* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Nitrogen-vacancy center wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
Cluster chemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
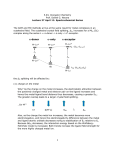
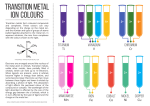
Transition Metal Chemistry and Coordination Compounds Lecture 18-20 The Transition Metals Oxidation States of the 1st Row Transition Metals (most stable oxidation numbers are shown in red) Aqueous oxoanions of transition elements One of the most characteristic chemical properties of these elements is the occurrence of multiple oxidation states. Mn(II) Mn(VI) Mn(VII) Mn(VII) Cr(VI) V(V) Effects of the metal oxidation state and of ligand identity on color [V(H2O)6]3+ [V(H2O)6]2+ [Cr(NH3)6]3+ [Cr(NH3)5Cl ]2+ Ionization Energies for the 1st Row Transition Metals Scandium Titanium Vanadium Chromium Manganese Iron Cobalt Nickel Copper Coordination Compounds A coordination compound typically consists of a complex ion and a counter ion. A complex ion contains a central metal cation bonded to one or more molecules or ions. The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. H H H H H •• Cl •• - C •• O •• •• •• N •• A ligand has at least one unshared pair of valence electrons O 22.3 Coordination Compounds The atom in a ligand that is bound directly to the metal atom is the donor atom. •• N O H H H H H The number of donor atoms surrounding the central metal atom in a complex ion is the coordination number. Ligands with: one donor atom two donor atoms three or more donor atoms monodentate bidentate H2O, NH3, Clethylenediamine polydentate EDTA Coordination Compounds bidentate ligand •• H2N CH2 CH2 •• NH2 polydentate ligand (EDTA) Bidentate and polydentate ligands are called chelating agents EDTA Complex of Lead What are the oxidation numbers of the metals in K[Au(OH)4] and [Cr(NH3)6](NO3)3 ? OH- has charge of -1 K+ has charge of +1 ? Au + 1 + 4x(-1) = 0 Au = +3 NO3- has charge of -1 NH3 has no charge ? Cr + 6x(0) + 3x(-1) = 0 Cr = +3 Naming Coordination Compounds • The cation is named before the anion. • Within a complex ion, the ligands are named first in alphabetical order and the metal atom is named last. • The names of anionic ligands end with the letter o. Neutral ligands are usually called by the name of the molecule. The exceptions are H2O (aqua), CO (carbonyl), and NH3 (ammine). • When several ligands of a particular kind are present, the Greek prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexa- are used to indicate the number. If the ligand contains a Greek prefix, use the prefixes bis, tris, and tetrakis to indicate the number. • The oxidation number of the metal is written in Roman numerals following the name of the metal. • If the complex is an anion, its name ends in –ate. 22.3 What is the systematic name of [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl ? tetraaquodichlorochromium(III) chloride Write the formula of tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(II) sulfate [Co(en)3]SO4 Crystal-Field Theory • Model explaining bonding for transition metal complexes – • Originally developed to explain properties for crystalline material – • Basic idea: – Electrostatic interaction between lone-pair electrons result in coordination. Energetics • CFT - Electrostatic between metal ion and donor atom i) Separate metal and ligand high energy ii) Coordinated Metal - ligand stabilized iii) Destabilization due to ligand -d electron repulsion iv) Splitting due to octahedral field. i ii iv iii d-Orbitals and Ligand Interaction (Octahedral Field) •Ligand s approac h metal d-orbitals pointing directly at axis are affected most by electrostatic interaction d-orbitals not pointing directly at axis are least affected (stabilized) by electrostatic interaction Ligand-Metal Interaction •Crystal Field Theory - Describes bonding in Metal Complexes • Basic Assumption in CFT: • Electrostatic interaction between ligand and metal d-orbitals align along the octahedral axis will be affected the most. More directly the ligand attacks the metal orbital, the higher the energy of the d-orbital. In an octahedral field the degeneracy of the five d-orbitals is lifted Splitting of the d-Orbitals • Octahedral field Splitting Pattern: • The energy gap is referred to as (10 Dq) , the crystal field splitting energy. The dz2 and dx2y2 orbitals lie on the same axes as negative charges. Therefore, there is a