* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. To research…
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
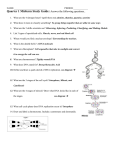
DNA Stations #1 Research Task: Genetic Disorders Task: You will research information that will examine a genetic disorder, explaining the causes of this disorder linking it to heredity and possible treatment options. This MUST be factual and should not contain any persuasive or “emotional” tone or observations. You may choose from the list below or you may research a genetic disorder of your choice but it must be preapproved from me first. Remember to cite your sources. Possible Topics: Diabetes Cystic Fibrosis Muscular Dystrophy Hemophilia Sickle Cell anemia Tay-Sachs disease Huntington’s Disease Hemochromatos is Angelman syndrome Color Blindness (genetic) Cri du chat Williams syndrome Rett Syndrome Turner syndrome Albinoism Duchenne muscular dystrophy 1. To research… a. Name the genetic disorder and briefly describe symptoms including any physical differences or obstacles b. Known or suspected causes (X-Linked, Mendelian being dominant vs. recessive, unknown) c. Any known treatments for the disorder. DNA Stations #2 Create a DNA model DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA consists of about 3 billion bases, and more than 99 percent of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to the way in which letters of the alphabet appear in a certain order to form words and sentences. DNA bases pair up with each other, A with T and C with G, to form units called base pairs. Each base is also attached to a sugar molecule and a phosphate molecule. Together, a base, sugar, and phosphate are called a *nucleotide. Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder’s rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder. An important property of DNA is that it can replicate, or make copies of itself. Each strand of DNA in the double helix can serve as a pattern for duplicating the sequence of bases. This is critical when cells divide because each new cell needs to have an exact copy of the DNA present in the old cell. *(http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/basics?show=all) Task: Using the exact symbols and colors given, create your own unique strand of DNA. The strand must contain 20 base pairs. Adenine (A) must ALWAYS match up with Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) must ALWAYS match up with Guanine (G). (stick letter stick together and curvy letters curve together) The base pairs connect and make the ‘steps’ or rungs of the DNA ladder. Base pairs always, always, always connect to a sugar as seen in the nucleotide picture to the left. Base Pair Symbols and colors to use. Thymine (T) Adenine (A) * Nucleotide consist of a sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate and a base (A, T, C, or G) . BASES ALWAYS PAIR UP WITH A SUGAR! Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) DNA Stations #3 DNA mistakes… A DNA strand is simply a string of *nucleotides joined together. The bases join in the middle. The information in DNA is stored as a code made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Adenine always pairs with Thymine and Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. ALWAYS!! If these base pairs do not match up * Nucleotide consist of a sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate and a base (A, T, C, or G) . BASES ALWAYS PAIR UP WITH A SUGAR! in this partnership then the genetic code is not correct. Mistakes in the pairing are what lead to genetic disorders. There are three ways that DNA can be altered when a gene mutation (change in DNA sequence) occurs. 1. Substitution – one base-pair is replaced by another (A A T C G T instead of A A A C G T) 2. Insertion – one or more base pairs is added to a sequence (A A T T C G T instead of A A T C G T) 3. Deletion – one or more base pairs is lost from a sequence Sickle Cell Anemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the DNA. People with Sickle Cell have red blood cells with sickle shaped hemoglobin that cannot hold as much oxygen. They get out of breath easily and have a lot of pain. Below is the base sequence for the normal protein for normal hemoglobin and the base sequence for the sickle cell hemoglobin. Find the mistake! What type of mutation is this? Normal: GGG CTT CTT TTT Sickle: GGG CAT CTT TTT DNA Stations #4 Mutations and adaptations * Go to my webpage. * Click on the 7th grade tab on the left hand side. * Scroll down and click on the yellow link in the Class Announcement box. Review the page and explain how a mutation can lead to an adaptation. Answer the questions on your student answer sheet as thoroughly as you can! The more the details you gather from this site the easier it will be later to connect how organisms are able to survive and evolve. DNA Stations Answer Sheet #1- Genetic Disorder Research a. b. c. Name __________________________ BL _______ #2- DNA model (remember Adenine always connects with Thymine and Cytosine always connects with Guanine, they can appear on either side of the ladder but they must always be paired together, pay attention to the coloring as well, that must be the same so we can compare models) #3- Genetic mutations Circle the wrong code in the Sickle Cell DNA. Below each letter in the code write its base pair partner. (Remember C with G and T with A) Normal: GGG CTT CTT TTT Sickle: GGG CAT CTT TTT Identify the type of mutation you believe this is and justify your reasoning. Create your own DNA code below with at least 12 base pairs (3 base pairs codes for an amino acid so this will give you 4 amino acids). Show a DNA sequence for the other two types of mutations. #4- Mutations to Adaptations Define adaptation. How can one individual organism’s helpful mutation influence future generations? Can an entire species adapt or evolve overnight or can it take many generations for it to occur? Explain the difference between structural adaptations and behavioral adaptations. What is speciation and how can this even happen? Coadaptation is also called co-evolution. Research another pair of organisms that mutated/adapted together and are dependent on each other. Name:_______________________Bl ___ TYPES OF SYMBIOSIS There are 3 basic types of symbiosis. Don’t forget that symbiosis is the relationship between two organisms of different species that benefits one or both organisms. M- Mutualism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits both organisms involved. C- Commensalism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits one organism and the other is not helped or harmed. P- Parasitism- a symbiotic relationship that benefits one organism and the other is harmed. Directions: Put the letter (M,C,P) by the statement that best describes the type of symbiosis. ____ 1. A tick living on a dog. ____ 2. The honey guide bird leading the honey badger to the bees hive, both eat the honey. ____ 3. A tapeworm living in a 7th grade students intestines. ____ 4. A bird building their nest in a tree. ____ 5. The hermit crab carrying the sea anemone on its back. ____ 6. The bristle worm living with the hermit crab. ____ 7. Head lice living on a human scalp. ____ 8. Mistletoe putting its roots into its host tree. ____ 9. The ants and the acacia tree living together and both receiving benefit. ____10. The egret, an insect eating bird, graze near some herbivores mouth. ____11. Orchids growing in tall tropical trees, the trees are not harmed but the orchids get sunlight. ____12. Bacteria living on a humans skin. ____13. The remora hitching a ride on a shark. ____14. Barnacles living on a whale. ____15. Bees and a flower. ____16. Bacteria living in the intestines of a cow to help it break down cellulose. ____17. The clownfish and the sea anenemoe. ____18. A sixth grader and their pet. ____19. The Rhino and the tick bird. ____20. The lichen- a very close relationship of algae and fungi in which the fungi is dependent on the algae and the algae is dependent on the fungi. Autotrophs are organisms that are able to make their own food through photosynthesis. These are frequently called producers. Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot make their own food and must eat in order to survive. These are frequently called consumers. The sun is the main source of energy for all living things on earth but it is transferred from one organisms to the next in its cells. Once an organism consumes another organism the energy transferred is energy that originated from the sun. This energy transfer can be displayed using a food web. The producers have the most amount of energy available from the sun and when they are consumed they transfer some of that to the next organism and when that organism is consumed it transfers some of the energy on. The energy transferred is less as each organism must use some of that energy to survive (cellular respiration, mitosis, etc) A food chain is shown below. A sudden decrease in the population of one type of organism in the food chain will affect all of the other organisms in the food chain. Grass Grasshopper Small bird Hawk A. Identify two changes that would likely happen to organisms in this food chain if most of the small birds in this area became diseased and died. B. Explain why each change is likely to occur. C. Explain the transfer of energy (from the sun) in the food chain above. D. Create your own food web with 5 organisms. Begin with an autotroph since all energy transferred begins with them. Explain the amount of energy transferred throughout the chain.