* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Specialization And Organization 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
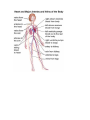
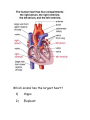
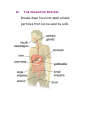
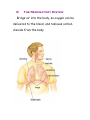
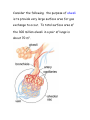
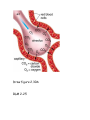
Body Systems in Humans The 3 main body systems in humans include: 1) The Circulatory System consists of the heart, blood, and the blood vessels (arteries and veins). this system circulates the blood around the body, delivering food particles (nutrients) and oxygen to every cell in the body. This system also carries away cell wastes such as carbon dioxide. Which animal has the largest heart? 1) Hippo 2) Elephant 3) Giraffe Did you know that the average heart rate (beats per minute) of a _____________ is ______________. a) human; 65-75 bpm b) elephant; 25 bpm c) shrew; 600 bpm Lab on your pulse rate. To get you pulse rate, locate your pulse on your neck. Then count the number of pulses/beats in 15 seconds; - multiply this number by 4 - this gives the beats per minute (bpm). We will get your pulse rate at rest, sitting, standing, after 1, 2, 3, and 4 minutes of exercise. We will graph and interpret your results and the classes. 2) The Digestive System Breaks down food into small soluble particles that can be used by cells. 3) The Respiratory System Brings air into the body, so oxygen can be delivered to the blood, and removes carbon dioxide from the body See page 146 BLM 2-22 BLM 2-23 BLM 2-24 The Respiratory System and the Circulatory System Connection The respiratory system exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide while the circulatory system transports those gases throughout the body. How does it happen? Answer – You breathe in air, it travels down the windpipe into the lungs into tiny air sacs called alveoli. Oxygen diffuses across the thin membranes (epidermal cells) into the circulatory system, while carbon dioxide diffuses into the lungs from the circulatory system. The circulatory system is composed of tubes (or blood vessels). - Arteries carry blood away from the heart. This blood is rich in oxygen. - Veins carry blood back to the heart. This blood is low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide. - Capillaries are made of epithelial tissue. They connect the arteries to the veins and is the place where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the cells and alveoli. See figure 2.29 on page 148. Consider the following: the purpose of alveoli is to provide very large surface area for gas exchange to occur. To total surface area of the 300 million alveoli in a pair of lungs is about 70 m2. Draw figure 2.30A BLM 2-25 The Circulatory and Digestive System Digestion breaks food down into smaller components. These nutrients are transferred into the circulatory system, which are then passed on to supply each cell with energy. The transfer of food from the digestive system to the circulatory system takes place at the inner lining of the small intestine. This lining is covered in tiny, finger-like projections called villi, which increases the surface area of the small intestine. Each villi contains a network of capillaries. Dissolved food particles are absorbed into the capillaries and onward the nutrients go to every part of the body How much surface area do all the villi supply for absorption? Nearly 300m2! Draw figure 2.31 into notes. Read “Off the Wall” on page 150. BLM 2-26 The Excretory System - it is involved in getting rid of wastes - the main organ involved in this system is the kidney. The kidney filters waste materials from the blood. - The lungs and the skin are also grouped into this system because they excrete wastes. Lungs eliminate carbon dioxide and water, and skin can eliminate water and excess salt through sweating (perspiration). - The excretory system also controls the concentration of important substances in the blood (such as sodium, calcium, potassium) by regulating how much of these substances are lost in the urine. The Sensory Awareness System -your body’s response to stimuli (such as temperature) is coordinated by the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and nerves) and the endocrine system (glands that produce chemical messengers called hormones) BLM 2-27 Page 153 #1-6