* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
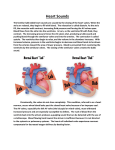
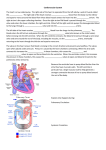
BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name:________________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. U10L1 NOTES: INTRODUCTION (web notes) 1. Left and Right Atria: ____________ ______________ • Right:_____________________ _________________________ _________________________. • Left: Collects blood from _________________________ _________________________. 2. Left and Right Ventricles: ____________________________ • Right: Sends blood to the _____________ via the Pulmonary Trunk. • Left: Sends blood to the _______________ via the Aorta 3. Atrioventricular Valves: Valves between the _________________ ___________________________. • Prevent _______________________ of blood • Right hand side "_______________________ cusps, or flaps • Left hands side "__________________" - two cusps 4. Chordae Tendineae: Strong, Fibrous strings that support the _________ Valve. • Keeps the valves from _____________________ with the force of blood flow. 5. Semi-Lunar Valves: Between __________________________________________ ______________________________________________. Page 1 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 • • Prevents backflow of blood from ______________________________________. Prevents backflow of blood from ______________________________________. 6. Pulmonary Trunk - Branches off to form the ______________________________. • _____________________________ from the right ventricle. 7. Septum - The wall of the ______________. • Separates the __________ and _____________ sides of the Heart Please click on the following link for detailed information and video on heart structure/function before attempting the practice: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hhw/contraction.html Page 2 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U10L1 PRACTICE: INTRODUCTION 1. Complete the following table. (14 marks) HEART STRUCTUE DESCRIPTION FUNCTION right atrium top right chamber collects deoxygenated blood from body left atrium right ventricle left ventricle coronary arteries coronary veins superior vena cava inferior vena cava pulmonary vein pulmonary artery aorta atrioventricular valves chordae tendineae semi-lunar valves septum Page 3 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U10L2 NOTES: THE HEART (web notes) Cardiac Cycle and Intrinsic Beat Contraction of the heart is _____________________________ process. • _____________ - Contraction of the Heart • _____________ - Relaxation of the Heart Each Heartbeat (Cardiac Cycle) Consists of: TIME 0.15 Sec 0.30 Sec 0.40 Sec =0.85 Sec ATRIA Systole Diastole Diastole VENTRICLES Diastole Systole Diastole Average rate of 70 beats per min The __________________ have a _______________________________ contraction because blood must be pumped throughout the body. The _________________ sound of the heart is due to the closing of the valves: First the _______________________________, then the semi-lunar. The beat of the heart is said to be intrinsic. It will beat ________________________ ________________________________ (meaning it can be removed from the body and still continue beating). The beat is controlled by a special type of tissue called ____________________, which has both _______________ and ___________________ tissue characteristics Page 4 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 There are two locations of Nodal Tissue in the Heart: 1. SA Node (__________________ Node) • Found in the upper wall of the __________________ _____________________. 2. AV Node (___________________ _______________________) • Found at the bottom of the ______________________ near the septum The SA Node (also called the _______________) initiates the heartbeat and sends out an ____________________________________ every 0.85 seconds. The impulse causes both atria to ____________________. The impulses are sent to the AV Node via the _______________________________________ (aka the antrioventricular bundle). When the impulse reaches the AV Node, an impulse is sent from the AV Node, up the Purkinje Fibers (found in the walls of the ventricles and the septum) which stimulates both ____________________________________ to contract from bottom upwards. An ________________________ registers the _________________ changes across the surface of the heart as it __________. The letters _______________ are the standard labels used to identify the parts of the ________. The P Curve records the ________________ _______________ of the __________ as they drive the blood out into their ventricles. The QRS is the ________________________ ________________________ as they drive the blood out into their respective arteries. Note the much higher peak of the QRS phase of the cardiac cycle in the picture to the right. This is due to the much longer stronger contraction of the ventricles pushing Page 5 of 13 blood out of the heart. BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 The T marks the ___________________ of the Ventricles (restoration of the normal electrical condition, preparing them for the next contraction). Autonomic Control of the Heart The rate of the heart can also be controlled by the ________________ ___________________________. The heart rate center is located in the _______________________________ of the brain. The SA Node is connected to the brain by the Vagus nerve (cranial nerve #10). This nerve pathway, part of the ____________________________ ________________________ (not under conscious control), has two system that affect the Heart Rate: 1. Parasympathetic System - ________________________________________. 2. Sympathetic System - Causes the heart beat to ______________ during times of stress. Factors such as need for _____________ or the blood pressure level determine which of these systems become active. When the brain perceives that the blood is getting delivered to the tissues too slowly, or if blood pressure is low, the brain will signal the ________________________________ ___________________________________________. Blood Pressure Ventricles pump a volume of blood (__________________) each time they contract. The arteries must have ____________________________________________ to withstand this pressure. The force of blood against the blood vessel walls is simply known as ___________________________________. Blood pressure is not constant. Page 6 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 The term systolic pressure (or Systole) refers to the ___________________________________________ This is the highest blood pressure reading. The term diastolic pressure (diastole) refers to the blood pressure when _________________________ _______________. This is the lowest blood pressure reading. Pulse: As blood is pumped through arteries, the _____________ ____________________, and then recoil. This swelling can be felt in any artery that runs close to the surface. Blood pressure is normally measured along the _______________________________ of the arm. A reading of ______________ is quite normal. • • 120 = Systolic Reading as ventricles contract 80 = Diastolic Reading as the ventricles relax A number of things can affect the blood pressure: Hypertension - _____________________________ Example: 140/90 or 125/90 