* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Fetal Heart Imaging
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
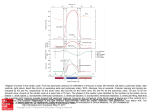
Introduction to Fetal Heart Imaging By Harry H. Holdorf The indications for a fetal echocardiogram: Maternal Drug Exposure and Diseases, Family History of Congenital Heart Disease, Increased Maternal Risk for Down Syndrome and Other Chromosomal Defects, Chromosome abnormalities and CHD. Abnormal findings include: Abnormal cardiac screening examination, abnormal heart rate or rhythm, fetal chromosomal anomaly, Extra-cardiac anomaly, Hydrops, Increased nuchal translucency, mono-chorionic twins, and unexplained severe polyhydramnios. The normal findings associated with a four chamber view: Left Ventricle to right ventricle ratio 1:1, left atrium to right atrium ratio 1:1, cardiac apex approximately 45 degrees, cardiac area approximately 1/3 of thoracic area, right ventricle retrosternal, left ventricle-left heart border, foramen ovale protrudes into left atrium, muscles of moderator bands in right ventricle thicker than muscle in left ventricle, tricuspid valve insertion more towards apex versus mitral valve. The normal orientation of the four-chamber view within the fetal chest: RV closest to anterior chest wall, apex pointing 45 degrees towards left chest wall, tricuspid valves offset from mitral valves. The checklist of a normal fetal cardiac study includes: 4 Chamber view, LVOT, RVOT, Ductal arch, septum, Right bifurcation, aortic arch. Aorto-pulmonary transportation: In the fetus, blood is oxygenated by the placenta. Blood returns from the placenta to the heart via the umbilical vein, which enters the liver via anastomose with the left portal vein. This richly oxygenated blood shunts through the ductus venosus to join the IVC and the left atrium. From there, the oxygenated stream is directed across the foramen ovale to the left side of the heart. Deoxygenated blood returns to the right atrium via the SVC and the IVC. This blood preferentially flows to the right ventricle and pulmonary artery, which trifurcates in the fetus. Flow in the branch pulmonary arteries is limited; the majority of the right ventricle output enters the ductus arteriosus to join the descending aorta; which perfuses most of the fetal torso with a mix of deoxygenated blood from the RV and the remainder of the oxygenated placental return. Define pulmonary atresia: Pulmonary atresia is a congenital malformation of the pulmonary valve in which the valve orifice fails to develop. The valve is completely closed thereby obstructing the outflow of blood from the heart to the lungs. Rates for normal, slow, and fast cardiac arrhythmias: Normal=100-180 Slow = under 100 Fast=Over 180 4 CHAMBER HEART VIEW: LEFT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT: RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT: FETAL CIRCULATION: FORAMEN OVALE, DUCTUS VENOSUS, AND DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS VSD: HYPOPLASTIC RIGHT HEART: HYPOPLASTIC LEFT HEART: ECTOPIC CORDIS: CARDIAC TUMOR: EBSTEINS ANOMALY: