* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9 Geography Investigating Australia`s Physical Environments Term 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
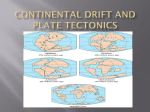
9 Geography Investigating Australia’s Physical Environments Term 1 Week 4 ORIGINS OF THE CONTINENT – SCIENTIFIC PERSPECTIVE: CONTINENTAL DRIFT Glossary Define the following words in your exercise book: Continental Drift, Tectonic plates, Fault mountains, Fold mountains, Tectonic processes, Core, Mantle, Crust Structure of the Earth: ................................. ................................ Outer....................... Inner........................ Plate Tectonics The Earth’s Surface or crust is split into a number of plates. These plates fit together like a giant jigsaw puzzle. The plates float on semi-molten rocks of the Earth’s mantle. Heating from the Earth’s core causes the semi-molten material in the mantle to churn in currents. These currents, called convection currents, carry the crustal plates up to as much as 15 centimetres per year. The movement of the plates is known as the theory of continental drift. Scientists believe that about 225 million years ago all the continents were joined. Since then they have broken up and moved apart to form the continents we know today. 9 Geography Investigating Australia’s Physical Environments Term 1 Week 4 Continental Drift In the short term, it seems as though the continents are stable, but the continents are mobile and have moved around earth over millions of years. The Earth’s solid outer crust is made up of a number of massive pieces – called continental plates – that float on top of the underlying mantle of liquid magma. The continents sit on top of these continental plates. Currents in the magma make the plates move Do you think that they continents have always looked as they do now, of have they changed shape or location throughout the Earth’s history? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… In early 1915, the German scientist Alfred Wegener developed a theory that the continents once formed a giant supercontinent that he called Pangaea. He speculated that Earth took this form about 245 million years ago, during the Triassic period of the Mesozoic era. (The Mesozoic is the era in which dinosaurs lived.) A few years after Wegener proposed his theory, South African geologist Alexander Du Toit further theorized that Pangaea divided into two supercontinents 205 million years ago. Du Toit called the northern supercontinent Laurasia and the southern one Gondwanaland. 9 Geography Investigating Australia’s Physical Environments Term 1 Week 4 P………………………… L………………………. & G………………………………… Proposed by …………………… Proposed by …………………… Fold Mountains Most of the world’s great mountain regions are formed when crustal rocks buckle as one plate slides under another (subduction). Some of the crust is forced down and becomes part of the magma; other rocks are forced upwards and bent or folded. Fault Mountains Faulting occurs when rocks crack and sections move up or down. This process forms both mountains and rift valleys. Rocks behave differently under pressure, depending on how brittle they are. Rocks close to the surface tend to be more brittle and will snap under pressure. Faults are formed when these rocks break. Evidence for Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Many fossils have been found which link continents together and support the idea that the continents were once joined together. They show that a plant or animal lived on the edge of two (or more) continents. This shows that the two areas would have had to have a similar climate (and so a similar latitude and longitude). An example is Antarctic Beech. Fossil evidence has also shown that areas of land which were previously underwater or at least at a low altitude have been uplifted. Fossil seashells have been found high in the Himalayas. The highest mountain range on Earth was under the sea until about 30 million years ago, when India collided with Asia and the rocks were thrust upwards to form the Himalayas. There is a continuous system of large ridges located some distance from the continents, often in mid-ocean. There are also deep open trenches at many places in ocean floors. These provide evidence of plate movement together (ridges) and apart (trenches). This theory has been confirmed by paleomagnetism and core sampling. 9 Geography Investigating Australia’s Physical Environments Term 1 Week 4 Questions: How are plate tectonics and continental drift related? .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. What is subduction, and how does it relate to the formation of mountains? .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. Unscramble the following words: daonawng ................................ sgredi ............................... ecro ............................... atlfu ............................... ontnecnit ............................... lodf ............................... telamn ............................... tcincote ............................... alestp ............................... tploygoenloa ............................... ocvnceitno ctesnurr ............................... lontem atimlare ............................... niod-urtlanaias tlaep ............................... Homework: Internet research (due next lesson) What did Alfred Wegener propose in 1912? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… What does Pangea mean? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… When did Pangea start breaking up? ……………………………………………………………………………………… What paleontological observations supported Wegener’s theory? …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………