Diet and lifestyle are often to blame for elevated blood pressure Reasons: • Stress • Plaques - ______________________________ • _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ __________________. (Arteriosclerosis) (Strokes, heart attacks...) • High Salt intake - retain water - _____________ • _______________________________________. • Smoking • Stimulants • Lack of exercise • Diet - amount and type • Working too hard • Age, Sex, Race Page 7 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Hypotension - _______________________ • ______________________________________________________________ o Example: 110/70 Reasons: • ______________________________________________________________ • _________________ • _________________ Proper kidney function can only be maintained if there is a sufficient _______________ ______________________ for filtration. Luckily the body can adjust blood pressure. Monitored by the _____________________ (part of the brain), the body can dilate (widen) arterioles thus _____________________ _________________ pressure in them, or constrict (narrow) them to _______________ ______________________________________. Page 8 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U10L2 PRACTICE: THE HEART 1. Compare and contrast the terms systole and diastole: a. in relation to the heart itself (2 marks) b. in relation to blood pressure readings. (2 marks) 2. The "lub-dub" sound of the heart is caused by the _______________________ closing and then the ________________________ closing. (2 marks) 3. Describe the nodal tissue of the heart including what it is, where it is found and what it does. (3 marks) Page 9 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 4. Explain the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic control of the heart beat and briefly explain how each is achieved. (6 marks) 5. Maintaining appropriate blood pressure in necessary to good health: a. What is considered "normal" blood pressure for an adult human? (1 mark) b. Define hypotension and its possible drawbacks. (2 marks) c. Define hypertension and identify some possible causes. (4 marks) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 10 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 10 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 10 ANSWER KEY U10L1 PRACTICE: INTRODUCTION 2. Complete the following table. (14 marks) HEART STRUCTUE DESCRIPTION FUNCTION right atrium top right chamber collects deoxygenated blood from body left atrium Top left chamber Collects oxygenated blood from lungs right ventricle Bottom right chamber Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs left ventricle Bottom left chamber Pumps oxygenated blood to body coronary arteries On/in cardiac muscle Supplies oxygenated blood to cardiac muscle coronary veins On/in cardiac muscle Removes deoxygenated blood from cardiac muscle superior vena cava From upper body, enters right atrium Collects deoxygenated blood from upper body and delivers to right atrium inferior vena cava From lower body, enters right atrium Collects deoxygenated blood from lower body and delivers to right atrium pulmonary vein Exits lung to left atrium Carries oxygenated blood from lung to left atrium pulmonary artery Exits right ventricle to lungs Carries deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs aorta Exits left ventricle to body Carries oxygenated blood from left ventricle to body atrioventricular valves Between atria and ventricles (aka AV valves) Prevents backflow of blood from ventricles to atria when ventricle contract chordae tendineae Attached to AV valves Ensues AV valves remain closed when ventricle contract semi-lunar valves In aorta and pulmonary artery Prevent backflow of blood from aorta and pulmonary artery into ventricles due to gravity septum Between left and right chambers Prevents Page 11 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U10L2 PRACTICE: THE HEART 1. Compare and contrast the terms systole and diastole: a. in relation to the heart itself (2 marks) systole = contraction of cardiac muscle…either of atria or ventricles diastole = relaxation of cardiac muscle…either of atria or ventricles b. in relation to blood pressure readings. (2 marks) systole = in blood pressure readings refers to the pressure that results specifically from contraction of the ventricles (represents the higher blood pressure number listed on top of the reading…for example 120/80 mm Hg means the systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg) diastole = in blood pressure readings refers to the pressure that results specifically from relaxation of the ventricles (represents the lower blood pressure number listed on bottom of the reading…for example 120/80 mm Hg means the diastolic pressure is 80 mm Hg) 2. The "lub-dub" sound of the heart is caused by the _______________________ closing and then the ___________________________________ closing. (2 marks) 3. Describe the nodal tissue of the heart including what it is, where it is found and what it does. (3 marks) = combination of nerve and muscle tissue within the right atria of the heart = controls the heart beat…the sinoatrial node (SA) in the top right of the right atrium is called the pacemaker and initiates atrial contraction (from the top of the atria downwards) approximately every 0.8 seconds whereas the Atrioventricular node (AV node) is near the bottom left of the right atrium and collects the electrical signal to pass on to the atrioventrical bundle (AV bundle) so that ventricle contraction can be initiated from the bottom of the ventricles upwards. Page 12 of 13 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 4. Explain the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic control of the heart beat and briefly explain how each is achieved. (6 marks) Intrinsic control = regulation of the heart beat by nodal tissue within the heart itself, this is regulated by the sinoatrial node which initiates atrial contraction approximately every 0.8 seconds, atrial contraction then triggers ventricle contraction via the AV node AV bundle Purkinje fibres Extrinsic control = regulation of the heart beat by the brain, this is regulated when the cardiac centre of the medulla oblongata either triggers the parasympathetic system to release acetylcholine from the Vagus nerve and thus, slow the signals from the SA and AV nodes (decreasing heart rate) or triggers the sympathetic system to release norepinephrine from the accelerator nerve and thus, speed up the signals from the SA and AV node (increasing heart rate). Whether the parasympathetic or sympathetic response is triggered depends on blood pressure and CO 2 , O 2 and H+ levels in the blood. 5. Maintaining appropriate blood pressure in necessary to good health: a. What is considered "normal" blood pressure for an adult human? (1 mark) = 120/80 mm Hg b. Define hypotension and its possible drawbacks. (2 marks) = low blood pressure (below 90/60 mm Hg) = dizziness, fainting, difficulty concentratin, blurred vision, nausea, fatigue, depression, thirst = may indicate improper heart beat or dehydration c. Define hypertension and identify some possible causes. (4 marks) =high blood pressure (below140/100 mm Hg) = high salt diet leading to water retention in blood, presence of plaques in arteries causing narrowing of the artery Page 13 of 13