* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 4 - spring 2005
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
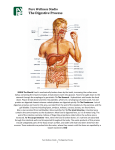
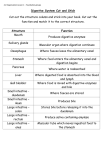
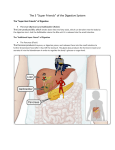
A&P 2-Spring 2005 Test 4 – Digestive Form A Name _______________________ Lab ______ 1. The correct sequence for the layers of the alimentary tube from inside to the outside is a. Mucosa, muscular layer, serosa, submucosa b. Mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, serosa c. Serosa, muscular layer, mucosa, submucosa d. Submucosa, mucosa, serosa, muscular layer 2. The teeth that are best adapted for grasping and tearing food are the: a. Incisors b. Cuspids c. Bicuspids d. Molars 3. The enzyme secreted by the salivary glands is: a. Pepsin b. Amylase c. Trypsin d. Sucrase 4. Which of the following would be an accessory organ of the digestive system? a. Esophagus b. Stomach c. Duodenum d. Pancreas 5. The movement of the digestive tract that propels food is: a. ingestion b. Churning c. Peristalsis d. intrinsic 6. Which of the following is not a salivary gland? a. Sublingual b. Submandibular c. Lingual d. Parotid 7. A relatively new treatment for ulcers has been introduced. This treatment inhibits the production of HCl in the stomach. If a person took this medication, which organic molecule would be affected the most? a. Carbohydrate b. Nucleic acid c. Lipids d. Proteins 8. What is the primary secretion of the esophagus? a. amylase b. mucus c. pepsin d. lipase 9. Which of the following is not a division of the pharynx? a. Nasopharynx b. Lingualpharynx c. Oropharynx d. Laryngopharynx 10. The chief cells of the gastric mucosa produce: a. Pepsinogen b. Hydrochloric acid c. Lipase d. Mucus 11. Which of the following is not a component of gastric juice? a. Pepsin b. Lipase c. Amylase d. HCl 12. Which of the following enzymes is necessary for the conversion of trypsinogen to Trypsin? a. Carboxypeptidase b. Intrinsic factor c. Enterokinase d. Chymotrypsin 13. Which of the following pancreatic secretions is responsible for the breakdown of proteins? a. Trypsin b. Chymotrypsin c. Carboxypeptidase d. All of these 14. Which of the following is not a secretion of the pancreas? a. Lipase b. Amylase c. Bicarbonate ions d. Bile 15. The liver functions to: a. Form glucose from glycogen b. Store vitamins c. Destroy damaged red blood cells d. All of the above 16. One of the major functions of the large intestine is to a. Secrete digestive enzymes b. Reabsorb water from chyme c. Regulate the release of bile d. Absorption of nutrients 17. Which of the following is the correct sequence of the small intestine? a. Duodenum, ileum, jejunum b. Jejunum, duodenum, ileum c. Ileum, duodenum, jejunum d. Duodenum, jejunum, ileum 18. Digestion of which of the following would be affected the most if the liver were severely damaged? a. Carbohydrates b. Lipids c. Proteins d. Nucleic acids 19. Which of the following cells in the liver aid in the removal of bacteria from the blood? a. Duodenum cells b. Hepatic cells c. Jail cells d. Kupffer cells 20. The primary function of the gallbladder is a. Production of bile b. Production of cholesterol for bile synthesis c. Storage of bile d. Electrolyte maintenance 21. The structure within the walls of the small intestine that increases absorption is called: a. Dyanna b. Rugae c. Villi d. Sinusoids 22. Which of the following is not a secretion from the small intestine walls? a. Nuclease b. Peptidase c. Disaccharidase d. Amylase 23. The primary function of the small intestine is: a. Water absorption b. Concentrating feces c. Nutrient absorption d. Pepsinogen production 24. Which of the following is the correct sequence for the large intestine? a. Transverse, ascending, descending, sigmoid b. Ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid c. Sigmoid, transverse, ascending, descending d. Descending, ascending, sigmoid, transverse 25. Enzymes that break down _____________ need to be made and secreted in their inactive form so they don’t breakdown the cells that made them. a. Carbohydrates b. Lipids c. Proteins d. Nucleic acids 26. The function of the hepatic portal circulation is to: a. carry toxins to the venous system for disposal through the urinary tract b. collect nutrients for processing and collect waste products before releasing them to the circulation for cellular use c. distribute hormones to the liver first, then to the rest of the body d. return glucose to the general circulation when blood sugar is low 27. The sheets of peritoneal membrane that hold the digestive tract in place are called: a. mesenteries b. visceral c. serosal lining d. mucosal lining 28. The epithelial membrane called the mucosa: a. absorbs mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones b. absorbs the end products of digestion into the lymphatic system c. contracts when stimulated d. is typically simple columnar 29. Chyme is found in the: a. mouth b. stomach c. esophagus d. all of the above 30. Which of the following is true concerning the number and type of permanent teeth? a. there are 32 permanent teeth not including the wisdom teeth b. there are 32 permanent teeth (17 upper and 15 lower) c. the number of permanent teeth is always equal to the number of baby teeth d. the number of upper permanent teeth is equal to the number of lower permanent teeth 31. The ducts that deliver bile and pancreatic juice from the liver and pancreas, respectively, unite to form the: a. portal vein. b. pancreatic duct c. bile duct d. hepatopancreatic duct 32. The layer of the digestive tube that contains blood vessels, lymphatic nodes, and a rich supply of elastic fibers is the: a. mucosa b. submucosa c. muscularis d. serosa 33. Where is “the mesentery” found? a. holding liver to diaphragm b. pancreas c. small intestines d. large intestines 34. Which is not an adaptation of the peritoneum? a. falciform ligament b. “the mesentery” c. dyanna mesentary d. mesocolon 35. ________ peritoneum covers the external surfaces of most digestive organs. a. parietal b. visceral c. mesentery d. organ 36. When swallowing, what goes up to cover the nasal opening? a. hiatus b. epiglottis c. uvula d. sphincter 37. Retroperitoneal is: a. behind peritoneum b. within peritoneum c. attached to organ d. attached to the cavity wall 38. What is the only organ that makes enzymes for all 4 categories of organic molecules? a. liver b. esophagus c. pancreas d. gall bladder 39. Ingestion is: a. food entering the mouth b. movement of food c. mixing of food d. breakdown of food 40. You have just eaten a meal high in complex carbohydrates. Which of the following enzymes will help to digest the meal? a. enterokinase b. amylase c. lipase d. trypsin 41. Ducts from the liver and the gall bladder unite to form the ______. This duct only carries bile. a. portal duct b. pancreatic duct c. common bile duct d. mallard duct 42. When the contents of the stomach enter the duodenum, an enzyme is released that causes some pancreatic enzymes present to change to their active state. This enzyme is: a. dyannase b. enterokinase c. lipase d. lactase 43. Which of the following is not characteristic of the large intestine? a. it does not contain villi b. it exhibits external muscular bands called teniae coli c. it is longer than the small intestine d. it has haustra 44. You have just eaten French fries, buttered toast, ice cream, and whole milk. Which of the following organs would be active in helping you to chemically digest this food? a. the pancreas b. the large intestines c. the small intestines d. the salivary glands 45. Falciform ligament: a. also called the lesser omentum b. is a mesentery that holds up the liver c. is a mesentery that holds the stomach to the liver d. is a mesentery that holds the small intestines together 46. Which is not measured by your digestive system? a. antigen level b. pH c. stretch d. osmolarity 47. When do glucagon levels rise? a. blood sugar levels too high b. blood sugar levels too low c. excessosugarosis d. minimalsugarosis 48. Segmentation is a form of: a. ingestion b. mechanical digestion c. chemical digestion d. enzyme 49. Chemical digestion begins in the _______ and ends in the ________. a. stomach; large intestine b. small intestine; large intestine c. mouth; large intestine d. mouth; small intestine 50. What is the primary source of energy? a. carbohydrates c. lipids b. vitamins d. nucleic acids