* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
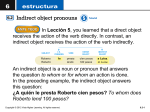
Download In Lección 5, you learned that a direct object receives the action of
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
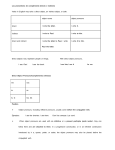
In Lección 5, you learned that a direct object receives the action of the verb directly. In contrast, an indirect object receives the action of the verb indirectly. An indirect object is a noun or pronoun that answers the question to whom or for whom EX: ¿A quién le presta Roberto cien pesos? To whom does Roberto lend 100 pesos? Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-1 In Lección 5, you learned that a direct object receives the action of the verb directly. In contrast, an indirect object receives the action of the verb indirectly. An indirect object is a noun or pronoun that answers the question to whom or for whom EX: ¿A quién le presta Roberto cien pesos? To whom does Roberto lend 100 pesos? Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-2 More Examples: Juan le manda flores a Juana. Juan sends her flowers to Juana. Juan sends whom/what? Flowers – direct object Juan sends flowers to whom? Juana – indirect object Juan le manda flores. Juan sends her flowers. What –Flowers/flores – direct object Whom/who –her is the indirect object. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-3 ¡Atención! The forms of indirect object pronouns for the first and second persons (me, te, nos, os) are the same as the direct object pronouns. Indirect object pronouns agree in number with the corresponding nouns, but not in gender. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-4 Using indirect object pronouns Spanish speakers commonly use both an indirect object pronoun and the noun to which it refers in the same sentence. This is done to emphasize and clarify to whom the pronoun refers. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-5 Indirect object pronouns are also used without the indirect object noun when the person for whom the action is being done is known. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-6 Indirect object pronouns are usually placed before the conjugated form of the verb. In negative sentences the pronoun is placed between no and the conjugated verb. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-7 Order/placement of indirect nouns & pronouns in a sentence ***Before conjugated verb EX: Le compra. ***Attach to an infinitive or gerund (-ing) verb EX: Voy a comprarte una camisa. Esta comprandote una camisa. ¡Atención! When an indirect object pronoun is attached to a present participle, an accent mark is added to maintain the proper stress. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-8 Because the indirect object pronouns le and les have multiple meanings, Spanish speakers often clarify to whom the pronouns refer with the preposition a + [pronoun] or a + [noun]. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-9 The irregular verbs dar (to give) and decir (to say; to tell) are often used with indirect object pronouns. Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-10 Copyright © 2012 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved. 6.2-11