* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immunization Update 2016
Self-experimentation in medicine wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Human mortality from H5N1 wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 wikipedia , lookup
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Avian influenza wikipedia , lookup
Transmission and infection of H5N1 wikipedia , lookup
Swine influenza wikipedia , lookup
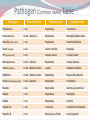
Kenneth McCall, BSPharm, PharmD Associate Professor | UNE Objectives Discuss the gap between current vaccination rates and Healthy People 2020 goals for vaccinations. Categorize each of the CDC recommended flu vaccines based upon live/inactivated, route, preparation, and storage. Discuss the influenza vaccines for 2016 including the new quadrivalent and mammalian cell vaccines. Identify vaccine contraindications and recommend vaccines based upon patient age and medical history. Apply ACIP recommendations and FDA approved indications for the CDC recommended vaccines. Recognize Maine state laws that regulate vaccine administration. 2 Outline Background & Principles of Vaccination Influenza Vaccines Quadrivalent inactivated Quadrivalent live Mammalian High Dose Intradermal Classification of Vaccines Live attenuated Weakened form of the “wild” virus or bacteria Inactivated Whole viruses or bacteria Fractions of viruses or bacteria *Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases, 12th Edition Classification of Vaccines Live attenuated: Measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, zoster, intranasal influenza Inactivated: hepatitis A, hepatitis B, influenza, pneumonia, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, HPV, meningicoccal *Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases, 12th Edition 7 Immunization Schedules US Center for Disease and Prevention (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) ACIP is a group of medical and public health experts who meet three times per year to discuss vaccine recommendations Published annually Adult schedule approved by American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists American College of Physicians American College of Nurse-Midwives 8 CDC ACIP 2016 Recommended Adult Immunization Schedule 11 12 Maine Pharmacist-Administered Immunization Regulations No Rx Required Rx Requireda Rx or Protocol Not Permitted Adult (≥18 years) with PCPb Influenza ✓-RPh or Intern ✓-RPh or Intern Other Vaccinesc Adult (≥18 years) without PCP Influenza ✓-RPh or Intern ✓-RPh or Intern Other Vaccinesc Child < 18 years ✗ Other Vaccinesc Child 7-17 years Influenza ✓-RPh only Child <7 years Influenza Intern administration permitted as indicated under direct supervision of licensed pharmacist a Verbal/phone authorization acceptable b Primary care physician or existing relationship with a nurse practitioner or an authorized practitioner in Maine c All vaccines licensed by the US FDA recommended by the CDC ACIP ✗ 13 What is the Healthy People 2020 goal for annual flu vaccination for adults 65 and older? 0% 100% 0% 0% 100% 2. 90% 3. 70% 4. 50% 1. 16 Influenza versus Common Cold Signs & Symptoms Influenza Common Cold Onset Sudden Gradual Fever High (>101°F) Less common (low grade) Cough Dry; can be severe Hacking or congested Headache Common Rare Myalgias Usual; severe Slight Can last 2-3 weeks Very mild Early and prominent Rare or never Common Mild to moderate Stuffy nose Sometimes Common Sneezing Sometimes Usual Sore throat Sometimes Common Fatigue/malaise Extreme exhaustion Chest discomfort ACIP Recommendations 2015-2016 Influenza Season All persons aged 6 months and older should receive influenza vaccine annually. Persons who care for severely immunosuppressed persons who require a protective environment should not receive LAIV, or should avoid contact with such persons for 7 days after receipt, given the theoretical risk for transmission of the live attenuated vaccine virus. Persons who report having had reactions to egg involving such symptoms as angioedema, respiratory distress, lightheadedness, or recurrent emesis; or who required epinephrine or another emergency medical intervention, may receive Flublok if they are aged 18 years or older and there are no other contraindications. LAIV: live attenuated influenza vaccine 18 2015-2016 Vaccine