* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marketing - Course ON-LINE
Consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Affiliate marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Online shopping wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Web analytics wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
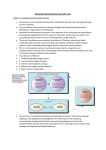
Digital Marketing Week 2 Digital Marketing Introduced What Is Marketing? Marketing Science or Art? 2 What Is Marketing? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X2leyjuolDM 3 What Is Marketing? Is marketing selling and advertising? 4 What Is Marketing? 5 What Is Marketing? (c…) Marketing Defined Marketing is the process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships to capture value from customers in return 6 Marketing Strategy and the Marketing Mix Figure. The Marketing Process 7 Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning Steps in Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning 8 Market Segmentation Market segmentation is dividing a heterogeneous market into smaller groups with distinct needs, characteristics, or behavior that might require seperate marketing strategies 9 Market Segmentation (c…) Segmenting the Market 10 Market Targeting Which customers will the company serve? Market targeting (Targeting) is the process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segments to enter. 11 Market Targeting Selecting Target Market Segments 12 Market Positioning How will we serve the customers? Product positioning is the way the product is defined by consumers on important attributes—the place the product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing products 13 Market Positioning (c…) Positioned on; Cadillac - Luxury Nissan - Economy Porsche Performance 14 E-marketing • E-Marketing Use of Internet and related digital information and communication technologies to achieve marketing objectives It includes both direct and indirect marketing elements and uses a range of technologies to help connect businesses to their customers. 15 The Online Purchasing Decision • Five stages in consumer decision process – – – – – Awareness of need Search for more information Evaluation of alternatives Actual purchase decision Post-purchase contact with firm The Consumer Decision Process and Supporting Communications The Online Purchasing Decision (cont.) • Decision process similar for online and offline behavior • General online behavior model – – – – – User characteristics Product characteristics Web site features: usability, security Attitudes toward online purchasing Perceptions about control over Web environment • Clickstream behavior A Model of Online Consumer Behavior The Online Purchasing Decision (cont.) • Two most important factors shaping decision to purchase online: – Utility: • Better prices, convenience, speed – Trust: • Most important factors: Perception of credibility, ease of use, perceived risk • Sellers can develop trust by building strong reputations for honesty, fairness, delivery (order fulfillment) E-marketing (c…) E- marketing management is the art and science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them • What customers will we serve? • How can we best serve these customers? 21 Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning Steps in Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning 22 Market Targeting Selecting Target Market Segments Targeting personally 23 Online vs. Off-line Marketing (c…) Offline: • Ability to meet with customers face-to-face • Customers can touch and feel to products – Easy to market • Great exposure (with some channels like TV) • Mass marketing opportunity Google’s first TV ad https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-usW1rIRTRg 24 Online vs. Off-line Marketing (c…) Online: • Consumers have more control • Customer input to the marketing • Power shift from companies to individuals • Wireless networking increases • Consumers have information, entertainment and communication when, where and how they want it • Appliance convergence • Semantic Web • Data collection Power shift Figure. Power shift 26 Appliance Convergence • The receiving appliance is separate from the media type. – Computers can receive digital radio and TV. – TV sets can receive the Web. • New types of “smart” receiving appliances will emerge. – Smart refrigerator has many digital appliances in one. – Global positioning systems (GPS) allow in-car communication and entertainment. 27 Web x.0 Company perspective: • Web 1.0 – I am talking, listen Monolog • Web 2.0 - Talk to me, I am listening Communication • Web 3.0 – I know you are special Semantic Web and Social Media 28 Semantic Web (Web 3.0) Semantic Web – Web of Data It is a system that enables machines to "understand" and respond to complex human requests based on their meaning. Such an "understanding" requires that the relevant information sources be semantically structured. 29 Semantic Web (c…) • Example: Word father girl Mp3 player Semantic elements male, human, parent female, human, young music, device, technology 30 Semantic Web (c…) Aim Semantic Web aims the machines to interpret data on Web pages as humans do, and to understand the wants of humans The main purpose is enabling users to find, share, and combine information more easily. 31 Semantic Web (c…) Aim (c…) - Machines cannot accomplish tasks without human leading, because web pages are designed to be read by people, not machines. - The semantic web is a vision of information that can be readily interpreted by machines, so machines can perform more of the tedious work involved in finding, combining, and acting upon information on the web. 32 Semantic Web (c…) Example: With one command only: • Computer lists the stores, which are open till 8 PM on Tuesdays, that sell flat screen HDTVs, have a size of bigger than 40 inch screen. • Computer sends the pictures of kids playing snowball on the last year’s winter to your brother 33 Semantic Web (c…) • Marketers want to give customers information when and where they want it. • They use several different receiving appliances to convey their messages. • The Semantic Web is an extension of the current Web making it easer to obtain information by: – Providing information based on type – Person, contact information, next available appointment, restaurant menu’s. 34 Characteristics of the Communication Characteristics of the new media: • Interactive • Intelligent • Individual – can be tailored • Integrated • Independent of time and location 35 Interactivity Figure. Summary of communication models (a) traditional media, (b) new media 36 Degree of Individualization Figure. Summary of degree of individualization for (a) taditional media (same message) (b) electronic media (unique messages and more information exchange between customers) 37 Integrated Marketing Figure. Channels requiring integration as part of integrated e-marketing strategy 38