* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prepositional and Appositive Phrases
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
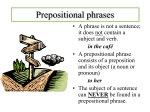
• Directions: Press F5 to begin the slide show. Press the enter key to view each part of the review. Phrases Part One Grade Seven What is a Phrase? • A phrase is a group of words. • Although each word in the group has its own part of speech, the group itself now takes on a new part of speech. (Think of the phrase as one thing. That one thing has its own part of speech.) • There will NEVER be a subject or verb in a phrase. Prepositional Phrases • One type of phrase is a prepositional phrase. • It must begin with a preposition. (If you don’t remember prepositions, look at the Power Point presentation on them or use your textbook or notebook for a list of them. There are fifty-seven as well as compound ones!) • It will end with a noun or pronoun that is called the object of the preposition. (Remember, to locate the object of the preposition, ask “who?” or “what?” after the preposition.) Examples of Prepositional Phrases Prep Op I walked across the street. Prep Op The car with the peeling paint is mine. Adjectival Prepositional Phrases • An adjective describes a noun or pronoun. • An adjectival phrase is a group of words working together to describe a noun or pronoun. • A prepositional phrase can be adjectival. This means that the entire phrase is describing a noun or a pronoun. Adjectival Prepositional Phrases • Consider this sentence: I saw a book about tools. • First, locate the prepositional phrase. It is: – “about tools.” • Then think about what the entire phrase describes. – It tells what kind of book it was. The phrase is describing “book.” • That is why “about tools” is an adjectival prepositional phrase. Adverbial Prepositional Phrases • An adverb describes a verb, adjective, or other adverb. • An adverbial phrase is a group of words working together to describe a verb, adjective, or adverb. • A prepositional phrase can be adverbial. This means that the entire phrase is describing a verb, adjective, or adverb. Adverbial Prepositional Phrases • Consider this sentence: I went to the store. • First, locate the prepositional phrase. It is: – “to the store.” • Then think about what the entire phrase describes. – It tells where the person went. “Went” is a verb. The phrase describes “went.” • That is why “to the store” is an adverbial prepositional phrase. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases • Prepositional phrases are diagrammed on a hockey stick with a tail. – The preposition goes on the diagonal line which is where you would hold the hockey stick. – The object of the preposition goes on the flat part where you would hit the puck. – Modifiers are hung beneath the object of the preposition. • Prepositional phrases are hung beneath the word they describe. Diagramming Prepositional Phrases • Consider this sentence. We took a test on Tuesday. • The prepositional phrase is “on Tuesday.” • It tells when they took the test. “Took” is a verb that is being described. • That means the hockey stick should go under “took.” • This is an adverbial prepositional phrase. We took test Friday Diagramming Prepositional Phrases • Consider this sentence. I went to the park. • The prepositional phrase is “to the park.” • It tells where they went. “Went” is a verb that is being described. • That means the hockey stick should go under “went.” • This is an adverbial prepositional phrase. I went park Diagramming Prepositional Phrases • Consider this sentence. The woman with the small child talked loudly. • The prepositional phrase is “with the small child.” • It tells which woman. “Woman” is a noun that is being described. • That means the hockey stick should go under “woman.” • This is an adjectival prepositional phrase. woman talked child Appositive Phrases • An appositive phrase renames or explains a noun in a sentence. • An appositive phrase is normally set off by commas. (The exception to this rule would be when the appositive is only a single word. Then it does not need to have commas around it.) • Appositives are noun phrases. App. Ex. The man, a doctor, said he would be with us in a minute. App. Ex. My cat Charlotte is ornery! Diagramming Appositive Phrases • An appositive is diagrammed in parenthesis after the noun it renames. • The only word that goes into the parenthesis is the actual word that renames. Any other words are modifiers and would be placed beneath the word in parenthesis. Diagramming Appositive Phrases Ex. The car, a Porsche, is expensive. car (Porsche) is expensive Diagramming Appositive Phrases Ex. The girl, a toddler with many loud toys, disrupted the storyteller. girl (toddler) disrupted storyteller toys • This completes the review of phrases. • Additional review can be done in the review folders housed in 106 and the library.