* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Empire
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman calendar wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
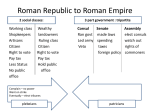
Roman Republic Expansion • Rome went through a period of rapid expansion. • Rome’s expansion led to some problems • People became greedy and forgot the values that made them strong • Many slaves from conquered peoples were sent to Rome • The rich could afford to buy them and expand the land they used – including public lands • Small family farms could not compete with the large estates • Many people sold their small farms and moved to the city • The cities had a growing landless poor population Bread and Circuses • All those people without jobs posed a serious threat – the possibility of a riot • In order to distract the masses from their poverty, the wealthy would give them Bread and Circuses • They would give free grain hand outs (for making bread) to the jobless • They would host entertainment on a grand scale in the Coliseum. Circus Maximus Gladiators Coliseum Discussion Question # 1 • What effect did expansion have on Rome? Reforms • Some powerful people were concerned over the plight of the small farmers • Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus (brothers) tried • They proposed taking back public lands and giving it to small farmers and lowering the price of food to help the plebeians. • The wealthy and powerful were angry over this – because they would lose money and land • They conspired to have the brothers murdered • Their attempt at reforms brought in an era of instability Tiberius and Gaius Gracchus Discussion #2 • What were the reforms meant to do? Army Changes • The backbone of the Roman Army had always been small farmers • Since their numbers were declining, a Roman general came up with a new way • Marius recruited soldiers from the cities, promising land for service • Marius had volunteers swear an oath of loyalty to the general, not the country Roman Legion • In order to get the Senate to authorize the giving of land the Generals had to become involved in politics. • These changes left a powerful legacy • With soldiers loyal to a specific general, the Army would be the basis of power from now on. • Example – Sulla 82 BC Discussion #3 • Why do American troops swear to uphold the Constitution and defend the United States? From Republic to Empire • For the next 50 years Rome was torn apart by civil wars. • One general, Julius Caesar, defeated all the others and took power • He made changes to the government • He was made dictator (absolute ruler) in 45 BC. This was usually a temporary position Julius Caesar • The Senators feared that he would keep the position for life, so they murdered him on the Senate floor. • Another round of civil wars resulted. • The victor, Octavian, was Caesar’s grandnephew and heir (the person who inherits your stuff) • Even though Octavian kept the Senate, he held all the real power • In 27 BC he was given the title Augustus (the revered one) • Augustus becomes the first Roman Emperor • After so much war the people are happy to have a stable government, even if it is a dictator. • “Those who would sacrifice essential liberty for temporary security deserve neither liberty nor security” – Benjamin Franklin Origin of the names of the months Only a few names of the month were derived from Roman deities. Most simply came from the numbers of the months or -- in two cases -- in honor of Roman emperors. • January Named after the Roman god of beginnings and endings Janus (the month Januarius). • February The name comes either from the old-Italian god Februus or else from februa, signifying the festivals of purification celebrated in Rome during this month. • March This is the first month of the Roman year. It is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. • April Called Aprilis, from aperire, "to open". Possible because it is the month in which the buds begin to open. • May The third month of the Roman calendar. The name probably comes from Maiesta, the Roman goddess of honor and reverence. • June The fourth month was named in honor of Juno. However, the name might also come from iuniores (young men; juniors) as opposed to maiores (grown men; majors) for May, the two months being dedicated to young and old men. • July It was the month in which Julius Caesar was born, and named Julius in his honor in 44 BCE, the year of his assassination. Also called Quintilis (fifth month). • August Originally this month was called Sextilis (from sextus, "six"), but the name was later changed in honor of the first of the Roman emperors, Augustus (because several fortunate events of his life occurred during this month). • September The name comes from septem, "seven". • October The name comes from octo, "eight" • November The name comes from novem, "nine". • December The name comes from decem, "ten". Discussion #4 • How did Rome go from a Republic to an Empire? Pax Romana 27 BC – 180 AD • The next four Emperors were from Augustus line • (Caligula) • After the last of Augustus line died/was killed (69 BC), another round of civil wars followed • This was part of the problem with their system of government, if your power is based on the Army, you have to make sure you have a good man take your place • Around 100 AD, a series of five good emperors began. • These included Trajan, Hadrian, and Marcus Aurelius • They made good choices, expanded the empire, selected good heirs, were tolerant of others Height of the Roman Empire • The time period starting with Augustus and lasting through the five good emperors was known as the Pax Romana or Roman peace. • It was a period stable government and relative peace. Discussion #5 • Why did the Pax Romana last so long?