large, unfavorable interaction between ligand (-) orbitals. These orbitals form the degenerate high energy pair of energy levels. The dxy , dyx and dxz orbitals bisect the negative charges. Therefore, there is a smaller repulsion between ligand & metal for these orbitals. These orbitals form the degenerate low energy set of energy levels. Splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral field eg 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g o is the crystal field splitting E(t2g) = -0.4o x 3 = -1.2o E(eg) = +0.6o x 2 = +1.2o The magnitude of the splitting (ligand effect) Strong field Weak field The spectrochemical series CO, CN- > phen > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > RCO2- > OH- > Cl- > Br- > I- The magnitude of the splitting (metal ion effect) Strong field Weak field increases with increasing formal charge on the metal ion increases on going down the periodic table The spectrochemical series •For a given ligand, the color depends on the oxidation state of the metal ion. •For a given metal ion, the color depends on the ligand. I- < Cl- < F- < OH- < H2O < SCN- < NH3 < en < NO2- < CN- < CO WEAKER FIELD SMALLER LONGER STRONGER FIELD LARGER SHORTER Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Electron Configuration in Octahedral Field • Electron configuration of metal ion: • s-electrons are lost first. • Ti3+ is a d1, V3+ is d2 , and Cr3+ is d3 • Hund's rule: • First three electrons are in separate d orbitals with their spins parallel. • Fourth e- has choice: • Higher orbital if is small; High spin • Lower orbital if is large: Low spin. • Weak field ligands • Small , High spin complex • Strong field Ligands • Large , Low spin complex Placing electrons in d orbitals Strong field Weak field Strong field Weak field d1 d2 d3 d4 When the 4th electron is assigned it will either go into the higher energy eg orbital at an energy cost of 0 or be paired at an energy cost of P, the pairing energy. d4 Strong field = Low spin (2 unpaired) Weak field = High spin (4 unpaired) P < o P > o Pairing Energy, P The pairing energy, P, is made up of two parts. 1) Coulombic repulsion energy caused by having two electrons in same orbital. Destabilizing energy contribution of Pc for each doubly occupied orbital. 2) Exchange stabilizing energy for each pair of electrons having the same spin and same energy. Stabilizing contribution of Pe for each pair having same spin and same energy P = sum of all Pc and Pe interactions Placing electrons in d orbitals d5 1 u.e. 5 u.e. d6 0 u.e. 4 u.e. d8 2 u.e. 2 u.e. d7 1 u.e. 3 u.e. d9 1 u.e. 1 u.e. d10 0 u.e. 0 u.e. To sum up •Electron Configuration for Octahedral complexes of metal ion having d1 to d10 configuration [M(H2O)6]+n. •Only the d4 through d7 cases have both high-spin and low spin configuration. Electron configurations for octahedral complexes of metal ions having from d1 to d10 configurations. Only the d4 through d7 cases have both high-spin and low-spin configurations. Colour in Coordination Compounds E = hn 22.5 The absorption maximum for the complex ion [Co(NH3)6]3+ occurs at 470 nm. What is the color of the complex and what is the crystal field splitting in kJ/mol? Absorbs blue, will appear orange. hc (6.63 x 10-34 J s) x (3.00 x 108 m s-1) = hn = = = 4.23 x 10-19 J 470 x 10-9 m (kJ/mol) = 4.23 x 10-19 J/atom x 6.022 x 1023 atoms/mol = 255 kJ/mol 22.5 Color Absorption of Co3+ Complexes of Color of Light Color of Complex • The Wavelength Colors of Some Complexes light absorbed Absorbed 3+ Ion 3+ the 700 Co(nm) [CoF6]of Red Green Complex Ion [Co(C2O4)3] 3+ 600, 420 Yellow, violet Dark green [Co(H2O)6] 3+ 600, 400 Yellow, violet Blue-green [Co(NH3)6] 3+ 475, 340 Blue, violet Yellow-orange [Co(en)3] 3+ 470, 340 Blue, ultraviolet Yellow-orange [Co(CN)6] 3+ 310 Ultraviolet Pale Yellow The complex with fluoride ion, [CoF6]3+ , is high spin and has one absorption band. The other complexes are low spin and have two absorption bands. In all but one case, one of these absorptionsis in the visible region of the spectrum. The wavelengths refer to the center of that absorption band. Colors & How We Perceive it 650 580 800 560 400 Artist color wheel showing the colors which are complementary to one another and the wavelength range of each color. 430 490 Complex Influence on Color •Compounds of Transition metal complexes solution. 650 580 800 400 430 [Fe(H2O)6 ]3+ [Ni(H2O)6]2+ [Co(H2O)6]2+ [Zn(H2O)6]2+ [Cu(H2O)6]2+ 560 490