* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
History of Nizari Ismailism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Imamate (Twelver doctrine) wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Usul Fiqh in Ja'fari school wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
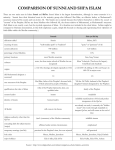
Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam There are two main sects in Islam: Sunni and Shi'ite. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination, although in some countries it is a minority. Sunnis have their historical roots in the majority group who followed Abu Bakr, an effective leader, as Muhammad's successor, instead of his cousin and son-in-law Ali. The Sunnis are so named because they believe themselves to follow the sunnah or "custom" of the Prophet. Shi'ites are those Muslims who followed Ali, the closest relative of Muhammad, as Muhammad's successor. Sufi Islam is not exactly a sect, but the mystical expression of Islam. It is therefore not included in the chart below. Sufism might be compared to Christian monasticism, in that both emphasize a quiet, simple life focused on obeying and experiencing God. Opinions of Sufis differ within the Muslim community. The following chart compares the similarities and differences between the major Islamic sects. Please note that, as with all charts of this kind, information is generalized and should not be used as the only basis of information. Sunnah Shia (or Shi'ah) adherents called Sunnis Shiites, Shi'i meaning of name "well-trodden path" or "tradition" "party" or "partisans" of Ali current adherents 940 million 120 million percentage of total Muslims 90% 10% primary locations most Muslim countries Iran, Iraq, Yemen subsects none, but four major schools of Muslim law are recognized Ithna 'Ashariyah (Twelvers; the largest), Isma'iliyah and Zaydiyah origins c. 632 CE; theology developed especially in 10th cent. c. 632-650 CE; killing of Ali's son Husayn in 680 CE is major event no yes Abu Bakr, father of the Prophet's favoured wife, 'A'ishah (elected by people of Medina) 'Ali ibn Abi Talib, husband of the Prophet's daughter Fatimah (designated by the Prophet) did Muhammad designate a successor? true successor of the Prophet qualifications for ruler of Islam tribe of the Prophet (Quraysh); later, any qualified ruler family of the Prophet imams mujtahids human leaders infallible manifestations of God and perfect interpreters of the Qur'an Al Mahdi will come in the future was already on earth, is currently the "hidden imam" who works through mujtahids to intepret Qur'an; and will return at the end of time religious authority other than the Qu'ran ijma' (consensus) of the Muslim community infallible imams concealing faith for self-protection (taqiya) affirmed under certain circumstances emphasized practiced in the Prophet's time, but now rejected still practiced Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem, Najaf, Karbala Eid al-Adha, Eid al-Fitr Eid al-Adha, Eid al-Fitr, Ashura current leaders identity of imams temporary marriage (mut'ah) holy cities major holidays