* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
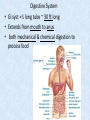
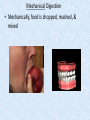
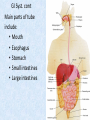
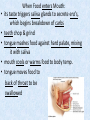
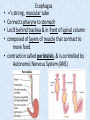
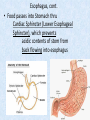
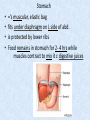
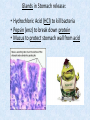
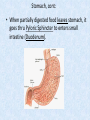
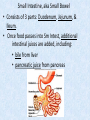
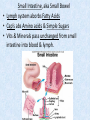
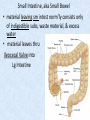
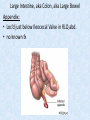
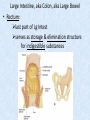
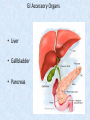
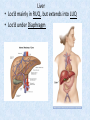
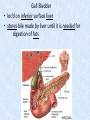
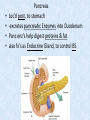
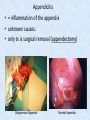
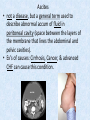
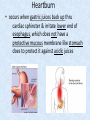
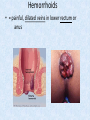
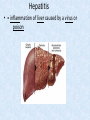
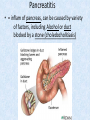
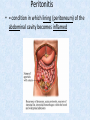
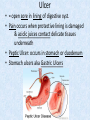
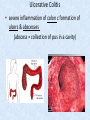
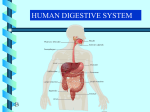
Chapter 7 Structure & Function of Human Body Digestive System OBJECT IVES Students should be able to: * Describe the primary anatomical features & physiological actions of systems for providing energy & for removing waste from body. * Name common diseases or disorders associated with each system. * Describe behaviors &actions for each body system that promote health & prevent major diseases & disorders. Digestive System, aka Gastrointestinal (GI) Syst. • Processes food to use for energy • takes in & digests: (to allow absorption) changes to: Carbs Glucose Proteins AA’s Lipids Fatty Acids • vits & minerals do not req digestion & are abs’d directly into caps • absorbs water • eliminates undigested food products (waste) Digestive System • GI syst =‘s long tube ~ 30 ft long • Extends from mouth to anus • both mechanical & chemical digestion to process food Mechanical Digestion • Mechanically, food is chopped, mashed, & mixed Chemical Digestion • Chemically, food broken down by Enzymes produced c in system or added by other organs. Enzymes break down food into absorbable nutrients. GI Syst. cont Main parts of tube include: • Mouth • Esophagus • Stomach • Small intestines • Large intestines • • • • • When Food enters Mouth: its taste triggers saliva glands to secrete enz’s, which begins breakdown of carbs teeth chop & grind tongue mashes food against hard palate, mixing it with saliva mouth cools or warms food to body temp. tongue moves food to back of throat to be swallowed • • • • • Esophagus =‘s strong, muscular tube Connects pharynx to stomach Loc’d behind trachea & in front of spinal column composed of layers of muscle that contract to move food. contraction called peristalsis, & is controlled by Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Esophagus, cont. • Food passes into Stomach thru Cardiac Sphincter (Lower Esophageal Sphincter), which prevents acidic contents of stom from back flowing into esophagus Stomach • • • • =‘s muscular, elastic bag fits under diaphragm on L side of abd. is protected by lower ribs Food remains in stomach for 2- 4 hrs while muscles contract to mix it c digestive juices Glands in Stomach release: • Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) to kill bacteria • Pepsin (enz) to break down protein • Mucus to protect stomach wall from acid Stomach, cont: • When partially digested food leaves stomach, it goes thru Pyloric Sphincter to enters small intestine (Duodenum). Small Intestine, aka Small Bowel • Consists of 3 parts: Duodenum, Jejunum, & Ileum. • Once food passes into Sm Intest, additional intestinal juices are added, including: • bile from liver • pancreatic juice from pancreas Small Intestine, aka Small Bowel • Digestion cont’s, but absorption also begins to occur thru network of small, finger-like projections called Villi, line the sm intest. • Each villus contains network of blood & lymph cap’s Villi Small Intestine, aka Small Bowel • Lymph system aborbs Fatty Acids • Cap’s abs Amino acids & Simple Sugars • Vits & Minerals pass unchanged from small intestine into blood & lymph. Small Intestine, aka Small Bowel • material leaving sm intest norm’ly consists only of indigestible subs, waste material, & excess water • material leaves thru Ileocecal Valve into Lg Intestine Large Intestine, aka Colon, aka Large Bowel • nutrients & water not abs’d in sm intest are abs’d here • large intest contains Bacteria that: work on