Coverage & Age Group Distribution of Influenza Positive Specimens Trivalent A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like virus A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2)-like virus B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (Yamagata) Quadrivalent A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like virus A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2)-like virus B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (Yamagata) B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus (Victoria) 19 A (H1N1) A (H3) B (Yamagata) B (Victoria) http://www.cdc.gov/flu/weekly/FluViewInteractive.htm Egg Allergy Recommendation Persons with egg allergy may tolerate egg in baked products (e.g., bread or cake). Tolerance to egg-containing foods does not exclude the possibility of egg allergy. Abbreviations: IIV = inactivated influenza vaccine, trivalent or quadrivalent; RIV3 = recombinant influenza vaccine, trivalent. 21 Influenza Vaccines – United States, 2015-2016 Influenza Season Trade name Manufacturer Presentation Mercury (from thimerosal) µg/0.5 mL Ovalbumin µg/0.5 mL Age indications Latex Route Inactivated influenza vaccine, quadrivalent (IIV4), standard dose Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine. 0.5 mL singleFluarix GlaxoSmithKline dose prefilled — ≤0.05 ≥3 yrs No IM† Quadrivalent syringe FluLaval ID Biomedical Quadrivalent Corp. Fluzone Sanofi Pasteur Quadrivalent Fluzone Intradermal¶ Sanofi Pasteur Quadrivalent 5.0 mL multi-dose <25 vial 0.25 mL singledose prefilled — syringe 0.5 mL singledose prefilled — syringe 0.5 mL single— dose vial 5.0 mL multi-dose 25 vial 0.1 mL single-dose prefilled — microinjection system http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6430a3.htm#Tab ≤0.3 ≥3 yrs No IM† § 6 through 35 mos No IM† § ≥36 mos No IM† § ≥36 mos No IM† § ≥6 mos No IM† § 18 through 64 yrs No ID** Influenza Vaccines, 2015-2016 Influenza Season cont’d Trade name Manufacturer Presentation Mercury (from thimerosal) µg/0.5 mL Ovalbumin µg/0.5 mL Age indications Latex Route Inactivated influenza vaccine, trivalent (IIV3), standard dose Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine. 0.5 mL singledose prefilled syringe Afluria Fluvirin Fluzone — <1 ≥9 yrs†† No IM† No IM† bioCSL Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics Sanofi Pasteur 5.0 mL multidose vial 24.5 <1 ≥9 yrs†† via needle;18 through 64 yrs via jet injector 0.5 mL singledose prefilled syringe ≤1 ≤1 ≥4 yrs Yes§§ IM† 5.0 mL multidose vial 25 ≤1 ≥4 yrs No IM† 5.0 mL multidose vial 25 § ≥6 mos No IM† http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6430a3.htm#Tab Influenza Vaccines, 2015-2016 Influenza Season cont’d Trade name Manufacturer Presentation Mercury (from thimerosal) µg/0.5 mL Ovalbumin µg/0.5 mL Age indications Latex Route Inactivated influenza vaccine, cell-culture-based (ccIIV3), standard dose Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine. Flucelvax Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics 0.5 mL singledose prefilled syringe — ¶¶ ≥18 yrs Yes§§ IM† Inactivated influenza vaccine, trivalent (IIV3), high dose Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine. Fluzone HighDose*** Sanofi Pasteur 0.5 mL singledose prefilled syringe — § ≥65 yrs No IM† Recombinant influenza vaccine, trivalent (RIV3), standard dose Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine. Flublok Protein Sciences 0.5 mL singledose vial — 0 http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6430a3.htm#Tab ≥18 yrs No IM† Influenza Vaccines, 2015-2016 Influenza Season cont’d Trade name Manufacturer Presentation Mercury (from thimerosal) µg/0.5 mL Ovalbumin µg/0.5 mL Age indications Latex Route Live attenuated influenza vaccine, quadrivalent (LAIV4) Contraindications*: Severe allergic reaction to any vaccine component, including egg protein, or after previous dose of any influenza vaccine. Concomitant use of aspirin or aspirin-containing medications in children and adolescents. In addition, ACIP recommends LAIV4 not be used for pregnant women, immunosuppressed persons, persons with egg allergy, and children aged 2 through 4 years who have asthma or who have had a wheezing episode noted in the medical record within the past 12 months, or for whom parents report that a health care provider stated that they had wheezing or asthma within the last 12 months. LAIV4 should not be administered to persons who have taken influenza antiviral medications within the previous 48 hours. Persons who care for severely immunosuppressed persons who require a protective environment should not receive LAIV4, or should avoid contact with such persons for 7 days after receipt. Precautions*: Moderate to severe acute illness with or without fever; history of Guillain-Barré syndrome within 6 weeks of receipt of influenza vaccine; asthma in persons aged 5 years and older; medical conditions which might predispose to higher risk for complications attributable to influenza. FluMist Quadrivalent† †† MedImmune 0.2 mL singledose prefilled intranasal sprayer — <0.24 (per 0.2 mL) http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6430a3.htm#Tab 2 through 49 yrs No IN Which of the following is the predominant flu strain of 2015-16? 0% 1. Type B strain in trivalent vaccine 0% 2. Type B strain not in trivalent vaccine 100% 3. Type A H1N1 strain 0% 4. Type A H3N2 strain 27 New Influenza Vaccines: Fluarix ® (GlaxoSmithKline) – inactivated, quadrivalent vaccine which contains two type A and two type B strains FDA approved December 2012 People ages 3 years and older Fluzone ® (Sanofi Pasteur) – inactivated, quadrivalent vaccine which contains two type A and two type B strains FDA approved March 2013 People ages 6 months and older Quadrivalent Flu Vaccines Facts A quadrivalent (4-strain) flu vaccine helps to provide protection against four flu virus strains (2 Type A and 2 Type B). 4-strain flu vaccines are made in the same way 3-strain flu vaccines are made. Quadrivalent flu vaccines are available as both shots and intranasal spray. Quadrivalent versus Trivalent Influenza Vaccine Excerpt from FDA Clinical Review: Fluarix Quadrivalent® Unmet Medical Need: “The B strain recommended for use in the yearly [trivalent] vaccine has been matched to the main circulating influenza B strain only in onehalf of the influenza season in the last eight years. 30 2015-2016 Vaccine Coverage: Trivalent versus Quadrivalent Trivalent A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like virus A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2)like virus B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (Yamagata) Quadrivalent A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)-like virus A/Switzerland/9715293/2013 (H3N2)like virus B/Phuket/3073/2013-like virus (Yamagata) B/Brisbane/60/2008-like virus (Victoria) Conclusion: quadrivalent does not provide significantly better coverage this flu season 31 Administration Fluarix®: 0.5-mL dose IM - deltoid 1 inch, 25 gauge needle 32 Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccines contain which of the following? 0% 1. Four type A strains 0% 2. Two type A strains, 1 type B, & 1 type C 100% 3. Two type A strains & 2 type B strains 0% 4. Four type B strains 34 New Influenza Vaccines: Flumist® Quadrivalent (MedImmune)– live attenuated vaccine which contains two type A and two type B strains FDA approved March, 2012 People ages 2 through 49 years Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine Indication Healthy people 2 through 49 years of age Contraindications I pick my nose! Pregnant women People who have long-term health problems with: heart disease kidney or liver disease lung disease metabolic disease, such as diabetes asthma anemia, and other blood disorders Anyone with a weakened immune system Severe egg allergy 36 Administration Flumist®: 0.1-mL dose in each nostril Intranasal 37 Intranasal Administration Active inhalation (sniffing) by the patient is not required Which of the following patients is a candidate for the live influenza vaccine? 2% 1. 45 yo man with severe egg allergy 95% 2. 27 yo healthy woman 0% 3. 38 yo man with diabetes 2% 4. 54 yo healthy man 2% 5. 19 yo pregnant woman 40 New Influenza Vaccines: Flucelvax® (Novartis)– trivalent inactivated vaccine grown in mammalian cells rather than chicken embryo cells. FDA approved November, 2012 Adults 18 years and older May contain a trace amount of egg protein. Administration Flucelvax®: 0.5-mL dose IM - deltoid 1 inch, 25 gauge needle 42 43 New Influenza Vaccines: Flublock® (Protein Sciences Corporation)– trivalent inactivated vaccine grown in insect cells rather than chicken embryo cells. FDA approved November, 2013 Adults 18 years and older. Doesn’t list “severe allergic reaction to egg protein” in the contraindications Administration Flucelvax®: 0.5-mL dose IM - deltoid 1 inch, 25 gauge needle 45 ACIP Recommendations for flu vaccination of person who report egg allergy. Select an influenza vaccine for a healthy 37year-old woman with severe egg allergy. 100% 1. Flublok 0% 2. Flumist 0% 3. Fluzone 0% 4. Fluarix 48 Why a high-dose influenza vaccine? • Clinical Need 31 studies from 1986 to 2002 found that post-vaccination titers in older adults were 2x to 4x less likely to produce sufficient protection against influenza Vaccine efficacy in a matched season: 70% to 90% in younger adults 17% to 53% in adults aged ≥65 years • HD Vaccine Efficacy RCTs and retrospective analyses demonstrate superior efficacy compared to IIV-SD Wang J, Vardeny O, Zorek J. High-dose influenza vaccine in older adults. JAPhA. 2016; 56:95-97. Methods: Retrospective cohort study HD vaccine (60 mcg of hemagglutinin per strain): N= 929,730 SD vaccine (15 mcg of hemagglutinin per strain): : N= 1,615,545 US Medicare beneficiaries 65 years and older who received influenza vaccine in a community pharmacy Primary outcome: probable episode of influenza-related illness defined by a community medical encounter with the provision of a rapid influenza test followed by dispensing of oseltamivir within a 2-day period 50 Izurieta_2015_Lancet Infect Dis How well does the study design limit bias? Who was enrolled in the study/who does the study apply to? What is the primary outcome, how was it measured and is the result statistically significant? What can we infer from these findings? Is the result clinically significant? Efficacy of HD Vaccine versus SD Vaccine Against Influenza-Related Illness Similar results to Diazgranados et al. Those who received IIV-HD 22% less likely to have influenzaassociated illness and 22% less likely to be admitted to the hospital for influenza Lancet Infect Dis 2015;15:293-300 52 Conclusions: IIV-HD versus -SD • Safety Injection site reactions have been reported at higher rates for IIV-HD, though most cases were mild and resolved within several days A 2015 study showed IIV-HD results in fewer serious complications • Cost Cost to administer is $19.75 higher than IIV-SD per individual A 2015 cost-utility analysis demonstrated a 587% financial return for the health care system alone (cost savings in the millions of dollars) • Implications for Pharmacists ACIP makes no recommendation for one influenza vaccine formulation over another for older adults Regardless of which formulation is recommended, be sure it is received in a timely manner so your patients have the best possible flu protection JAPhA. 2016; 56:95-97. 53 Administration Fluzone HD®: 0.5-mL dose IM - deltoid 1 inch, 25 gauge needle 54 Intradermal Influenza Vaccine Indicated for persons 18 through 64 years of age Contraindications Severe egg allergy Associated with higher rates of injection site reactions (erythema, induration, swelling, and pruritus, but not pain) than the IM inactivated influenza vaccines Erythema (>75%) Induration (>50%) Swelling (>50%) Pain (>50%) Pruritus (>40%) 56 Intradermal vs Traditional IM needle Length 30 Gauge Needle and Less Volume Methods: Multicenter, randomized, double-blind controlled study ID vaccine (9 mcg of hemagglutinin per strain) N=1,803 IM vaccine (15 mcg of hemagglutinin per strain): N=452 in adults 18 to 60 years of age. Human Vaccines. 2010;6:346-54. Comparison of local side effects to ID and IM influenza vaccine 90 80 70 Percent 60 50 IM 15 mcg 40 ID 9 mcg 30 20 10 0 Erythema Swelling Induration Pain Human Vaccines. 2010;6:346-54. 60 Intradermal Injection Technique 1. Remove needle cap 2. Hold microinjection system between thumb and middle finger Do not place fingers on the windows 3. Insert needle rapidly perpendicular to the skin 4. Inject using the index finger 5. Remove needle from the skin and activate the needle shield by pushing firmly on the plunger Which side effect is more common with the intradermal influenza vaccine than the IM influenza vaccine? 