* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Energy?
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
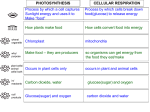
Name _____________________________ Date ___________________________ Pd. ______ Directions: Read the entire packet and use the information to answer the questions on the last page. What is Energy? Energy causes things to happen around us. Look out the window. During the day, the sun gives out light and heat energy. At night, street lamps use electrical energy to light our way. When a car drives by, it is being powered by gasoline, a type of stored energy. The food we eat contains energy. We use that energy to work and play. Energy Is the Ability to Do Work. Energy can be found in a number of different forms. It can be chemical energy, electrical energy, heat (thermal energy), light (radiant energy), mechanical energy, and nuclear energy. Stored and Moving Energy Energy makes everything happen and can be divided into two types: Stored energy is called potential energy. Moving energy is called kinetic energy. With a pencil, try this example to know the two types of energy. Put the pencil at the edge of the desk and push it off to the floor. The moving pencil uses kinetic energy. Now, pick up the pencil and put it back on the desk. You used your own energy to lift and move the pencil. Moving it higher than the floor adds energy to it. As it rests on the desk, the pencil has potential energy. The higher it is, the further it could fall. That means the pencil has more potential energy. Changing Energy Energy can be transformed into another sort of energy. But it cannot be created AND it cannot be destroyed. Energy has always existed in one form or another. Here are some changes in energy from one form to another. Stored energy in a flashlight's batteries becomes light energy when the flashlight is turned on. Food is stored energy. It is stored as a chemical with potential energy. When your body uses that stored energy to do work, it becomes kinetic energy. If you overeat, the energy in food is not "burned" but is stored as potential energy in fat cells. When you talk on the phone, your voice is transformed into electrical energy, which passes over wires (or is transmitted through the air). The phone on the other end changes the electrical energy into sound energy through the speaker. A toaster changes electrical energy into heat and light energy. (If you look into the toaster, you'll see the glowing wires.) A television changes electrical energy into light and sound energy. ENERGY AND LIFE The capture and use of energy in living systems is dominated by two processes: photosynthesis and respiration. Through these two processes living organisms are able to capture and use all of the energy they require for their activities. Photosynthesis Plants can capture the electromagnetic energy from the sun by a chemical process called photosynthesis. The overall chemical reaction involved in photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2. In simple terms, we can say it the following way Carbon Dioxide + Water (+ sun energy) Glucose + Oxygen The product of photosynthesis is the carbohydrate glucose and oxygen which is released into the atmosphere. All of the sugar glucose is produced in the specialized photosynthetic cells of plants and some other organisms. Glucose is produced by chemically combining carbon dioxide and water with sunlight. This chemical reaction is catalyzed (make happen) by chlorophyll acting in concert with other pigment, lipid, sugars, protein, and nucleic acid molecules. Sugars created in photosynthesis can be later converted by the plant to starch for storage, or it can be combined with other sugar molecules to form specialized carbohydrates such as cellulose (remember this molecule?), or it can be combined with other nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur, to build complex molecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. In general, animals cannot produce their own energy via photosynthesis. Instead, they capture their energy by the consumption and assimilation of the biomass of plants or other animals. Thus, animals get the energy they need for maintenance of their bodies tissues, growth, and reproduction indirectly from photosynthetic organisms. Respiration The oxidation of sugar by organisms is called respiration. This process occurs in both plants and animals. In most organisms, respiration releases the energy required for all metabolic processes. This chemical reaction can be described by the following simple equation: C6H12O6 + 6O2 >>> 6CO2 + 6H2O + released energy One of the products of respiration is energy, which is released via the chemical decomposition of glucose. Other products of this chemical reaction are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Energy Questions Name _________________________________ 1. What do living organisms need energy for? 2. What are the two main forms of energy and provide two examples of each. 3. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? 4. What are two things plants will do with the sugars they produce during photosynthesis? 5. What are the reactants and products of cell respiration? 6. What relationship exists between the reactants and products of photosynthesis and cell respiration? Using the sun, chloroplast and mitochondria pictures below, diagram this relationship. Make sure you show where the reactants and products of photosynthesis and cell division are coming and going! 7. Explain why we can say that even though animals are not photosynthetic, they are almost entirely dependent on the sun for energy? 8. If a meteor impacted the earth and caused the atmosphere to fill with a dark cloud of dust that blocked a significant amount of sunlight from hitting our planet, what impact do you think it might have on the plants and animals on our planet? Make sure you explain your answer! 9. There is a growing concern about rising CO2 levels in our planet’s atmosphere. What do you think might be a reason for this increase? What do you think might we consider doing to help eliminate some of the excess C02?