* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnetic Induction Faraday`s Law
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
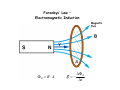
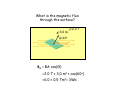
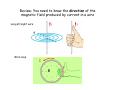
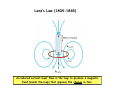
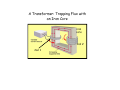
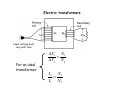
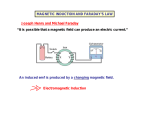
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday’s Law – Part II 1831 PHYS 219 Test III Thursday; December 17, 2009 8AM PHYS 112 Lecture 14 Faradays’ Law – Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic flux ΦB = B ⋅ A ΔΦ B E =− Δt What is Magnetic Flux? Magnetic Flux is the product of an area (m2) with a component of a magnetic field (T) passing perpendicularly through it. Convenient to define area vector A ΦB = BA cos(Θ) Units: ΦB = T•m2=1 Weber = 1 Wb What is the magnetic flux through the surface? =3.0 m2 =2.0 T =60o ΦB = BA cos(Θ) =2.0 T × 3.0 m2 × cos(60o) =6.0 × 0.5 Tm2= 3Wb Review: You need to know the direction of the magnetic field produced by current in a wire Long straight wire Wire loop I B Faraday’s Law: An induced emf is produced in a coil whenever the magnetic flux changes with time. ∆ΦB E =-N ∆t Subtle Point: The negative sign indicates that the induced emf acts to “oppose” the change in magnetic flux that causes it. Key Idea: An emf is produced by the changing magnetic flux. The emf in turn produces an induced current I. What is the induced emf if the magnetic field through a six turn coil increases at a rate of 0.17 T/s? E=- ΔΦ B Δ( B i A) ΔB =− = −A Δt Δt Δt A = π R 2 = 0.88 m 2 E=− The negative sign indicates that the induced emf acts to “oppose” the change in magnetic flux that causes it ΔB = +0.17 T/s Δt E = -(0.88 m 2 )(0.17 T/s)= - 0.15 V Since coil has six turns, E = 6 × (- 0.15)= - 0.90 V Induced Voltage: a simple example What is Va-Vb? N=1 Uniform B B ro = 1m constant rate of reduction 1 T a time b 0.001 s Lenz’s Law (1804-1865) An induced current must flow in the loop to produce a magnetic field (inside the loop) that opposes the change in flux. Lenz’s Law – Predicting the direction of the induced current (Focus on the Change in Flux w.Time) a) b) motion toward loop Iind Iind N N motion away from loop loop ΦΒ loop ΦΒ increasing time increasing time The induced current always produces a magnetic field that opposes (counteracts) the change in flux It is often easier to take the absolute value of Farady’s Law to find the magnitude of the induced emf and use Lenz’s Law to find the direction of the induced current that results. A Transformer: Trapping Flux with an Iron Core iron core Coil 2 Coil 1 Electric transformers Input voltage must vary with time For an ideal transformer ΔV1 N1 = ΔV2 N 2 I 2 N1 = I1 N 2 A transformer has 10 turns on the primary and 100 turns on the secondary. If 110V is applied to the primary, how much voltage appears across the secondary?