* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Convection Currents - Effingham County Schools
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
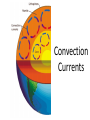
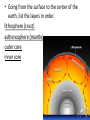
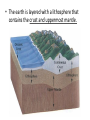
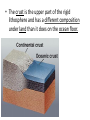
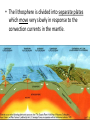
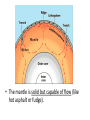
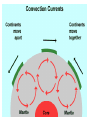
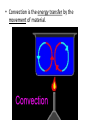
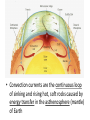
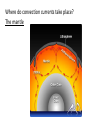
Convection Currents • Going from the surface to the center of the earth, list the layers in order. lithosphere (crust) asthenosphere (mantle) outer core inner core • The earth is layered with a lithosphere that contains the crust and uppermost mantle. • The crust is the upper part of the rigid lithosphere and has a different composition under land than it does on the ocean floor. • The lithosphere is divided into separate plates which move very slowly in response to the convection currents in the mantle. • The mantle is solid but capable of flow (like hot asphalt or fudge). • Below the rigid lithosphere, the mantle consists of hot rock of tar-like consistency, which slowly moves or flows. This is also called the asthenosphere. • Convection is the energy transfer by the movement of material. • Convection currents are caused by as heated molten rock in the mantle become less dense and rise. At the same time other molten rock cools and become more dense so they sink. • Convection currents are the continuous loop of sinking and rising hot, soft rocks caused by energy transfer in the asthenosphere (mantle) of Earth • Heat from the mantle and core creates convection currents. • Convections currents in the mantle cause the tectonic plates to move. Where do convection currents take place? The mantle • • • • Less dense things rise while more dense things sink.