* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Religious Diversity in the Middle East
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Nizari Ismailism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
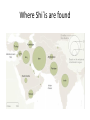
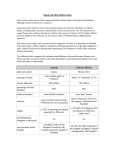
Religious Diversity in the Middle East Carl Ernst Carolina Center for the Study of the Middle East and Muslim Civilizations UNC at Chapel Hill What is diversity? Ethnicity Language National origin Religious identity Gender Economic class Urban-rural Sura 110 in his hand Omar ibn Sayyid (1772-1864), enslaved Muslim scholar in NC ما االسالم؟ What do we mean by Islam? Religious meaning: submission to God (Muslim: one who submits to God) Social meaning: one who conforms to religious practices (prayer, fasting, pilgrimage, alms, statement of faith) Political meaning: group religious identity with no reference to belief or religious practice Ideological meaning: anti-colonial identity formulated against “the West” Islam, history, and culture Islamic: relating to Islamic religious texts, Islamic law, worship, religious practices Islamicate: non-religious cultural and social traditions associated with Muslims but which also include non-Muslim participation Multiple pre-Islamic traditions and cultures (Egypt, Iran, India, etc.) Who defines Islam? Nation-states Tax-free status (IRS), visas (INS), prisons, military al-Azhar Constitutions and legal codes, most of European colonial origin State-approved academies (madrasas) like al-Azhar in Cairo, or new Uzbekistan college Other agents Shi`i jurists like Iraqi leader Sistani Sunni academies: Deoband in India European and American scholars Religion by the numbers – 1.6 billion Muslims worldwide Muslims by region Middle East Muslim populations Islamic religious pluralism Perhaps 15% are Shi`is (esp. Iraq, Iran, Lebanon, also South Asia) Including Twelvers, Isma`ilis, Bohras Offshoots: Druze, Alawis, Baha’is Perhaps 85% Sunni 4 classical legal schools New reformist movements (Wahhabi, Salafi; “fundamentalism”) Sufi spirituality Local saints, Sufi orders (both Shi`i and Sunni) Music, poetry, dance traditions Secularism `Ali and Shi`ism • first four Caliphs (successors to Muhammad) – Abu Bakr, 632-634 – `Umar, 634-644 – `Uthman, 644-656 – `Ali, 656-661 • Rise of the party or faction (shi`a) of `Ali; his partisans called Shi`is 10 The declaration of Ghadir Khumm • Muhammad: “him for whom I am the master, so this Ali is his master” • Was `Ali named as Muhammad’s successor? 11 Ali’s death, Karbala, and martyrdom • Mu`awiya, member of the old Meccan family opposing Muhammad, establishes Umayyad dynasty, which is criticized for immorality • `Ali’s son Husayn raises revolt, massacred in Karbala (680) by army of Yazid (son of Mu`awiya) 12 Karbala 13 Husayn • 14 Varieties of Shi`ism • Twelvers recognize 12 Imams succeeding Muhammad; dominant in Iraq, Iran • Ismai`ilis broke away after 6th Imam: – Nizaris (15 million) led by Agha Khan, regarded as 49th Imam – Bohras (1 million, India) led by Syedna, counted as 53rd absolute representative of Fatimid caliphs • Zaydis, open to competitive selection of Imams, 35% of population in Yemen (Houthis) Where Shi`is are found Sunni acceptance of Shi`is – or the lack thereof Controversy: Visiting Imams’ or Sufi saints’ Shrines Note: Egypt figure is questionably low Offshoots of Shi`i Islam • Alawites (a.k.a. Nusayris), Syria (4 million) – Affiliated with Twelver Shi`ism; revere `Ali, Muhammad, and Salman the Persian • Alevis, Turkey (ca. 7 to 11 million) – Linked with Bektashi dervishes (Ottoman empire) and Qizilbash tribes (involved in post-1500 Safavid revolution in Persia) • Druze, Lebanon-Syria-Palestine (1 million) – Breakaway followers of deified Fatimid Caliph alHakim (11th cent.); esoteric philosophy • Baha’is, Iran-Israel-US-etc. (7 million) – Outgrowth of 19th-cent. Persian Shi`ism, transformed into universalist movement; persecuted in Iran Pre-Islamic religious groups • Zoroastrians: followers of Persian prophet Zoroaster (ca. 1200 BCE; 30,000 in Iran; 100,000 in India, called Parsis) • Mandeans, Iraq-Iran (ca. 75,000); ancient dualistic Gnostic teachings • Yezidis, worshipers of Peacock Angel, 1M • Ahl-e Haqq (People of Truth): Kurdish esoteric group with Sufi and Bektashi elements; 2M? Middle Eastern Christians • • • • • • • • Copts, Egypt, 10-15 million Armenians, 8 million Syria, 2M (“Assyrians”, Syriac-Aramaic speakers) Lebanon, 1.5M (Melkite, Catholic) Iraq, 400,000 Iran, 350,000 (Armenian, Georgian) Turkey, 300,000 Palestine, 50,000 Mizrahi (Arab/Oriental) Jews • Israel: 3M • Iran: 8,700 • Communities in Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Azarbaijan, Georgia (8000 to 15,000 each) The new intolerance of ISIS: diversity under threat


































![2013chapter0.ppt [兼容模式]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002898662_1-e8a437736f7c2b25ea015c0d1428106d-150x150.png)