* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrhythmia
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
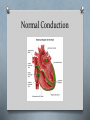
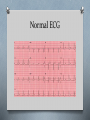
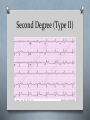
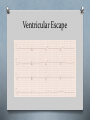
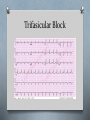
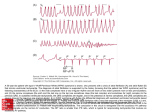
Cardiology II Arrhythmias Objectives O Describe the normal conduction in the heart O Describe pathophysiology of bradycardias O Describe pathophysiology of tachycardias O Describe treatment of the above Case O A 55 year old male calls 911 because his “heart is racing.” He initially is alert, oriented, and has mild shortness of breath. On physical exam, he has a regular tachycardia at 180, and monitor shows a regular, narrow-complex tachycardia. He denies chest pain. Midway through transport, he becomes less responsive, and his blood pressure drops as he starts sweating profusely. Normal Conduction ECG waveform Normal ECG Sinus Arrhythmia Bradycardias O Caused by damage to the conduction system resulting in a “broken road” or by drugs (beta blocker, calcium channel blockers) O If due to drugs, reversible. If not, many require a permanent pacemaker O Our goal is to temporarily support the heart rate until one of those two happen. O Atropine or External Pacing are options. Sinus Bradycardia First Degree AV Block Second Degree (Type I) Second Degree (Type II) Third Degree Block Junctional Rhythm Accelerated Idioventricular Ventricular Escape Ventricular fibrillation What is this? Asystole Branch Blocks O “Hiccups” on the conduction highway past the AV node O Can involve the right bundle, the left bundle, or divisions of the left bundle Right Bundle Branch Block Left Bundle Branch Block Bifasicular Block RB/LA Bifasicular Block – RB/LP Trifasicular Block Tachycardias O Any heart rate greater than 100. O The key is using the pattern to determine what is causing the tachycardia O The treatment is even more diverse, thus, knowing the pattern is critical to choosing the correct therapy. O The three main branches of tachycardia are atrial, nodal, and ventricular Sinus Tachycardia Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fib with Abberancy Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Flutter Atrial Flutter AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia Wolfe Parkinson White Lown-Ganong-Lavine AV Reciprocating Tachycardia Ventricular Tachycardia Torsades de Pointe Miscellaneous LVH RVH Hyperkalemia Digoxin Toxicity Brugada Syndrome Wellen’s Syndrome Treatment Summary O EMT O ABCs O Call for ALS O Rapid Transport O AEMT O IV O Cardioversion of V-tach, V-fib O Paramedic O Atropine, pacing for bradycardias O Vagal Maneuvers, Adenosine for narrow complex tachyarrhythmias O Amio, cardioversion for wide complex tachyarrhythmia