17% 1. Injection site pain 0% 2. Headache 0% 3. Fever 67% 4. Injection site swelling 17% 5. Malaise Age Indication for Influenza Vaccines: United States, 2015-2016 0.5-2 years 2 years 3 years 4-8 years 9-17 years 18-49 years 50-64 years 65+ years ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Fluarix Quad ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ FluLaval Quad ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Flucelvax ✓ ✓ ✓ Flublok2 ✓ ✓ ✓ Fluzone Intradermal Quad ✓ ✓ Vaccine Fluzone / Fluzone Quad Flumist Quad Fluvirin Afluria1 Fluzone High-Dose 1. 2. Age indication per package insert is >5 years; however the ACIP recommends >9 years. FDA labeled age indication expanded in 2015 to 18 years and older (now including adults 65+). ✓ 64 Characteristics of Influenza Vaccines: United States, 2015-2016 Vaccine Live Fluzone / Fluzone Quad Flumist Quad Mercury Egg Protein ✓1 ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Fluarix Quad FluLaval Quad ✓ ✓ Fluvirin ✓1 ✓ Afluria ✓1 ✓ Flucelvax Latex ✓2 ✓3 ✓3 Flublok Fluzone Intradermal Quad ✓ Fluzone High-Dose ✓ 1. 2. 3. Multi-dose vials contain mercury. Single-dose prefilled syringes are mercury-free. Estimated to contain <50 femtograms (5x10-8 mcg) of total egg protein per 0.5 ml dose. Syringe tip may contain natural rubber latex. 65 Which of the following influenza vaccines is NOT indicated for a 72-year old woman? 0% 1. Inactivated trivalent IM vaccine 0% 2. Inactivated quadrivalent vaccine 20% 3. Inactivated high dose vaccine 80% 4. Inactivated trivalent intradermal vaccine A 35-year-old woman requests an annual flu shot. She has ulcerative colitis and is taking Prednisone 40 mg QD. Which flu vaccine(s) is/are appropriate? 0% 1. Influenza intradermal vaccine 33% 2. Influenza intramuscular vaccine 0% 3. Influenza high dose vaccine 0% 4. Flumist nasal spray 0.2 ml nasal 67% 5. Either 1 or 2 0% 6. Either 2 or 3 0% 7. Either 2 or 4 Pneumococcal Disease Pneumococcal disease is caused the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae Clinical Features Pneumonia Otitis media Sinus infections Bacteremia Meningitis Risk Factors Asplenia Chronic heart, pulmonary, liver, or renal disease Cigarette smoking Cerebrospinal fluid leak Age less than 2 years, or 65 years and older Complex immunization recommendation for adults 69 Streptococcus Pneumoniae 90 serotypes identified The 10 most common serotypes are estimated to account for about 62% of invasive disease worldwide Up to 36% of adult CAP Up to 50% of HAP 13-19% of all cases of meningitis CDC: Vaccines and Immunizations. Pneumococcal Disease. http://www.cdc.gov/. Accessed 30 July 2014. 70 Pneumococcal Vaccines Pneumovax 23® (PPSV23, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine) • Prevnar 13® (PCV13, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) ACIP Recommendations on Pneumococcal Vaccinations in Adults PPSV23 (Pneumovax®) Age Who receives the vaccine? ≥65 years old • Vaccination history unclear or never received vaccine before • Revaccinate: If patient received vaccine before the age of 65 and it has been ≥ 5 years since administration 2-64 years old • • • • • • Chronic cardiovascular disease (CHF, cardiomyopathies) Chronic pulmonary disease (COPD) Diabetes mellitus Alcoholism Chronic liver disease Cerebrospinal fluid leaks Re-vaccination after 5 years if: • functional or anatomic asplenia • Immunocompromising conditions • Chronic kidney disease 19-64 years old • Cigarette smokers • Asthma 76 PCV13 (Prevnar®) Age Who receives the vaccine? 6 weeks through 5 years old Routine series at 2, 4, 6, and 12 through 15 months. Minimum intervals: Dose 1 to Dose 2: 4 weeks Dose 2 to Dose 3: 4 weeks Dose 3 to Dose 4: 8 weeks 6-18 years old Children 6 through 18 years who have not received PCV13 previously, and are at high risk for invasive pneumococcal disease because of: • Anatomic or functional asplenia (including sickle cell disease) • Immunocompromising conditions, including HIV infection • Cochlear implant • CSF leaks should receive a single dose of PCV13 (regardless of any previous history of PCV7 and/or PPSV23). 