* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is a plant? Kingdom Plantae Protista Bacteria (Monera)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
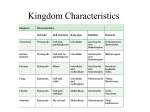
Traditionally, two groups of organisms: Animals and Plants What is a plant? Introduction to Classification Animal Plant mobile heterotrophic determinate growth stationary autotrophic indeterminate growth Botany LS1203 Traditional Classification of Organisms: Two Kingdoms Animal Plant Multicellular animals Vascular plants (ferns, conifers, flowering plants) Protozoa Bryophytes (mosses, liverworts, hornworts) Algae (kelps, seaweeds, "pond scum") Fungi (mushrooms, morels, yeast) Slime molds Water molds Bacteria (Bacteria, Archaea) Kingdom Plantae eukaryotic cells cell plate forms during cell division cell wall framework of cellulose autotrophic – chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b sporic life cycle multicellular primarily terrestrial Protista • Organisms that did not make the cut to be plants – Algae (kelps, seaweeds, "pond scum") – Fungi (mushrooms, morels, yeast) – Slime molds – Water molds – Bacteria Bacteria (Monera) • • • • prokaryotic cells autotrophic and heterotrophic primarily viewed as unicellular cell walls of peptidoglycan • Protozoa 1 Fungi • • • • • eukaryotic cells heterotrophic cell walls made of chitin zygotic life cycle multicellular and unicellular Archaea • The Archaea differ from the Bacteria: cell wall components, the organization of the DNA, the structure of membrane lipids, and the structure of ribosomes. • Three groups of Archaea – extreme halophiles (textbook: salt bacteria); ex. Halobacterium halobium, found in the GSL – extreme thermophiles (textbook: sulfolobus bacteria); ex. found in sulfur hot springs, such as those at Yellowstone – methanogens (textbook: methane bacteria); ex. produce methane, such as the archaea that live in cows and digest cellulose Domains • Archaea – Archaea Kingdom • Bacteria – Bacteria Kingdom • Eukarya – Animal Kingdom – Plant Kingdom – Fungi Kingdom – Protista Kingdom Five Kingdom Classification • Three Kingdoms for complex (multicellular) eukaryotes, with classification partly based on nutritional status and life cycle: Plantae: autotrophic; sporic life cycle Animalia: heterotrophic (ingestion); gametic life cycle Fungi: heterotrophic (absorptive); zygotic life cycle • A catch-all Kingdom for the remaining eukaryotes (Protista) • A single Kingdom for all prokaryotes (Monera) • Problem: people were starting to find prokaryotes that were different from the "standard" bacteria. Carl Woese. 1981. Six Kingdoms. Eukaryotic Kingdoms Animalia - Multicellular animals Plantae - Vascular plants (Seed Plants – angiosperms and gymnosperms, Seedless Vascular Plants), Bryophytes Fungi (Mycota) - Fungi Protista - Protozoa, Algae, Slime molds Prokaryotic Kingdoms Bacteria - includes the cyanobacteria Archaea - methanogens, extreme thermophiles, and extreme halophiles Levels of Classification Domain Kingdom Phylum (Division) Class Order Family Genus Species -ophyta -opsida -ales -aceae 2