* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Mutations
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
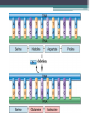
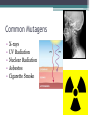
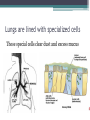
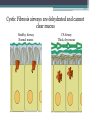
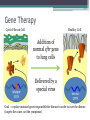
Bell Ringer 3.24 1. Where does translation occur in the cell? 2. Why do we need RNA to make proteins? 3. How can different codons code for the same amino acid? Gene Mutations DNA: ATGGTAGCTAACCTT DNA Comp: mRNA: tRNA: AA: DNA: CAGGAATTGCTCGAT DNA Comp: mRNA: tRNA: AA: DNA: GTACTCAAGGTCTAG DNA Comp: mRNA: tRNA: AA: DNA: TTTCAATCGACCAAC DNA Comp: mRNA: tRNA: AA: • Mutation = a change in the DNA sequence ▫ Can change the protein as well • A mistake that’s made during replication or transcription • Can be: ▫ Harmful: diseases or deformities ▫ Helpful: organism is better able to survive ▫ Neutral: organism is unaffected MOST mutations are NEUTRAL! 1. What does CGC code for? 2. What does CGG code for? 3. What does AGG code for? 4. What does AGA code for? 5. What does CGA code for? Why are so many mutations neutral? • If a mutation occurs in a gamete cell (sex cell), that mutation is passed onto offspring. • If a mutation occurs in a body (somatic) cell, that mutation affects only the organism and is not passed onto offspring. Point Mutations Bases are mismatched or one base is changed. (aka substitution) The Dog Bit the Cat The Dog Bit the Car Both of these are sentences. One works perfectly, the other does not. The point mutation leaves a sentence with words, but it does not make sense. The change of one amino acid (word) changes how the protein (sentence) works. Point mutations can be harmful when a mistake results in the wrong amino acid. One single change can affect the entire protein. Silent (Point) Mutations Not harmful when a mistake is carried into mRNA but still results in the same amino acid. Frameshift Mutations • Bases are inserted (addition) or deleted. • Usually harmful because it can result in the coding of many wrong amino acids. The Dog Bit the Cat Addition: The Dog eBi tth eCa t Deletion: The DoB itt heC at One base pair is deleted or added, and the entire strand “shifts” over The deleted “G” or the inserted “E” alters the entire sequence Causes of Mutations Mutagen: Anything that causes a change in DNA Common Mutagens • • • • • X-rays UV Radiation Nuclear Radiation Asbestos Cigarette Smoke Cystic Fibrosis (CF) • Recessive genetic disorder • An individual with CF has thick mucus in the lungs and airways, leading to many lung problems. • Why is there a build up of mucus? Lungs are lined with specialized cells These special cells clear dust and excess mucus Mutations in the CFTR gene blocks CFTR protein function Healthy Cell Cystic Fibrosis Cell Changes in the DNA sequence lead to a protein that cannot reach the plasma membrane Cystic Fibrosis airways are dehydrated and cannot clear mucus Healthy Airway Normal mucus CF Airway Thick, dry mucus Cystic Fibrosis airways accumulate bacteria and inflammatory cells Pseudomonas aeruginosa Too many inflammatory cells can cause permanent lung-cell damange Cystic Fibrosis Activity YOU be the Investigator! Complete Part 1 of the Activity Upon analysis of samples, you now have two patients that may have Cystic Fibrosis. To give either patient an official diagnosis, you must sequence their DNA to see if they have the cftr mutation. Complete Part 2 of the Activity Current Cystic Fibrosis Treatments 1. Bronchodilators ▫ ▫ Opens up airways Oral, injectable, or inhalable drugs 2. Airway clearance techniques ▫ ▫ Removes mucus Coughing and assist devices 3. Antibiotics ▫ ▫ Treat infections in airways Oral, injectable, or inhalable drugs Gene Therapy Cystic Fibrosis Cell Healthy Cell Addition of normal cftr gene to lung cells Delivered by a special virus Goal → replace mutated genes responsible for disease in order to cure the disease (targets the cause, not the symptoms) Agenda 3.25… Bell Ringer 1. How do feel about your performance the 1st nine weeks? 2. What areas do you feel like you did well in? 3. What areas do you feel like you need to work on? 4. Does your grade match your work ethic? 5. Explain #4. By the bell you need… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Bell Work/TOTD complete. Mutations Practice Web Quest (Extra credit) Cell Membrane!!!! DNA Paper Model!! Missing work turned in.. 1. Tests/Quizzes 2. Test Corrections 3. Missing classwork/homework 4. Extra credit