77 PCV13 (Prevnar®), cont’d Age Who receives the vaccine? Adults 19 years old and older Adults 19 and older who have not received either PCV or PPSV previously, and are at high risk for invasive pneumococcal disease because of: • Anatomic or functional asplenia (including sickle cell disease) • Immunocompromising conditions, including HIV infection • Cochlear implant • CSF leaks should receive a single dose of PCV13. (This should be followed with a dose of PPSV at least 8 weeks later. Those who have indications for revaccination with PPSV should receive a second dose at least 5 years after the first.) Adults 19 and older with any of these conditions who have received one or more doses of PPSV previously should receive a single dose of PCV13 at least one year after the last dose of PPSV. [Note that use of PCV13 for persons 18 through 49 years of age, while recommended by ACIP in these circumstances, is off-label.] Appropriate intervals between doses of PCV and PPSV can be found in PCV MMWR (for children) and PSV MMWR (for adults). http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/vis/vis-statements/pcv13-hcp-info.html 78 ACIP Recommendations on Pneumococcal Vaccinations in Adults Both PCV13 and PPSV23 should be administered routinely in series to all adults aged ≥ 65 years. Pneumococcal vaccine-naïve persons. Adults aged ≥65 years who have not previously received pneumococcal vaccine or whose previous vaccination history is unknown should receive a dose of PCV13 first, followed by a dose of PPSV23. The dose of PPSV23 should be given 6–12 months after a dose of PCV13. If PPSV23 cannot be given during this time window, the dose of PPSV23 should be given during the next visit. The two vaccines should not be coadministered, and the minimum acceptable interval between PCV13 and PPSV23 is 8 weeks. MMWR September 19, 2014 / 63 (37) Pneumococcal vaccine-naïve persons aged > 65 years *minimum interval between sequential administration of PCV13 and PPSV23 is 8 weeks; PPSV23 can be given later than 6-12 months after PCV13 if this window is missed. Persons who previously received PPSV23 at age > 65 years *minimum interval between sequential administration of PCV13 and PPSV23 is 8 weeks; PPSV23 can be given later than 6-12 months after PCV13 if this window is missed. Persons who previously received PPSV23 before age 65 years who are now aged > 65 years Administration Pneumovax® & Prevnar®: 0.5 mL dose 1 inch, 25 gauge needle Intramuscular (IM) - deltoid CDC: Vaccines and Immunizations. Pneumococcal Disease. http://www.cdc.gov/. Accessed 30 July What is the Healthy People 2020 goal for pneumococcal vaccination for adults 65 and older? 0% 100% 0% 0% 100% 2. 90% 3. 70% 4. 50% 1. A 65-year-old man who is pneumonia vaccine naïve. What pneumonia vaccine(s) is/are recommended? 2% 1. Pneumovax only 0% 2. Prevnar only 3% 3. Both; Pneumovax prior to Prevnar 95% 4. Both; Prevnar prior to Pneumovax Which of the following statements about the administration of influenza and pneumonia vaccines is true? 100% 1. Same day, opposite arm, separate syringe 0% 2. Same day, same arm, mixed in 1 syringe 0% 3. Must be separated by at least 7 days 0% 4. Must be separated by at least 4 weeks Which of the following vaccines is a live vaccine? 0% 1. Pneumovax 100% 2. Flumist 0% 3. Prevnar 0% 4. Fluarix 0% 5. Fluzone HD Pathogen (Common name) Table Pathogen Classification Transmission Complication Influenza (flu) virus Respiratory Pneumonia Pneumococcus Gram + Bacteria Respiratory Meningitis/Bacteremia Varicella (chicken pox) virus Respiratory Bacterial infection Zoster (shingles) virus Latent varicella Neuralgia HPV (genital warts) virus Sexual contact Cervical cancer Meningococcus Gram - Bacteria Respiratory Invasive disease Tetanus (lockjaw) Gram + Bacteria-toxin wound Respiratory failure Diphtheria Gram + Bacteria-toxin Respiratory Myocarditis/Neuritis Pertussis (whooping cough) Gram - Bacteria Respiratory Pneumonia Measles virus Respiratory Diarrhea, pneumonia Mumps virus Respiratory Meningitis Rubella virus Respiratory Arthritis Hepatitis A virus Fecal-oral Acute/chronic hepatitis Hepatitis B virus Blood-serous fluids Acute hepatitis Adult Vaccine Table Vaccine Vaccine Type Route / Reconstitute Series Storage Influenza IIV Inactivated IM / No 1x annually Fridge Flumist Live Intranasal / No 1x annually Fridge Pneumovax Inactivated IM or SQ / No 1-2 doses Fridge Zostavax Live SQ / Yes 1 dose Freezer Gardasil (HPV9) Cervarix (HPV2) Inactivated IM / No 3 doses Fridge Td Inactivated IM / No 1 q 10 years Fridge Tdap Inactivated IM / No 1x, then Td Fridge Varivax Live SQ / Yes 2 doses Freezer MMR Live SQ / Yes 1-2 doses Fridge or Freezer Menactra, Menveo Menomune (MPSV4) Inactivated IM / No 1-2+ doses Fridge Havrix, Vaqta Inactivated IM / No 2 doses Fridge Recombivax-HB Engerix-B Inactivated IM / No 3 doses Fridge