxapram, Prethcamide The analeptics stimulate respiration in subconvulsive doses, but margin of safety is narrow. The patients may get convulsions while still in coma. Mechanical support to respiration and other measures to improve circulation are more effective and safe. 3. Convulsants Strychnine is an alkaloid from seeds of Strychnos nux vomica. It acts by blocking post-synaptic inhibition produced by the inhibitory transmitter glycine. Strychnine is a potent convulsant. The convulsions are tonic-clonic and symmetrical. There are no valid use of strychnine now. Picrtoxin is obtained from “fish berries” of East Indies Anamirta cocculis. It produces asymmetrical clonic convulsions by blocking presynaptic inhibition mediated through GABA. Picrotoxin has no therapeutic indication now. Bicucculline is a synthetic convulsant. It has picrotoxin like action. It is GABA-A blocker and used only as a research tool. Pentylenetetrazol is a powerful CNS stimulants, acting by direct depolarization of central neurones. It is commonly used convulsant for testing anticonvulsive drugs in laboratory animals.