* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide set 2 – Plant Evolution and diversity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
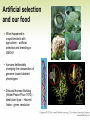
Chapter 17 Principles of Plant Evolution Topics • Principles of evolution and plants • Key aspects of plant speciation • Plant cladogram • Artificial selection • Green revolution and our food Natural selection and plant evolution • Evolution – change in genetic composition in population gene pool over generations – can lead to speciation • Remember five natural events/causes that change allele frequencies from HW principle • In most cases natural selection – most important: Sotols in West Texas • Mutations cause variation in gene pool • Some mutations can affect the fitness • Those individuals may be less or more adapted to the environment than other Individuals • Fit enough – survive and reproduce Two conditions must be met before natural selection can occur • Overproduction • Variation in phenotype Many Elderberry seedlings • Natural selection acts only on phenotype changes existing genome/alleles - does not cause mutations • It is population not individual that evolves and adapts • natural selection does not happen if • all individuals are identical – take examples, drought, floods, predation, pathogens etc. • habitat supports the survival, growth and reproduction of all individuals equally • Usually, loss of individuals and reduced reproduction are not caused by a single factor • A mutation may be potentially advantageous, but it may never have the opportunity to improve the fitness of the plant or the species • Whether a particular mutation/allele is beneficial or not depends entirely on the habitat, which may also change with time Sympatric and allopatric speciation: Reproductive barriers • Sympatric speciation - common in plants - reproductive isolation within one population • Isolation mechanisms may be prezygotic, such as cellular/gamete incompatibility; or postzygotic, such as hybrid sterility, breakdown or inviability • Discuss polyploidy in plants – new variants due to differences in genome; 30 – 80% of plants • Draw plant cladogram with 10 phyla. • Discuss alternation of generation and how natural selection acted on it. Artificial selection and our food • What happened in crops/livestock with agriculture – artificial selection and breeding or GMOs? • humans deliberately changing the composition of genome toward desired phenotypes • Discuss Norman Borlaug (Nobel Peace Price 1970) – ideal plant type – Harvest Index - green revolution