* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 7R: Parts of Speech Suffixes + Vocab Parallel Structure
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
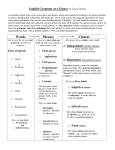
Lesson 7R: Parts of Speech Suffixes + Vocab Parallel Structure SSR: 9 Minutes No journal entry today Lesson Goals Today Develop and review the parts of speech Apply knowledge of parts of speech to word parts, and identify suffixes of words Breakdown parallel structure in writing Parts of Speech Review Why: to understand vocabulary development, you need to be able to understand word parts, and how they affect the part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, etc.) Prefixes Roots Suffixes Noun: Person, Place, Thing, Idea Proper Noun: Person, Place (Mr. Shockley, Avon High School) Common Nouns: unspecific (pencil, dog) Concrete Noun: tangible (dog, school, principal) Abstract Noun: intangible (bravery, principle, love) Verbs: Actions or States of Being Action Verbs: What the Subject/Noun is doing (run, jump, play) Helping Verb: Help an action verb (could run, does jump, will play) Infinitive Verb: has “to” in front (to be, to have, to hold) Adjectives: Describe or Modify Nouns/Pronouns What kind, which one, how many Adorable, bewildered, clumsy, disgusted, elegant, fancy, grotesque, handsome, innocent, jealous, kind, lazy, mushy, nasty, obnoxious, poised, quaint, repulsive, sparkling, talented, unusual, victorious, witty, zany Adverbs: Describe/Modify Adjectives, Adverbs, Nouns Explain how, when, where, why Most often: “ly” Swiftly: how something was done Suffixes At the end of the word Identify the part of speech of the word Add the meaning of the word Rebellion: “Act or Process of” is the meaning of suffix “—ion” Example Word Sheet Remember that the word you create has to match the part of speech! Syntax + Parallel Structure Page 12 Whether creating narratives or other forms or writing, writers use sentence structure (syntax) to create the effects they want. Using parallelism is one way of creating balanced sentence structure by creating a series at the word, phrase, or clause level. Parallel structure consists of two or more words, phrases, or clauses that are similar in length and grammatical form. A phrase is a group of related words that together function as a single part of speech. A clause is a group of words containing both a subject and a predicate. Parallelism in Writing Using parallelism is one way of creating balanced sentence structure by creating a series at the word, phrase, or clause level. Words: simple nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, gerunds; e.g., “My guinea pig eats nuts, seeds, and lettuce leaves.” Phrases: prepositional phrases (prepositions followed by nouns); e.g., “My cat raced in the door, onto the table, and into my lap.” Clauses: parallel subject and verb; e.g., “We swept the floor, we dusted the mantle, and we cooked a hot meal to welcome our guests.” Examples: Identify Parallel Structure Look for that repetition or balance in words, phrases, and clauses “But, in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate, we cannot consecrate, we cannot hallow this ground.” “. . . government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the earth.” Section 3 Describe each chunk as using parallelism with words, phrases, or clauses. Highlight the parallelism in each chunk. “To strengthen, perpetuate, and extend this interest [slavery] was the object for which the insurgents would rend the Union, even by war…” “With malice toward none; with charity for all; with firmness in the right, as God gives us to see the right, let us strive on to finish the work we are in…” Homework: Separate Sheet Bottom of Page 13 Rewrite the sentences (1-4) with correct parallel structure Due next class