* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria and Viruses Powerpoint
Foot-and-mouth disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Elsayed Elsayed Wagih wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Avian influenza wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
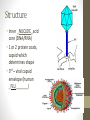
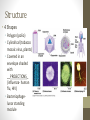
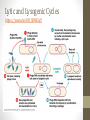
Viruses and Bacteria Viruses • Central question----What is a pathogen? A DISEASE-CAUSING agent. • How are pathogens passed to others? Infection Definition: Viruses • Tiny, _NON-LIVING______ particles • Smaller than bacteria • Nonliving characteristics • • • • • Do _NOT_____ carry out respiration Do _NOT_____ grow and develop Do not metabolize Not made of ___CELLS_____________ However, Does contain ___DNA________or RNA Definition: Viruses • Able to replicate inside living things called a _HOST__ cell • Viruses are named after the diseases that they cause or the organ or tissue that they infect. _ADENOVIRUS__causes a common _COLD_________ and infects the adenoid tissue in the back of the throat and nasal cavity. Structure • Inner _NUCLEIC_acid core (DNA/RNA) • 1 or 2 protein coats, capsid which determines shape • 3rd – viral capsid envelope (human _FLU_______) Structure • 4 Shapes • Polygon (polio) • Cylindrical (tobacco mosaic virus, plants) • Covered in an envelope shaded with __PROJECTIONS_ (influenza- human flu, HIV) • Bacteriophagelunar standing module Recognition and Reproduction • _SHAPE____is important for replication of a virus. Viruses recognize and attach _SPECIFIC______receptors. For example, animal viruses attach to _ANIMAL__ cells. • First, viruses must find a site on plasma membrane of the _HOST______________. • Viral protein coat is important for recognition of specific cells. Viruses are species specific. Recognition and Reproduction • The 3 dimensional shape on plasma membrane of the virus _INTERLOCKS_____ with shape on the host membrane. • A T4 _BACTERIOPHAGE, which is a virus that attaches and infects _BACTERIA_ uses a tail fiber to attach to E.coli. Recognition and Reproduction • In the 1980s the announcement of the eradication of __SMALLPOX_ had occurred because it only infected _HUMANS__ and doctors were able to quarantine people and get rid of the virus. However, the flu is difficult to eradicate because it is _NOT________ species specific AND IT CAN CHANGE/ADAPT. Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles https://youtu.be/kYf_Sl8W3qY Types of Viruses • Chicken pox, HPV- HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS, examples of items that can be spread through contact. • HIV is a RETROVIRUS_ which is a virus that contains RNA and _REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to other diseases and that is when the disease can be called AIDS_. Types of Viruses • West Nile- Caused by _INFECTED MOSQUITOES___. West Nile Virus is a flavivirus commonly found in Africa, West Asia, and the Middle East. It is closely related to St. Louis encephalitis virus, which means _HEAD_ swelling which is also found in the United States. The virus can infect humans, birds, mosquitoes, horses and some other mammals. Types of Viruses • SARS- Severe Acute _RESPIRATORY_ Syndrome. SARS was first reported in Asia in February 2003. Over the next few months, the illness _SPREAD___ to more than two dozen countries in North America, South America, Europe, and Asia before the SARS global outbreak of 2003 was contained. According to the World Health Organization (_WHO_________), a total of 8,098 people worldwide became sick with SARS during the 2003 outbreak. Of these, 774 died. Symptoms include fever, headaches, __PNEUMONIA_. Cause is _AIRBORNE__. Types of Viruses • Avian Flu- This _INFLUENZA___ virus occurs naturally among _BIRDS___. Wild birds worldwide carry the viruses in their intestines, but usually do not get sick from them. Avian influenza is very _CONTAGIOUS__ among birds and can make some domesticated birds, including chickens, ducks, and turkeys, very sick and kill them. Infected birds shed influenza virus in their __SALIVA_, nasal secretions, and feces. Able to CHANGE like other flu viruses. No _PREVENTION_ available except the H5N1 vaccine. _PANDEMIC_or worldwide problem. Types of Viruses • Mad cow disease is caused by a _PRION__. A prion is a microscopic _PROTEIN___ particle SIMILAR_____ to a _VIRUS_ but lacking nucleic acid, thought to be the infectious agent responsible for Mad Cow disease and certain other degenerative diseases of the _NERVOUS____system. Also known as, BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy) is a progressive neurological disorder of cattle that results from infection. • Read up on Swine Flu Vaccines • In order to prevent some viruses, there are _VACCINES, which are injections that have a small dose of the _PATHOGEN______mixed into it and it helps build up the body’s immunity against the disease. Bacteria • Your bacteria pamphlet is going to be your bacteria notes. You can X out the bacteria pages in the packet as they are the same material.