* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.THE SOLAR SYSTEM
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
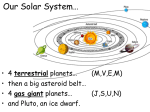
BIOLOGY & GEOLOGY Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.1. What is a planetary system? A planetary system consists of the various non-stellar objects orbiting a star such as planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and interstellar dust. 1.2. Our Solar System The Solar System is our Planetary System. The Solar System is about five billion years old. It is an exciting place made up of a star we call the Sun, and celestial bodies, such as planets, dwarf planets, moons or satellites, asteroids, comets, and many other smaller bodies. The Solar System is made up of all the planets that orbit our Sun. In addition to planets, the Solar System also consists of moons, comets, asteroids, dwarf planets, and dust and gas. Figure 1. The Solar System 1st ESO 5.1 BIOLOGY & GEOLOGY Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM 1.3. Components of our Solar System The Sun. It is a medium-sized star. It is the only star in our Solar System. The Sun contains around 98% of all the material in the Solar System. It is composed of approximately 75% hydrogen, 25% helium and small percentages of oxygen, carbon, iron and other elements. The surface temperature of the Sun can reach 5500ºC. But the temperature in the solar nucleus (where nuclear fusion occurs) is much higher, around 15 000 000ºC. Figure 2. The Sun The celestial bodies (including other planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and interstellar dust) orbit the Sun. The Sun gives heat and light to the celestial bodies. The Planets. They are celestial bodies revolving around a star. In our Solar System there are eight planets which travel around the Sun in a different orbit. In its orbit, there are not many other objects like the planet. The planets’ orbits are ellipticals. o The four smaller inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, also called the terrestrial planets, are primarily composed of rock and metal. Figure 3. The inner planets. o The four outer planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune, also called the gas giants, are composed largely of gases and are bigger than the terrestrials. Figure 4. The outer planets. Planets that are closer to the Sun revolve faster than those that are farther away from the Sun. 1st ESO 5.2 BIOLOGY & GEOLOGY Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM Dwarf Planet. It is smaller than a planet and in its orbit there are many similar objects. There are many dwarf planets in our Solar System. The most known is Pluto, which is smaller than one of Neptune's moons (Triton). Others dwarf planets are Ceres and Eris. Figure 5. From left to right are the dwarf planets Ceres, Pluto, and Eris. Moons or satellites. They are celestial bodies which orbit a planet. Earth has one natural satellite called the Moon. There are many of them, such as Phobos and Deimos (Mars moons). Figure 6.The moon. Asteroids. They are rock and metal bodies of varied dimensions. They are grouped in two large belts: the asteroid belt and the Kuiper belt. o o The asteroid belt which is located between the orbits of the planets Mars and Jupiter. The Kuiper belt which is located beyond the orbit of Neptune. Figure 7a.The asteroid belt. 1st ESO Figure 7b.Two asteroids. 5.3 BIOLOGY & GEOLOGY Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM Comets. A comet is composed of dust and rock particles mixed with frozen water, methane, and ammonia. In our Solar System there are many comets which orbit around the Sun. They release gas clouds when they are near the sun. There are two types of comets: Figure 8.A comet. o o Short-period comets: they are originated in the Kuiper belt and travel around the Sun. The Halley comet is the most famous of this type of comets and can currently be seen from the Earth every 75 years. Long-period comets: they are originated in the Oort Cloud and their travel around the Sun are longer than the short-period comets. The Oort Cloud. There is more to our Solar System beyond the Kuiper Belt. The Oort Cloud is a huge spherical cloud that surrounds the entire system. It holds millions of small pieces of ice and rock that slowly orbit the Sun. Billions of comets surround the solar system in the Oort Cloud. Figure 9.The Oort cloud. 1st ESO 5.4 BIOLOGY & GEOLOGY Unit 5: THE SOLAR SYSTEM VOCABULARY English Pronunciation Spanish Asteroid ['æstərɔ:ɪd] Asteroide Asteroids belt ['æstərɔ:ɪd] / [belt] Cinturón de asteroides Celestial body [] / ['bɒdɪ] Cuerpo celeste Comet ['kɒmɪt] Cometa Dwarf planet [dwɔ:f] / ['plænɪt] Planeta enano Earth [ɜ:ɵ] Tierra Galaxy ['gæləksɪ] Galaxia Heat [hɪ:t] Calor Jupiter ['dʒʊ:pɪtər] Júpiter Kuiper belt [] / [belt] Cinturón de Kuiper Light [laɪt] Luz Mars [mɑ:z] Marte Mercury ['mɜ:kjʊrɪ] Mercurio Milky Way ['mɪlkɪ] / [weɪ] Vía Láctea Moon [mʊ:n] Luna Neptune ['neptjʊ:n] Neptuno Oort Cloud [] / [klaʊd] Nube de Oort Orbit ['ɔ:bɪt] Órbita Planet ['plænɪt] Planeta Planetary System ['plænɪtəri] / ['sɪstəm] Sistema planetario Pluto ['plu:təʊ] Plutón Satellite ['sætəlaɪt] Satélite Saturn ['sætɜ:n] Saturno Solar System ['səʊlər] / ['sɪstəm] Sistema Solar Star [stɑ:r] Estrella Sun [sʌn] Sol Universe ['jʊ:nɪvɜ:s] Universo 1st ESO 5.5