* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06-Nuclear shorter
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Strangeness production wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
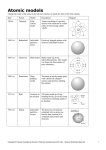
Modern Physics By Neil Bronks Atoms Mass Number Number of protons + Neutrons. 12 6 C Atomic Number Number of protons In a neutral atom the number of electrons and protons are the same. In Carbon it is……… 6 Gravitational - Only Positive - Very long range Electromagnetic – Positive and negative 4 Forces of Nature Strong Nuclear – Holds nucleus together - Very Short Range Weak NuclearAssociated with beta decay Radiation J’ai fais ça ! Decay of nucleus by the emission of a particle or a ray. Discovered by Henri Becquerel Units 1 Bq is one decay per second Natural happens without outside bombardment Artificial happens due to bombardment Alpha Particles U Th He 238 92 234 90 Helium Nuclei Positive Charge Heavy so not very penetrating Very Ionizing 14 N 7 +42He 178O + 11H 4 2 Beta Particle ß Th Pa 234 90 234 91 Fast electron from the nucleus Negative charge Moderately Penetrating Moderately ionizing 14 14 O + 0 ß N 7 8 -1 0 1 Gamma Ray High energy e-m wave (A Photon) No charge - not deflected by field Very penetrating – Need lead to stop most of them Not very ionizing Release energy after reaction Penetrating Power Paper Al foil Concrete Particles in Fields Charged particles move in a circular path as the force is always at right angles to the direction of motionFleming's Left Hand Rule Solid State Detector This a P-N junction in reverse bias. This creates a huge depletion layer. - + P N A piece of radiation passes through the depletion layer and creates enough carriers to carry one pulse of current. Experiments All experiments the same stick a DETECTOR in front of a source and count the decays. Move it away for distance and plot Time for half life and plot Put things in front for penetration Half-Life Atoms Not Decayed Time 1 2 3 4 Calculations =0.693/T½ =0.693/3s -1 =0.231s Activity Calculations Rate of Decay = x number you started with dN/dt = - xN Start with 4000 particles and =0.231 Activity = 4000 x 0.231=924 Bq Isotopes Same atomic number different mass number Rutherford Scattering – alpha particles fired at gold foil. Nucleus A small number of high energy alphas are Deflected More pass unaffected - So the nucleus is very small Some reflected completely back - Nucleus totally positive. Cockcroft and Walton Hydrogen discharge tube Proton 4000kv Accelerated by An electric field Alpha strikes the screen Producing a flash that Is seen with the microscope 0kv Alpha Alpha Lithium Target Alpha Alpha Nobel Prize for Physics Proton + Lithium 2xAlpha + Energy Proves Einstein’s Law E=mc2 First Transmutation by artificial Bombardment of an element 7 3 Li p Energy 1 1 4 2 4 2 Ernest Walton Use Famous Formula E=mc2 E= 3.96x10-30 Kg x (3x108 m/s) E = 3.56x10-13 Joules 2 Fusion Fusion is the joining together of 2 light nuclei to make one nucleus with release of energy. Caused by a super fast collision at high temperature in a magnetic bottle. 2 1H 2 1H Fission-The breaking apart of a heavy nucleus to form smaller products with release of energy. 1. Subtract mass in a.m.u. 2. Convert to kg 3. Use E=mc2 Uranium-235 Also produced 3 fast neutrons that can cause another fission and so a chain reaction Moderators slow down the neutrons to the right speed Control Rods stop the reaction and prevent meltdown Hot water to turbine Fuel rods contain the Uranium-235 (Enriched to ensure chain reaction) Nuclear Equation U n Kr Ba 3 n Energy 238 92 1 0 97 36 139 56 1 0 In the isotope U-238 the neutrons must be slowed down by a moderator – Graphite Only need one neutron for stable Chain Reaction (Self sustaining) more than one =Meltdown (China Syndrome) Leptons Fundamental particles 1/1846 of an a.m.u. Does not feel the strong nuclear force Matter – Electron , Muon, Tau, …… Anti-matter – Positron, Anti-Tau Anti-matter first suggested by Paul Dirac Annihilation Matter combining with anti-matter to form energy in the form of e-m radiation e01+ e01e+10 + e-10 2hf (2) 2 photons conserve momentum ? Annihilation 2 photons conserve momentum Matter combining with anti-matter to form energy in the form of e-m radiation e10+ e01- An electron and a positron collide to make energy. All the mass of the electrons gets turned into gamma waves Matter turns 2 So Energy E=mc Into energy To find frequency of wave E = 2h.f Use Planks Equation E=hf h= planks constant f= frequency 3.01x10-10 Joules = (6.6x10-34 js)x(f) f= 3.01x10-10 Joules / 6.6x10-34 js = 4.56x1023 Hz Pair Creation A matter and anti-matter pair being created by energy from an e-m wave e+ eAn electron and a positron are created from a gamma ray. (We can also get a proton and an anti-proton) We do the calculation in reverse To find energy of wave E = h.f As we get 2 electrons E = 2mc2 Annihilation and Production p+ p- p+ p- + 0 - New particles are produced from the KE of the colliding protons They must conserve charge If we carry in 4Gev (1.6x10-19 . 4x109= 4x10-10 J) As Energy to make 3 Pions is E=mc2 =(3x 2.4842x10-28xcxc) =6.7x10-11 J Subtracting we find the KE after collision. Quarks - Inside the Hadrons 6 Quarks 6 Anti-Quarks – Opposite Signs UP +2/3 DOWN -1/3 STRANGE -1/3 TOP CHARMED +2/3 BOTTOM -1/3 +2/3 Baryon Meson Beta decay In β− decay, the weak force converts a neutron into a proton while emitting an electron and an antineutrino n0 → p+ + e- + νe This explains loss in energy and momentum. Pauli proposed it’s existence in 1930 but was not discovered until 1956 as it is so weakly interacting with other particles. Particle Zoo Hadrons Subject to all forces Baryons Mesons 3 Quarks Quark + Anti-quark Proton uud Pion ud Leptons Fundamental particles Do not feel Strong Nuclear Force