* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sociology Ch. 4 S. 1: Building Blocks of Social Structure
Social norm wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic interactionism wikipedia , lookup
Professionalization wikipedia , lookup
Social exclusion wikipedia , lookup
Differentiation (sociology) wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Labeling theory wikipedia , lookup
Sociology of knowledge wikipedia , lookup
Sociological theory wikipedia , lookup
Social development theory wikipedia , lookup
Structural functionalism wikipedia , lookup
Social group wikipedia , lookup
The Social Construction of Reality wikipedia , lookup
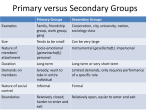
Sociology Ch. 4 S. 1: Building Blocks of Social Structure Obj: identify and describe the two major __________________ of social ______________; analyze how these two components of social structure affect _____________ interaction. Social structure gives a _____________ its enduring characteristics and makes patterns of human interaction predictable. Sociologists have viewed society as a system of interrelated parts-as a structure-since the time of Auguste Comte. However, social structure as a concept has often been very loosely defined. Throughout this textbook, the term social structure will mean the ___________ of interrelated statuses and roles that guide human interaction. A ___________ is a socially defined position in a group or in a society. Each status has attached to it one or more roles. A role is the behavior-the rights and obligations-expected of someone occupying a particular status. Status To understand social structure, one must be familiar with the concept of ________. Each individual in society occupies several statuses. For example, an individual can be a teacher, a father, a husband, an African American, and a church ___________ all at the same time. Statuses are ways of defining where individuals _____ in society and how they relate to others in society Ascribed and Achieved Statuses While some statuses are _______________, others are ____________ through effort. An ascribed status is assigned according to qualities beyond a person's control. Ascribed statuses are not based on an individual's abilities, efforts, or accomplishments. Rather, they are based on a person's inherited traits or are assigned automatically when a person reaches a certain age. You hold the status of teenager or young adult, for example, because of your age. You did nothing to earn this status. Neither can you _____________ it. Other examples of ascribed statuses include your sex family heritage, and race. Individuals acquire an achieved status through their own ____________ efforts. These efforts include special skills, knowledge, or abilities. For example, a person achieves the status of basketball player because of his or her physical skills and knowledge of the game. Similarly, someone achieves the status of _____________ because of his or her acting abilities. Unlike their ascribed statuses, people have some control over their achieved statuses. In a complex society such as the United States, the list of achieved statuses is almost endless. For example, all _____________________ are achieved statuses. Other achieved statuses include husband or wife, parent, high school or college graduate, and athlete. Master Status All individuals hold many statuses. For most people, one status tends to take rank above all others. This status plays the greatest _________ in shaping a person's life and determining his or her social identity and is called a master status. A ____________ status can be either achieved or ascribed. In the United States, an adult's master status is usually achieved. For example, occupation, _______________, marital status, or parenthood can serve as a master status. A person’s master status ______________ over the course of his or her life. During the teenage years, being a student or athlete often serves as a master status. During much of adulthood, on the other hand, master status is often based on one's occupation. Finally, in late adulthood-generally after a person ____________ from his or her primary occupation-volunteer work, ______________, grandparenthood, or past accomplishments serve as a person's master status. Roles Statuses serve simply as social ___________________. Roles are the component of social structure that brings statuses to life. As Ralph Linton noted, you occupy a status, but you play a role. You play many different roles every _____. At home you probably play the role associated with the status of son or daughter. At school you play the role associated with the status of ________________. You may also perform the roles that go along with the status of a reporter on the school newspaper or of a member of the gymnastics team. Most of the roles you perform have reciprocal roles. _________________ roles are corresponding roles that define the patterns of interaction between related statuses. For example, one cannot ___________ the role associated with the status of husband without having someone else perform the role that goes along with the status of _________. Other statuses that require reciprocal roles include doctorpatient, athlete-coach, friend-friend, employee-employer, leader-follower, and sales clerk-customer. Role Expectations and Role Performance Ideally, when people interact with one another their behavior corresponds to the particular roles they are playing. The ________________ determined behaviors expected of a person performing a role are called role ___________________. For example, doctors are expected to treat their patients with skill and care. Parents are expected to provide emotional and physical security for their children. ____________ officers are expected to uphold the law. In reality, people’s role ____________________ - their actual role behavior-does not always match the behavior expected by society. Some doctors do not give their patients the best possible care. Some parents mistreat their children. Occasionally, this problem arises because role behaviors considered appropriate by a certain segment of society are seen as inappropriate by society as a ___________. Even when someone tries to fulfill a role in the manner expected by society, actual performance may fall short of expectations. This problem occurs, in part, because each of us is asked to ________________ many roles, some of which are contradictory. Role Conflict and Role Strain Even within a ______________ status, there are many interrelated roles to perform. Sociologists call the different roles attached to a single status a role set. Each of us, because we hold more than one status, must deal with many _____________ sets in our daily lives. The often contradictory expectations within and between our role sets can lead to role ___________ and role strain. Role conflict occurs when ____________________ the role expectations of one status makes it difficult to fulfill the role expectations of another status. In other words, role conflict occurs between statuses. For example, to be a good employee an individual needs to go to work. However, to be a good ___________, that individual needs to stay home and take care of a sick child. Role strain, on the other hand, occurs when a person has difficulty meeting the role expectations of a single status. The boss who must maintain the morale of workers while getting them to work long periods of overtime is likely to experience role _________________. Social Institutions Statuses and their related roles determine the structure of the various ____________ in society. When these statuses and roles are organized to satisfy one or more of the basic needs of society, the group is called a social institution. The basic ___________ of a society include providing physical and emotional support for its members, transmitting knowledge, producing goods and services, and maintaining social _____________. Although _____________________ have recognized many significant social institutions, some scholars have focused on the major ________________________ of family, the economy, politics, education, and religion. Sociologists have also studied the social institutions of the media, medicine, and science. You will take a closer look at these social institutions in later ________________.