Undigested substances make Vit K (nec for blood clotting) as well as some B-complex vits Large Intestine, aka Colon, aka Large Bowel Appendix: • Loc’d just below Ileocecal Valve in RLQ abd. • no known fx Large Intestine, aka Colon, aka Large Bowel • Rectum: last part of Lg Intest serves as storage & elimination structure for indigestible substances GI Accessory Organs • Liver • Gallbladder • Pancreas Liver • Loc’d mainly in RUQ, but extends into LUQ • Loc’d under Diaphragm Liver • produces thick, green liquid, called Bile • Bile breaks down lipids (fat) into fatty acids for absorption Other Fx’s Liver • Maint’s Blood Sugar levels • Filters out & destroys old RBCs & saves iron to be used again • Stores Vits • makes Prothrombin, nec for Blood Clotting • filters out harmful toxins (poisons) that have been swallowed, including alcohol & many drugs Gall Bladder • loc’d on inferior surface liver • stores bile made by liver until it is needed for digestion of fats • • • • Pancreas Loc’d post. to stomach excretes pancreatic Enzymes into Duodenum Panc enz’s help digest proteins & fat also fx’s as Endocrine Gland, to control BS Digestive System Animation Peristalsis Animation (Gastric Antrum) Major GI Diseases Appendicitis • = inflammation of the appendix • unknown causes. • only tx is surgical removal (appendectomy) Gangrenous Appendix Normal Appendix Ascites • not a disease, but a general term used to describe abnormal accum of fluid in peritoneal cavity (space between the layers of the membrane that lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities). • Ex’s of causes: Cirrhosis, Cancer, & advanced CHF can cause this condition. Cirrhosis = gp of chronic diseases that involve scarring of liver tissue, which dec’s ability of liver to perform its fx’s Cholelithiasis & Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis = stones in gallbladder Cholecystitis = inflammation of gallbladder. Laproscopic Cholecystectomy Colon Cancer • abnormal growth in large intestines that damages tissue & can cause blockage of digestive system. Constipation • inability to pass feces thru anus • causes abd distention & discomfort. • most common causes are: lack of dietary fiber inadequate fluids certain meds lack of exercise Diarrhea • passage of freq & watery stools • can be caused by certain diseases, stress, meds, & diet Diverticulosis • = weakening of colon wall leading to outpouching (diverticula) in wall • diverticula can trap digestive material & become infected • Diverticulitis = inflam of diverticula Gastroenteritis • = inflam mucous membranes (inner) lining stomach & intestines • Causes include food poisoning, infection, & toxins Gastritis = lining of stomach inflamed & can be caused by spicy foods & certain meds Heartburn • occurs when gastric juices back up thru cardiac sphincter & irritate lower end of esophagus, which does not have a protective mucous membrane like stomach does to protect it against acidic juices Hemorrhoids • = painful, dilated veins in lower rectum or anus Hepatitis • = inflammation of liver caused by a virus or poison Pancreatitis • = inflam of pancreas, can be caused by variety of factors, including Alcohol or duct blocked by a stone (choledocholitiasis) Peritonitis • = condition in which lining (peritoneum) of the abdominal cavity becomes inflamed Ulcer • = open sore in lining of digestive syst. • Pain occurs when protective lining is damaged & acidic juices contact delicate tissues underneath • Peptic Ulcer: occurs in stomach or duodenum • Stomach ulcers aka Gastric Ulcers Ulcerative Colitis • severe inflammation of colon c formation of ulcers & abscesses (abscess = collection of pus in a cavity) Age Related Changes GI System Decrease in: • peristalsis • control of external sphincter • taste & appetite • saliva production • liver size, weight, & efficiency • gastric acid secretion Increase in: • gum disease • constipation • indigestion Preventive Measures GI Dis • • • • • • Eat an adequate amt fiber Drink plenty of water Avoid excessive alcohol. Avoid large amounts of high-fat foods. Avoid fad diets & other extreme eating habits. Avoid pushing hard during bowel movements (avoid constipation). • Do not rely on regular use of laxatives. • Make routine dental appointments for examination & cleaning of teeth. • Have flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy performed at the age & frequency recommended by your health care provider. Question • Which of the following is considered an agerelated change for the digestive system? A. Increased liver size B. Decreased peristalsis C. Increased appetite B. Decreased peristalsis