* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Iowa Wing Bloodborne Pathogens
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
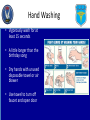
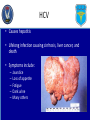
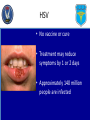
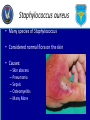
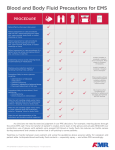
Iowa Wing Bloodborne Pathogens and Other Diseases of Concern Created by: Casey L. C. Schroeder, MLS Captain, CAP Health Services Officer Outline • • • • • • • Universal Precautions OSHA Regulations CAP Regulations Disease Transmission Prevention of Transmission Diseases of Concern Questions Universal Precautions • Infection control procedures to protect members from infectious agents • Involve the use of protective barriers: – Gloves – Masks – Personal hygiene (hand washing) Universal Precautions • Require that all human blood be considered infectious • Require other body substances be considered infectious • Consists of both: – Bloodborne pathogens – Body substance isolation Universal Precautions • Must follow UP and safe practices each time you provide care or are near crash sites • Precautions include: – Personal Hygiene – Personal Protective Equipment – Engineering and work practices – Equipment cleaning and disinfecting OSHA Regulations • Required by employees for whom there is “reasonable anticipation” of exposure • Good Samaritan actions are not covered under this • Ground Teams and CAP do not fall under this standard CAP Regulations • Does not require that you directly care for victims • If you chose, use universal precautions, safe practice, and common sense at all times Disease Transmission • Possible for you to infect someone and vice versa • Pathogen: – Disease causing organisms such as: • • • • Fungi Parasites Viruses Bacteria Disease Transmission • Pathogen can enter the body: – Direct – Indirect – Airborne – Vector-borne Disease Transmission • 4 factors required for infection: – Pathogen – Appropriate entry site – Enough of the pathogen – Susceptibility to the pathogen • Prevent any one of these, infection does not occur Cross-Contamination • Form of indirect exposure that poses a particular risk of disease transmission • Everything touched is considered contaminated • Common activities: – – – – – Pens & Pencils Eye glasses Scratching your nose or face Door knobs or handles Phones & Radios Hand Washing • Single best defense against disease transmission • Visibly soiled hands use soap and water • Do not use hand sanitizer if visibly soiled Hand Washing • Vigorously wash for at least 15 seconds • A little longer than the birthday song • Dry hands with unused disposable towel or air blower • Use towel to turn off faucet and open door Hand Washing • Use alcohol-based hand sanitizers (60% to 95%) only when not visibly soiled • Ensure you apply the amount prescribed on the bottle • Rub hands thoroughly until product dries PPE • Only works if it does not permit blood or other body fluids to pass • Should be free of holes, tears, rips, and other defects • Immediately replace if this is the case • Should be correct size • Ensure it is readily available PPE • Glove removal – With soiled gloves, start with either hand – Carefully pinch glove near the wrist, touching only the outside of the glove – Slowly pull the glove off, which will turn it inside out – With the gloved hand, ball the dirty glove into the gloved hand PPE • Glove removal (cont’d) – Examine cuff of the soiled glove for a clean area – Slide an ungloved finger under the cuff, touching only the inside of the glove – Slowly pull the soiled glove off, turning it inside out – Dispose of soiled gloves – WASH HANDS with soap and water immediately after Glove Removal Disease of Concern • Some diseases: – HIV – HBV – HCV – HSV – Staphylococcus aureus HIV • Transmitted by: – Blood – Semen or Vaginal secretions – Childbirth with an infected mother – Breast-feeding – Body fluids – CSF HIV • Who can contract this virus: – Every one regardless of age, gender, sexual orientation, or race • US rate: >1 million people infected • Iowa: 102 new HIV cases each year • No external factors or symptoms HBV • Causes hepatitis • Lifelong infection causing cirrhosis, liver cancer, and death • Symptoms include: – – – – Jaundice Loss of appetite Fatigue Many others HBV • Transmission: – Blood or body fluids – Sharing drug needles – Needle sticks or sharp biohazard exposure – Childbirth from infected mother – Sexual intercourse HBV • Three shot vaccine • 43,000 new cases in 2007 for the US • Approximately 1.4 million people infected in the US • Iowa: 24 new cases each year HCV • Causes hepatitis • Lifelong infection causing cirrhosis, liver cancer, and death • Symptoms include: – – – – – Jaundice Loss of appetite Fatigue Dark urine Many others HCV • Transmission: – Blood or body fluids – Sharing drug needles – Needle sticks or sharp biohazard exposure – Childbirth from infected mother – Sexual intercourse HCV • No vaccine or treatment • 43,000 new cases in 2007 for the US • Approximately 1.4 million people infected in the US • Iowa: 24 new cases each year HSV • Causes cold sores • Symptoms include: – Pain around mouth and lips – Blister that breaks open and leaks a clear fluid • Transmission – Touching the sore – Touching saliva that contains the virus HSV • No vaccine or cure • Treatment may reduce symptoms by 1 or 2 days • Approximately 140 million people are infected Staphylococcus aureus • Many species of Staphylococcus • Considered normal flora on the skin • Causes: – – – – – Skin abscess Pneumonia Sepsis Osteomyelitis Many More Staphylococcus aureus • Transmission – Skin contact – Fomite (towels, bandages, etc) – Contaminated surfaces and items • Risk factors: – – – – Athletic facilities Dormitories Military barracks Households Staphylococcus aureus • Prevention – Proper hygiene • Treatment through antibiotics • Estimated 89,785 infections in 2008 • Estimated 15,249 deaths in 2008 Points to Remember • Proper Hygiene • Always use PPE • Infection is both ways • Always assume blood and other body fluids are infectious Questions?